how designing hospitals for Indigenous people might benefit everyone
- Written by Timothy O'Rourke, Senior Lecturer, School of Architecture, The University of Queensland
Welcome to the next article in our Designing Hospitals series, where we explore how architecture and design shape our hospitals and medical centres. Today, we look at what Indigenous people tell us they need in hospital design.
Last year, New South Wales health minister Brad Hazzard proposed segregated Indigenous waiting areas in the emergency departments of the state’s public hospitals.
The novel policy suggested a link between Indigenous participation in health care and the design of health-care spaces.
One response called the proposal “absurd” and “apartheid”. It questioned whether racially segregated rooms were the answer to Indigenous patients leaving the emergency department without receiving care.
What was the evidence that redesigning waiting rooms would benefit Indigenous patients and their carers?
How we use evidence to design better hospitals
Evidence-based design aims to use research and evidence to improve hospital architecture for patients, carers and staff.
Studying physical environments that reduce patient stress, for example, is one area that has led to design changes in waiting areas, in-patient rooms, and wayfinding (how people navigate through a building).
It has also led to increasing integration of landscaping in health-care facilities and an interest in the benefits of therapeutic gardens.
But this research has largely ignored Indigenous people, despite the persistent health gap and the fact that cross-cultural design principles are being used for other buildings such as housing and prisons.
Read more: Re-imagining a museum of our First Nations
Here’s what we did
Our research attempted to determine how design can improve the way Indigenous people experience hospitals. The team included architects, anthropologists and statisticians.
We used a survey to examine the preferences and experiences of 600 Indigenous people at two locations: a metropolitan city (Townsville) and an inland regional city (Mount Isa).
We then interviewed a further 55 Indigenous people, and held meetings with the Indigenous liaison team at the Townsville Hospital.
Here’s what we found
The results reinforced anecdotal evidence that many Indigenous people find hospitals uncomfortable, alienating, and stressful.
One interviewee told us:
When you’ve got people looking you up and down, it makes you feel bad. All eyes on you, makes you shame always, like you shouldn’t be there.
Many of us find hospitals stressful. But a higher proportion of Indigenous people avoid hospital appointments or leave hospital against medical advice than non-Indigenous people.
Yes, culturally appropriate, high-quality care is of primary importance in the delivery of health services.
However, the survey results and stories confirmed hospital design matters to Indigenous patients and their families.
These preferences relate to Indigenous people’s cultural and social background, which is influenced by location and histories of colonisation.
Read more: What do Aboriginal Australians want from their aged care system? Community connection is number one
How can we improve hospital design?
Our study confirmed that Indigenous social networks, related to both kinship and community, affect hospital use.
Indigenous patients attract larger numbers of carers and visitors, whether in maternity wards, outpatient clinics, intensive care, or in palliative care. Interviews with hospital staff supported these observations.
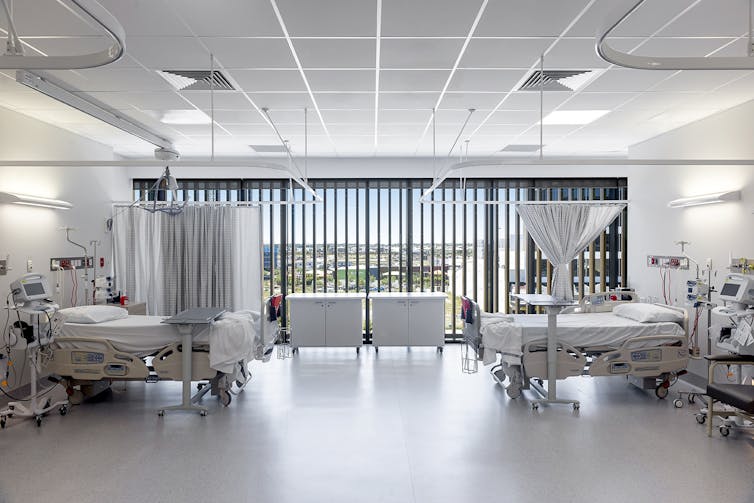 The views from this patient room in the Sunshine Coast University Hospital create a connection to the outdoors that Indigenous patients highly value.
Architectus, Author provided
The views from this patient room in the Sunshine Coast University Hospital create a connection to the outdoors that Indigenous patients highly value.
Architectus, Author provided
For in-patients, the larger visitor groups often stay longer, which can also place burden on staff and resources.
Existing guidelines on hospital design, however, tell us hospital wards are usually designed to accommodate only a few visitors at one time.
The results of our study indicated that larger in-patient rooms, semi-private waiting rooms located in wards, and connection to outdoors would begin to offer comfort to Indigenous visitors and families who may feel unwelcome in larger numbers.
Read more: Ms Dhu coronial findings show importance of teaching doctors and nurses about unconscious bias
Our research found clinics or hospital waiting rooms are rarely private enough for Indigenous people. We also found Indigenous patients and visitors feel more comfortable if they can see who is coming and going.
This visual monitoring can help maintain social relationships, either avoiding individuals — a cultural requirement in close-knit communities — or embracing supportive kin.
The spatial solution might be a challenge — providing flexible seating arrangements that offer semi-private spaces with clear views of entries. Larger waiting rooms adjoining outdoor areas would be a good start.
Can landscapes and gardens help?
The results of our study confirmed that Indigenous patients and visitors strongly preferred outdoor spaces, not just for the benefits of more natural settings, or to escape the air-conditioning, but also for social contact.
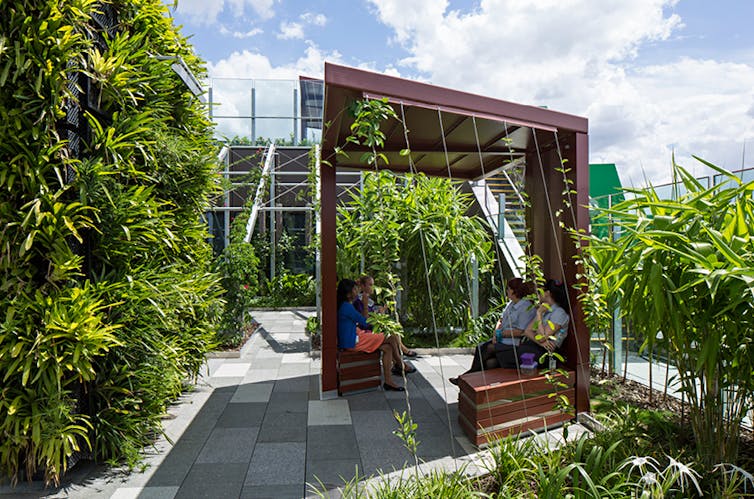 This roof garden at the Queensland Children’s Hospital offers semi-private spaces for social interaction and is preferred by Indigenous patients and visitors.
Conrad Gargett Lyons, Author provided
This roof garden at the Queensland Children’s Hospital offers semi-private spaces for social interaction and is preferred by Indigenous patients and visitors.
Conrad Gargett Lyons, Author provided
This can be to gather in private or to seek out familiar faces entering or leaving the hospital.
Although not often designed for such, outdoor areas are commonly used for grieving and cultural rituals around death. With this diversity of use, outdoor spaces deserve as much design attention as the interiors.
Evaluating how design works
Newer clinics and hospitals include design features, such as Indigenous art, which recognise Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander culture. But we need to make cross-cultural design more widespread and effective if we want Indigenous people to feel more comfortable in hospital.
Revised hospital design guidelines can raise awareness, but they may not capture the diversity of Indigenous people using different types of health facilities across a big continent.
Read more: Meet the remote Indigenous community where a few thousand people use 15 different languages
This makes consultation with local Indigenous people essential if their needs and preferences are to be accommodated in new health-care buildings.
Evaluating the design of newly built hospitals also contributes to evidence about architecture, and what might work better for both patients and staff, including Indigenous people.
Governments are hyper-sensitive about criticism of new hospitals. However, evaluating their design identifies worthy and repeatable design, as well as failures.
The modest design changes needed to improve the experience of Indigenous patients are likely to benefit all people who use our public hospitals.
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander organisations in Townsville and Mount Isa were essential in reaching the survey participants. Professor Paul Memmott, Professor Michele Haynes, Dr Bernie Baffour, Sue York, Carys Chainey, Georgia Betros, Kali Marnane and Alex Bond contributed to the research mentioned in this article.
Read other articles in our Designing Hospitals series:
From army barracks to shopping malls: how hospital design has been a matter of life and death
Authors: Timothy O'Rourke, Senior Lecturer, School of Architecture, The University of Queensland


















