High-speed rail on Australia's east coast would increase emissions for up to 36 years
- Written by Greg Moran, Senior Associate, Grattan Institute
Bullet trains are back on the political agenda. As the major parties look for ways to stimulate the economy after the COVID-19 crisis, Labor is again spruiking its vision of linking Melbourne, Sydney, Canberra and Brisbane with high-speed trains similar to the Eurostar, France’s TGV or Japan’s Shinkansen.
In 2013 when Labor was last in government, it released a detailed feasibility study of its plan. But a Grattan Institute report released today shows bullet trains are not a good idea for Australia. Among other shortcomings, we found an east coast bullet train would not be the climate saver many think it would be.
 Anthony Albanese releasing a high-speed rail study in 2013. The idea has long been mooted.
AAP/Lukas Coch
Anthony Albanese releasing a high-speed rail study in 2013. The idea has long been mooted.
AAP/Lukas Coch
The logic seems simple enough
Building a bullet train to put a dent in our greenhouse gas emissions has been long touted. The logic seems simple – we can take a lot of planes and their carbon pollution out of the sky if we give people another way to get between our largest cities in just a few hours or less.
And this is all quite true, as the chart below shows. We estimate a bullet train’s emissions per passenger-kilometre on a trip from Melbourne to Sydney would be about one-third of those of a plane. We calculated this using average fuel consumption estimates from 2018 for various types of transport, as well as the average emissions intensity of electricity generated in Australia in 2018.
Read more: Coronavirus is a 'sliding doors' moment. What we do now could change Earth's trajectory
If we use the projected emissions intensity of electricity in 2035 – the first year trains were expected to run under Labor’s original plan – the fraction drops to less than one-fifth of a plane’s emissions in 2018.
It should be remembered that while coaches might be the most climate-friendly way to travel long distances, they can’t compete with bullet trains or planes for speed.
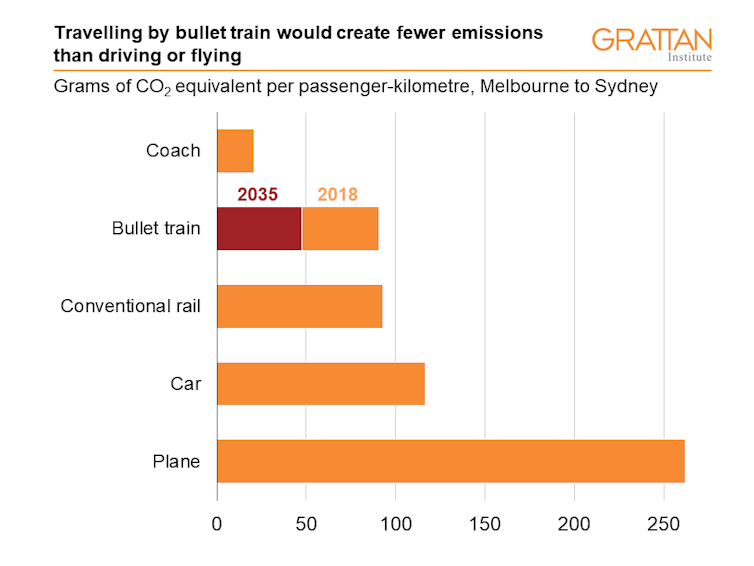 Notes: Average occupancy estimates are 38.5 (coach), 320 (bullet train), 119 (conventional rail), 2.26 (car), and 151.96 (plane). Plane emissions include radiative forcing. For more detail, see 'Fast train fever: Why renovated rail might work but bullet trains won’t'.
There’s a catch
So, where’s the problem? It lies in construction. A bullet train along Australia’s east coast would take about 15 years of planning, then would be built in sections over about 30 years. This construction would generate huge emissions.
In particular, vast emissions would be released in the production of steel and concrete required to build a train line from Melbourne to Brisbane. These so-called “scope 3” emissions can account for 50-80% of total construction emissions.
Read more:
Look beyond a silver bullet train for stimulus
Scope 3 emissions are sometimes not counted when assessing the emissions impact of a project, but they should be. There’s no guarantee the quantities of concrete and steel in question would have been produced and used elsewhere if not for the bullet train.
And the long construction time means it would be many years before the train actually starts to take planes out of the sky. This, combined with construction emissions, means a bullet train would be very slow to reduce emissions. In fact, we found it would first increase emissions for many years.
Slow emissions benefit
As the chart below shows, we estimate building the bullet train could lead to emissions being higher than they otherwise would’ve been for between 24 and 36 years.
This period would start at year 15 of the project, when planning ends and construction starts. At the earliest, it would end at year 39. This is the point at which some sections of the project would be complete, and at which enough trips have been taken (and enough plane or car trips foregone) that avoided emissions overtake emissions created.
This means the train might not actually create a net reduction in emissions until almost 40 years after the government commits to building it – and even this is under a generously low estimate of scope 3 emissions. If scope 3 emissions are on the high side, emission reductions may not start until just after the 50-year mark – 36 years after construction began.
Notes: Average occupancy estimates are 38.5 (coach), 320 (bullet train), 119 (conventional rail), 2.26 (car), and 151.96 (plane). Plane emissions include radiative forcing. For more detail, see 'Fast train fever: Why renovated rail might work but bullet trains won’t'.
There’s a catch
So, where’s the problem? It lies in construction. A bullet train along Australia’s east coast would take about 15 years of planning, then would be built in sections over about 30 years. This construction would generate huge emissions.
In particular, vast emissions would be released in the production of steel and concrete required to build a train line from Melbourne to Brisbane. These so-called “scope 3” emissions can account for 50-80% of total construction emissions.
Read more:
Look beyond a silver bullet train for stimulus
Scope 3 emissions are sometimes not counted when assessing the emissions impact of a project, but they should be. There’s no guarantee the quantities of concrete and steel in question would have been produced and used elsewhere if not for the bullet train.
And the long construction time means it would be many years before the train actually starts to take planes out of the sky. This, combined with construction emissions, means a bullet train would be very slow to reduce emissions. In fact, we found it would first increase emissions for many years.
Slow emissions benefit
As the chart below shows, we estimate building the bullet train could lead to emissions being higher than they otherwise would’ve been for between 24 and 36 years.
This period would start at year 15 of the project, when planning ends and construction starts. At the earliest, it would end at year 39. This is the point at which some sections of the project would be complete, and at which enough trips have been taken (and enough plane or car trips foregone) that avoided emissions overtake emissions created.
This means the train might not actually create a net reduction in emissions until almost 40 years after the government commits to building it – and even this is under a generously low estimate of scope 3 emissions. If scope 3 emissions are on the high side, emission reductions may not start until just after the 50-year mark – 36 years after construction began.
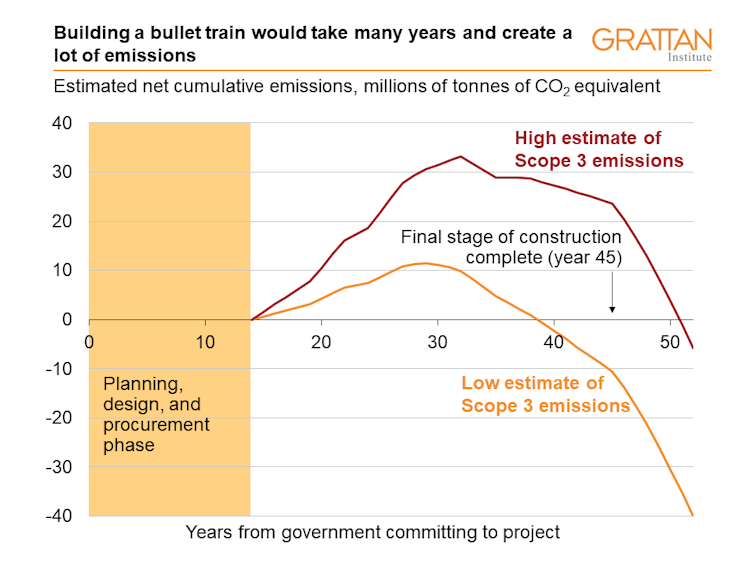 Notes: Estimates derived from the 2013 feasibility study of the Melbourne-to-Brisbane bullet train, and other sources. The feasibility study assumed that government would commit to the project in 2013. For more detail, see 'Fast train fever: Why renovated rail might work but bullet trains won’t'.
The bullet train would create a net reduction in emissions from the 40- or 50-year mark onwards. But the initial timelines matter.
The world needs to achieve net zero emissions by about 2050 if we’re to avoid the worst impacts of climate change. All Australian states and territories have made this their goal. Unfortunately, a bullet train will not help us achieve it.
The way forward
Hitting the 2050 net-zero emissions target implicit in the Paris Agreement remains a daunting but achievable task. Decarbonising transport will play a big part, including the particularly tricky question of reducing aviation emissions.
But during the most crucial time for action on emissions reduction, a bullet train will not help. Our efforts and focus ought to be directed elsewhere.
Milan Marcus assisted in the preparation of this piece.
Read more:
Delays at Canberra: why Australia should have built fast rail decades ago
Notes: Estimates derived from the 2013 feasibility study of the Melbourne-to-Brisbane bullet train, and other sources. The feasibility study assumed that government would commit to the project in 2013. For more detail, see 'Fast train fever: Why renovated rail might work but bullet trains won’t'.
The bullet train would create a net reduction in emissions from the 40- or 50-year mark onwards. But the initial timelines matter.
The world needs to achieve net zero emissions by about 2050 if we’re to avoid the worst impacts of climate change. All Australian states and territories have made this their goal. Unfortunately, a bullet train will not help us achieve it.
The way forward
Hitting the 2050 net-zero emissions target implicit in the Paris Agreement remains a daunting but achievable task. Decarbonising transport will play a big part, including the particularly tricky question of reducing aviation emissions.
But during the most crucial time for action on emissions reduction, a bullet train will not help. Our efforts and focus ought to be directed elsewhere.
Milan Marcus assisted in the preparation of this piece.
Read more:
Delays at Canberra: why Australia should have built fast rail decades ago
Authors: Greg Moran, Senior Associate, Grattan Institute



















