Captured! Radio telescope records a rare 'glitch' in a pulsar's regular pulsing beat
- Written by Jim Palfreyman, PhD candidate in astronomy, University of Tasmania
Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars and sometimes they abruptly increase their rotation rate. This sudden change of spin rate is called a “glitch” and I was part of a team that recorded one happening in the Vela Pulsar, with the results published today in Nature.
Approximately 5-6% of pulsars are known to glitch. The Vela pulsar is perhaps the most famous – a very southern object that spins about 11.2 times per second and was discovered by scientists in Australia in 1968.
It is 1,000 light-years away, its supernova occurred about 11,000 years ago and roughly once every three years this pulsar suddenly speeds up in rotation.
Read more: Fifty years ago Jocelyn Bell discovered pulsars and changed our view of the universe
These glitches are unpredictable, and one has never been observed with a radio telescope large enough to see individual pulses.
To understand what the glitch may be, first we need to understand what makes a pulsar.
Collapsing stars
At the end of a typical star’s life, one of three things can happen.
A small star, similar to the size of our Sun, will just quietly expire like a fire going out.
If the star is sufficiently large, a supernova will occur. After this massive explosion the remains will collapse. If the object is sufficiently large then its escape velocity will be greater than the speed of light, and a black hole will be formed.
But if we have a Goldilocks-sized star that is large enough to go supernova, but small enough not to be a black hole, we get a neutron star.
Read more: Explainer: why you can hear gravitational waves when things collide in the universe
The gravity is so strong that the electrons orbiting the atom are forced into the nucleus. They combine with protons in the nucleus to form neutrons.
These objects are estimated to have a mass of about 1.4 times the mass of our Sun, and a diameter of 20km. The density is such that a cupful of this material would weigh as much as Mt Everest.
They also rotate quite quickly (and very gradually slow down over time) as well as having a massive magnetic field, three trillion times that of the Earth. Electromagnetic radiation emits from both ends of this huge rotating magnet.
Now if one of the poles of this rotating magnet happens to sweep past Earth, we see a brief “flash” in radio waves (and other frequencies too) once every rotation. This is called a pulsar.
The hunt for a ‘glitch’
In 2014 I started a serious observing campaign with the University of Tasmania’s 26m radio telescope, at the Mount Pleasant Observatory, with a goal to catch the Vela Pulsar’s glitch live in action.
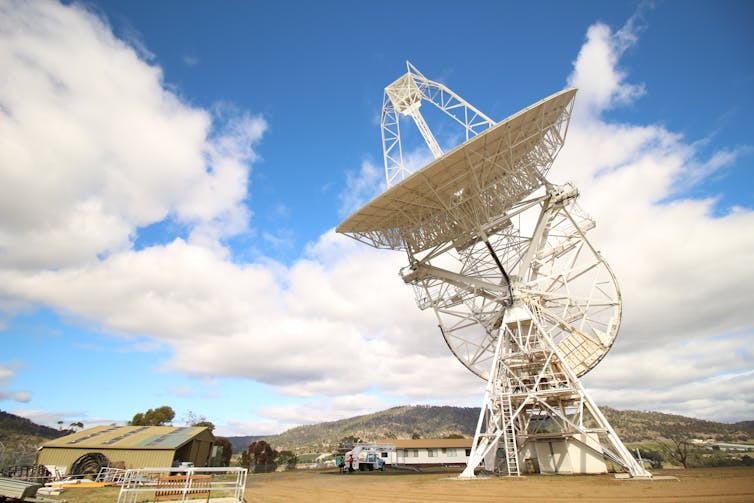 The 26m antenna at the Mount Pleasant Radio Observatory.
University of Tasmania, Author provided
The 26m antenna at the Mount Pleasant Radio Observatory.
University of Tasmania, Author provided
I collected data at the rate of 640MB for each 10 second file, for 19 hours a day, for most days over nearly four years. This resulted in over 3PB of data (1 petabyte is a million gigabytes) that was collected, processed and analysed.
On December 12, 2016, at approximately 9:36pm at night, my phone goes off with a text message telling me that Vela had glitched. The automated process I had set up wasn’t completely reliable – radio frequency interference (RFI) had been known to set it off in error.
So sceptically I logged in, and ran the test again. It was genuine! The excitement was incredible and I stayed up all night analysing the data.
What surfaced was quite surprising and not what was expected. Right as the glitch occurred, the pulsar missed a beat. It didn’t pulse.
The pulse before this “null” was broad and weird. Nothing like I’d ever seen or heard of before.
The two pulses following turned out to have no linear polarisation which was also unheard of for Vela. This meant the glitch had affected the strong magnet that drives the emission that comes from the pulsar.
Following the null, a train of 21 pulses arrived early and the variance in their timings was a lot smaller than normal – also very weird.
The glitch explained, sort of
So what causes glitches? The hypothesis that is best supported is that the neutron star has a hard crust and a superfluid core. The outer crust is what slows down, while the superfluid core rotates separately and does not slow down.
This is a very simplified explanation. What really happens is quite complex and involves microscopic superfluid vortices unpinning from the crust’s lattice.
Read more: Stars for sale, but no, you can't really buy an official star name to remember someone
After about three years the difference in rotation between the core and crust gets too great and the core “grips” the crust and speeds it up. The data seems to show that it took about five seconds for this speed-up to occur. This is on the faster end of the scale that the theorists had predicted.
All this and other information could help us understand what is called the “equation of state” – how matter behaves at different temperatures and pressures – in a laboratory that we simply cannot create here on Earth.
It also gives us, for the first time, a glimpse into the inside workings of a neutron star.
Authors: Jim Palfreyman, PhD candidate in astronomy, University of Tasmania