new report shows how the nation's gas expansion puts Australians in harm’s way
- Written by Tim Baxter, Fellow - Melbourne Law School; Senior Researcher - Climate Council; Associate - Australian-German Climate and Energy College, University of Melbourne
Australia’s latest emissions data, released this week, contained one particularly startling, and unjustifiable, fact. Against all odds, in a year when emissions fell in almost every sector, Australia’s export gas industry still managed to do more climate damage.
A new Climate Council report released today, to which I contributed, sheds more light on the problem of Australia’s expanding gas industry.
It reveals in alarming detail how gas emissions are cancelling out the gains won by Australia’s renewables boom. It also shows how gas emissions are almost certainly under-reported, and uncovers the misleading claims underpinning the Morrison government’s gas-led economic recovery.
This is clearly an unsustainable state of affairs. Australia has this year been in the grip of a climate crisis: unprecedented drought, the Black Summer bushfires and another mass bleaching of the Great Barrier Reef. The gas industry escalates this risk and puts more Australians in harm’s way.
 The Jeeralang gas power station in Victoria. The gas industry is cancelling out gains won by renewables.
Climate Council
The Jeeralang gas power station in Victoria. The gas industry is cancelling out gains won by renewables.
Climate Council
Gas: bucking the trend
As is now well known, COVID-19 restrictions helped trigger a fall in carbon dioxide emissions globally.
In Australia, emissions from transport dropped by 24% compared with April–June last year, as people stayed out of cars and planes.
Emissions from electricity dropped by around 5% in the quarter, compared with the corresponding quarter last year. This was mostly due to continued wind and solar expansion; demand for electricity dropped only marginally.
Overall, industrial demand for electricity was roughly the same as last year. Meanwhile, although office blocks and shopping centres were shuttered, power was needed in the domestic sector to heat homes and charge iPads for homeschooling.
Overall, almost every sector, including gas, also produced fewer emissions in the June quarter than in the same period the year before. Across the economy, emissions for the quarter were 7% lower than the same period last year. This result is represented in the graph below.
While emissions from the gas sector declined in the lockdown months, the sector’s poor emissions performance over the full 12 months to June meant it managed to increase its emissions over the year – one of the few sectors to do so.
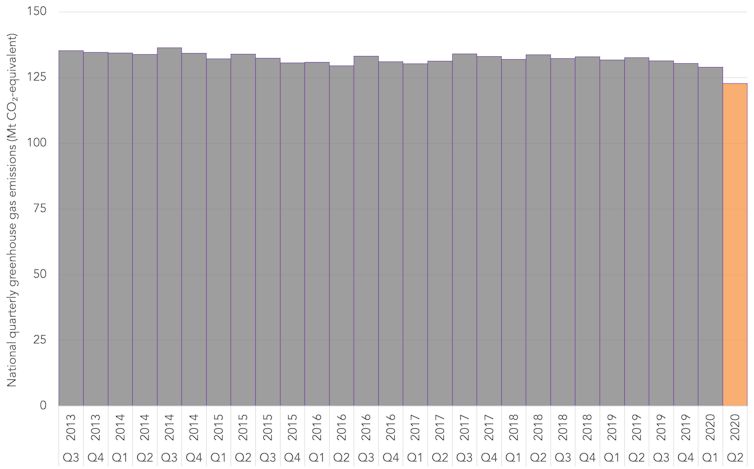 Australia’s quarterly emissions since the 2013 election, highlighting the most recent quarter in orange.
Author supplied. Data source: Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources
Australia’s quarterly emissions since the 2013 election, highlighting the most recent quarter in orange.
Author supplied. Data source: Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources
How did gas get this bad?
Australia became the world’s largest exporter of liquefied gas in 2019. Our report shows almost three-quarters of gas extracted in Australia in 2019 was compressed and processed to send overseas, as shown below.
Remarkably, on top of this, in 2019 the Australian gas export industry was itself the second-largest user of gas in Australia for the first time. More than a quarter of gas consumed in Australia was used to liquefy and chill gas for export overseas.
So the Australian gas export industry uses or exports nearly 80% of the gas it extracts each year – four times the amount needed to service the country’s own needs. Clearly claims of a shortfall in domestic gas supplies, such as those used to justify the recent Narrabri Gas Project approval, are bogus.
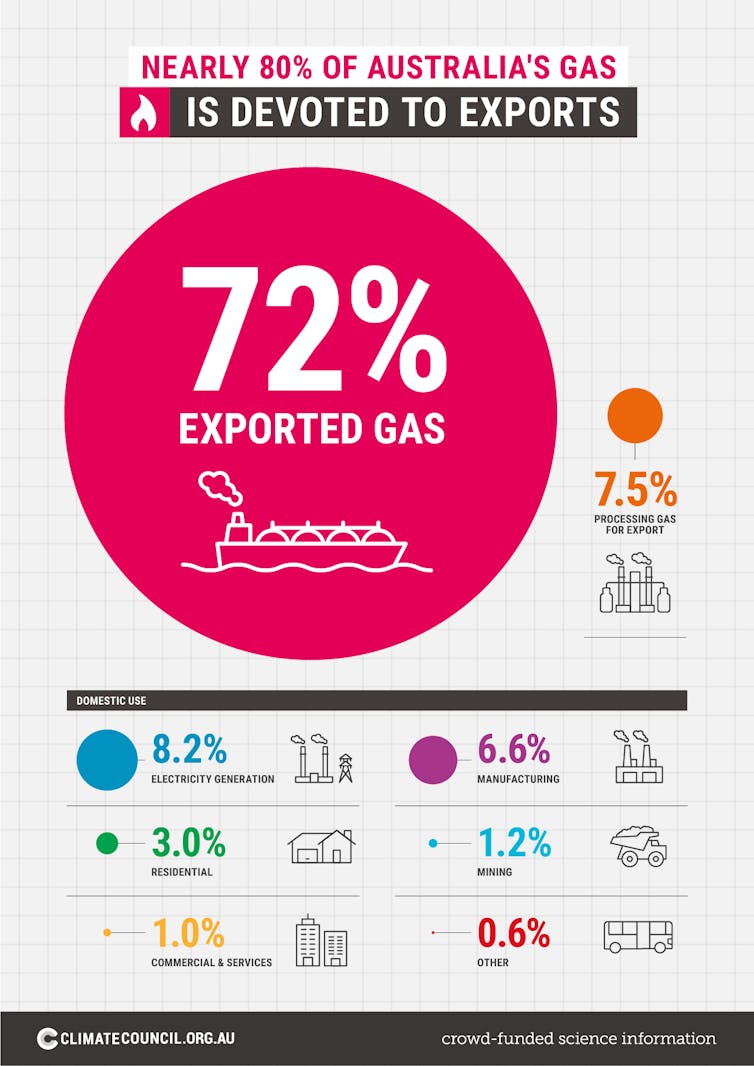 Chart showing 72% of Australia’s gas is exported and 7.5% is used by the gas export industry to process exports.
Climate Council
Chart showing 72% of Australia’s gas is exported and 7.5% is used by the gas export industry to process exports.
Climate Council
A worse problem than we thought
The reports shows rising gas emissions are cancelling out gains made by Australia’s record build of solar and wind generation capacity. Between 2005 and 2018, emissions from the electricity sector fell by 15 million tonnes per year. Emissions from the gas sector increased by 25 million tonnes per year in the same period.
Our report also highlights serious problems with official estimates of gas emissions along the supply chain. These estimates are based on decades-old research designed for the US gas industry.
Read more: Climate explained: methane is short-lived in the atmosphere but leaves long-term damage
Australia is also underestimating the harm caused by gas emissions. Methods used by the federal government to quantify the relative impact of methane are incomplete and ignore recent scientific advances. If methane’s effect was considered completely, this would further increase the assessed impact of the gas industry on Australia’s emissions.
Underpinning all this, the international gas market is in crisis as a result of a global oversupply. The drastic increase in Australia’s gas exports in recent years has left us dangerously exposed to international boom-and-bust market cycles, and subsequent job losses and power price volatility.
Most of Australia’s gas is expensive to produce compared to international competitors. The centrepiece of the federal government’s gas-led recovery, a stretch goal of A$4 per gigajoule for gas, has been described by the extraction industry’s own lobbyists as a “myth”. And several Australian export plants were recently declared by banking giant HSBC as “at risk”.
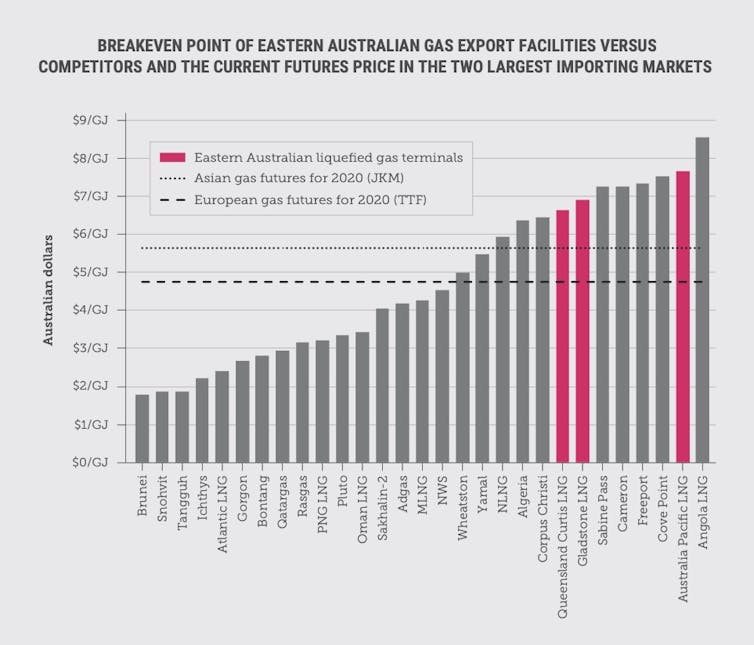 Australia’s three east coast gas export facilities were recently declared ‘at risk’ by HSBC.
Climate Council
Australia’s three east coast gas export facilities were recently declared ‘at risk’ by HSBC.
Climate Council
Seizing the opportunity
Fossil fuel extraction and consumption in Australia makes up 80% of our annual emissions. But as the Climate Council report shows, this figure is likely a gross underestimate. And of course, it does not account for the additional emissions produced when Australia’s gas exports are burned overseas.
COVID created a temporary blip in global emissions. If we don’t use it as an opportunity to consider a planet without coal, oil and gas consumption, the climate gains will amount to nothing.
Authors: Tim Baxter, Fellow - Melbourne Law School; Senior Researcher - Climate Council; Associate - Australian-German Climate and Energy College, University of Melbourne


















