after 1.5 billion years in flux, here's how a new, stronger crust set the stage for life on Earth
- Written by Fabio A Capitanio, Lecturer in Geophysics, Monash University
Our planet is unique in the Solar system. It’s the only one with active plate tectonics, ocean basins, continents and, as far as we know, life. But Earth in its current form is 4.5 billion years in the making; it’s starkly different to what it was in a much earlier era.
Details about how, when and why the planet’s early history unfolded as it did have largely eluded scientists, mainly because of the sparsity of preserved rocks from this geological period.
Our research, published today in Nature, reveals Earth’s earliest continents were entities in flux. They disappeared and reappeared over 1.5 billion years before finally gaining form.
Early Earth: a strange new world
The first 1.5 billion years of Earth’s history were a tumultuous period that set the stage for the rest of the planet’s journey. Several key events took place, including the formation of the first continents, the emergence of land and the development of the early atmosphere and oceans.
All of these events were the result of the changing dynamics of Earth’s interior. They were also catalysts to the first appearances of primitive life.
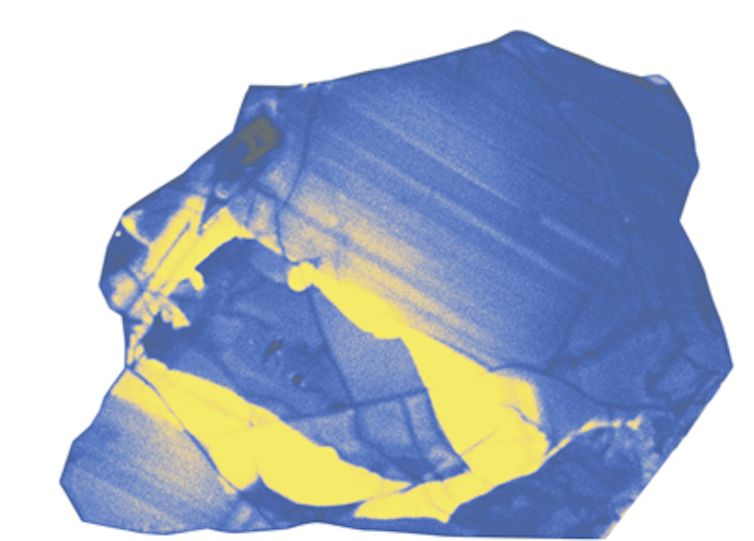 This almost 4.4 billion-year-old zircon crystal, retrieved from Western Australia’s Pilbara region, is one of the oldest rock fragment ever found. In reality it’s smaller than the head of a pin.
Author provided
This almost 4.4 billion-year-old zircon crystal, retrieved from Western Australia’s Pilbara region, is one of the oldest rock fragment ever found. In reality it’s smaller than the head of a pin.
Author provided
The preserved record of Earth’s first 500 million years is limited to just a few tiny crystals of the mineral zircon. Over the next billion or so years, kilometre-long (and larger) fragments of rock were generated and preserved. These would go on to forge the cores of major continents.
Scientists know about the properties of rocks and the chemical reactions that must occur for their constituent minerals to be made. Based on this, we know early Earth boasted very high temperatures, hundreds of degrees hotter than today’s.
Read more: Earth's rock-solid connections between Canada and Australia contain clues about the origin of life
An epic metamorphosis
Earth’s crust today is made of thick, buoyant continental crust that stands proud above the sea. Meanwhile, below the oceans are thin but dense oceanic crusts.
The planet is also broken into a series of plates that move around in a process called “continental drift”. In some places, these plates drift apart and in other they converge to form mighty mountains.
This dynamic movement of Earth’s tectonic plates is the mechanism by which heat from its interior is released into space. This results in volcanic activity focused mainly at the plate boundaries. A good example is the Ring of Fire — a path along the Pacific Ocean where volcanic eruptions and earthquakes are frequent.
To unravel the processes that operated on early Earth, we developed computer models to replicate its once much hotter conditions. These conditions were driven by large amounts of internal “primordial heat”. This is the heat left over from when Earth first formed.
 Today, Earth has a silica-rich continental crust above sea level and a thin (but dense) silica-poor crust in the ocean.
Shutterstock
Today, Earth has a silica-rich continental crust above sea level and a thin (but dense) silica-poor crust in the ocean.
Shutterstock
Our modelling shows the release of primordial heat during Earth’s early stages (which was three to four times hotter than today’s) caused extensive melting in the upper mantle. This is the mostly solid region below the crust, between 10km and 100km deep.
This internal melting created magma which, through a plumbing system, was thrust out as lava onto the crust. The shallow mantle left behind, dry and rigid, became welded to the crust and formed the first continents.
The pulse of first life
Our research revealed a lag between the formation of Earth’s first crust and the development of the mantle keels at the base of the first continents.
The first formed crust, which was present between 4.5 billion and 4 billion years ago, was weak and prone to destruction. It progressively became stronger over the next billion years to form the core of modern continents.
This process was crucial to continents becoming stable. When magma was purged from Earth’s interior, rigid rafts formed in the mantle beneath the new crust, shielding it from further destruction.
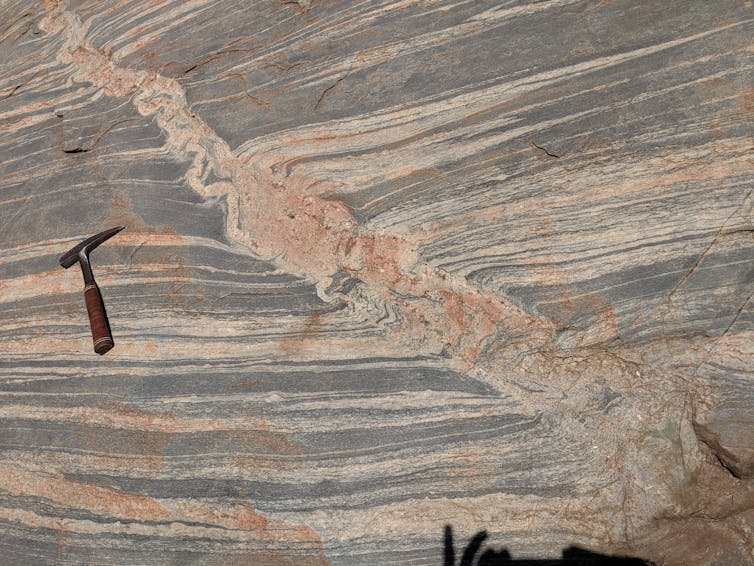 Pictured is banded igneous rock built up from multiple layers of magma. This rock is from Western Australia’s Pilbara Region.
Author provided
Pictured is banded igneous rock built up from multiple layers of magma. This rock is from Western Australia’s Pilbara Region.
Author provided
Moreover, the rise of these rigid continents ultimately led to weathering and erosion, which is when rocks and minerals break down or dissolve over long periods to eventually be carried away and deposited as sediment.
Early erosion would have changed the composition of Earth’s atmosphere. It would have also provided nutrients to the oceans, seeding the development of life.
From our observations, we conclude the breaking of Earth’s early crust was necessary to make way for a sturdier replacement. And had this not happened, we would not have the continents, nor life, as we know it.
Read more: Magnetism of Himalayan rocks reveals the mountains' complex tectonic history
Authors: Fabio A Capitanio, Lecturer in Geophysics, Monash University


















