Want to become a space tourist? You finally can — if you have $250,000 and a will to sign your life away
- Written by Cassandra Steer, Senior Lecturer, ANU College of Law; Mission Specialist, ANU Institute for Space, Australian National University
Billionaire Jeff Bezos’s space launch company Blue Origin has announced it will sell its first flights into microgravity to the highest bidder.
Blue Origin and its two greatest competitors in the “space tourism” field, SpaceX and Virgin Galactic, claim to be advancing humanity through the “democratisation” of space. But these joyrides aren’t opening up access to space for all.
A changing landscape
At face value, the prospect of a space tourism industry is exciting.
It promises an easier path to space than the one followed by astronauts, who must go through higher education, intense training and extremely competitive selection processes. Astronauts must also have the right nationality, because few countries have access to human spaceflight programs.
In theory, the opening up of a commercial spaceflight industry should make space more accessible and democratic. But this is only partly the case; what was once the domain of only the richest countries is now an industry headed predominantly by commercial entities.
Adding to this, these companies are prepared to take more risks than government programs because they don’t have to justify their spending — or failures — to the public. Blue Origin and SpaceX have seen many explosions in past tests, yet fans watch with excitement rather than dismay.
This has pushed the rapid development of space technologies. Reusable rockets — particularly SpaceX’s Falcon 9, which just made its tenth successful launch — have reduced the cost of launching tenfold.
Besides driving down costs, reusable technology is also working to solve the problem of sustainability.
 A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying 60 Starlink communications satellites lifted off on May 9, 2021.
AP/Craig Bailey
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying 60 Starlink communications satellites lifted off on May 9, 2021.
AP/Craig Bailey
Considering sustainability
There have been thousands of launches since 1957, when the first human-made object (Sputnik I) was launched by the Soviets. Apart from Falcon 9, however, every single launch vehicle has been used once and disposed of immediately — akin to throwing away an aeroplane after one flight.
Launch numbers are increasing each year, with 114 carried out in 2020 alone. Over the weekend, the uncontrolled reentry of debris from China’s Long March 5B rocket made world news because of its sheer size and the risk of damage. It is just one example of the problems of space debris and traffic management.
Safety is a key issue for human spaceflight. Currently, there are about 3,400 operational satellites in orbit and about 128 million pieces of debris. There are are hundreds of collision risks each day, avoided by expensive and difficult manoeuvres or, if the risk is low enough, operators wait and hope for the best.
If we add more human spaceflight to this traffic, countries will need to adopt stricter requirements to de-orbit satellites at the end of their lives, so they burn up on reentry. Currently, it’s acceptable to de-orbit after 25 years, or to put a satellite into an unused orbit. But this only delays the problem for the future.
Nations will also need to implement the 2019 United Nations guidelines on the Long-term Sustainability of Activities in Outer Space.
Read more: Space can solve our looming resource crisis – but the space industry itself must be sustainable
The environmental impact of launches are another important factor. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 burns as much fuel as an average car would over 200 years, for a single launch.
On the ground there are impacts on terrain and waterways, which we have to keep in mind when building future launch sites in Australia. Launch permits currently require environmental impact statements, but these should include long-term effects and carbon footprints as well.
Keeping billionaires in check
In the coming years, it will be crucial for independent spaceflight companies to be tightly regulated.
Virgin Galactic has long advocated a “shirtsleeve” environment wherein customers can experience the luxury of spaceflight unhindered by awkward spacesuits. But the death of one of its test pilots in 2014 is evidence spaceflight remains dangerous. High altitudes and pressure require more precaution and less concern for comfort.
Although regulators such as the US Federal Aviation Administration have strict safety requirements for space tourism, pressurised spacesuits are not among them — but they should be. Also, space tourism operators can require passengers to sign legal waivers of liability, in case of accident.
And while it’s laudable SpaceX and Blue Origin are making technological leaps, there is little in their business plans that speaks to diversity, inclusivity and global accessibility. The first space tourists were all wealthy entrepreneurs.
In 2001 Dennis Tito paid his way to a seat on a Russian Soyuz rocket to visit the International Space Station (ISS). Since then, there have been eight more space tourists, each paying between US$20 million and US$30 million to fly through the Russian program.
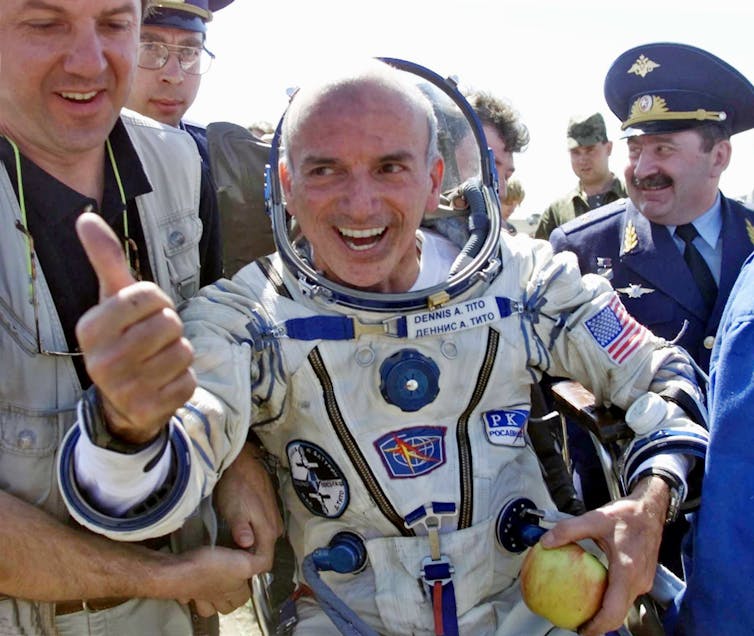 60-year-old American multimillionaire Dennis Tito became the first paying space tourist in 2001.
AP Photo/Mikhial Metzel
60-year-old American multimillionaire Dennis Tito became the first paying space tourist in 2001.
AP Photo/Mikhial Metzel
In 2022, the Axiom crew is scheduled to fly on a SpaceX Dragon flight to the ISS. Each of the three wealthy, white, male passengers will have paid US$55 million for the privilege. Meanwhile, Blue Origin’s upcoming auction will last five weeks, the highest bidder winning a seat for a few minutes of microgravity.
Virgin Galactic’s 90-minute joyrides, also scheduled to fly as early as 2022, have already sold for US$250,000. Future tickets are expected to cost more.
A matter of time?
Of course, conventional recreational air travel was also originally for the wealthy. Early cross-continental flights in the United States costed about half the price of a new car. But technological advances and commercial competition meant by 2019 (pre-COVID) there were nearly five million people flying daily.
Perhaps it’s only a matter of time before space tourism becomes similarly accessible. Ideally, this would mean being able to fly from Sydney to London in a matter of hours.
Then again, spaceflight carries much greater risks and much greater costs than airflight, even with reusable rockets. It’s going to be a long time before these costs are driven down enough to allow the “democratisation” of space.
This is a compelling narrative which commercial spaceflight companies are eager to adopt. But there will always be a portion of society that won’t have access to this future. Indeed, as many science-fiction stories predict, human spaceflight or habitation in space may only ever be accessible to the very wealthy.
We know there are benefits to space-based technologies — from tracking climate change, to enabling global communications and health services, to learning from scientific experiments on the ISS. But when it comes to space tourism, the payback for the average person is less clear.
Authors: Cassandra Steer, Senior Lecturer, ANU College of Law; Mission Specialist, ANU Institute for Space, Australian National University