Children learn science in nature play long before they get to school classrooms and labs
- Written by Amy Cutter-Mackenzie-Knowles, Executive Dean, Faculty of Education, Southern Cross University
The number of preschools pursuing learning through nature play is growing fast worldwide. However, the effectiveness and impacts of this approach is largely untested, and we recently completed the first large-scale study in the world to explicitly research nature play in early childhood education.
By mapping the learning of scientific concepts in nature play in a range of early childhood settings, we demonstrated how young children engage with science long before they get to school classrooms and labs.
Our research shows nature play is a highly effective way of embedding STEM — science, technology, engineering and mathematics — in early childhood education. These areas share connections and practices, and research increasingly shows that “regardless of ability, young children are ready, willing, and able to engage in STEM activities”.
What exactly is nature play?
Nature play is a popular way to respond to parent and teacher concerns about children’s limited time in nature and potentially too much screen time. It’s generally seen as unstructured play in natural settings, involving child-led interactions with nature.
Inspiration for nature play is often attributed to Scandinavian “forest school” models. However, its origins run far deeper. Indigenous practices, for instance, notably understandings of Country and self as entangled, rather than separate, support many of the key features of nature play.
Early childhood education in some countries such as Germany, Finland and Denmark has a long tradition of nature play. For instance, “kindergarten” means “children and garden” in German, showing kindergarten’s roots in nature-based learning.
What was the research project?
Our research project in urban and regional early childhood settings in Queensland uncovered a vast number of key concepts explored through nature play. Many were connected with Indigenous ways of knowing about the planet. Others were more aligned with environmental science or STEM concepts.
With funding from the Queensland government’s Education Horizon scheme, our team worked with 20 early childhood education centres. There were ten sites in South-East Queensland, nine in Central Queensland and one in far north-western Queensland.
The project design involved both children and early childhood educators as researchers — 31 educators and 152 children (aged four to five) in all. The children and the educators collected data to research their own nature play experiences and practices.
Read more: Don’t worry, your child’s early learning doesn’t stop just because they’re not in childcare
We explored children’s activities, ideas and beliefs about nature, and their relationships with/as nature. Understandings were diverse and ranged from seeing humans as separate from nature, to humans being part of nature — humans as nature.
The recently published Research Handbook of Childhoodnature found centring childhood in nature, as childhoodnature — with humans being understood as part of nature — is a vital foundation for nature play. As one four year old said:
“When I’m outside I learn about nature. Nature is what we’re in now. The trees are nature. The sky is nature. The creek is nature. The ants are nature. We are nature too, because we look after nature – and not break it.”
We found educators’ lack of confidence or understanding of science concepts need not limit exploration of STEM in early childhood education. Instead, participating educators reframed any limits to their knowledge as “an opportunity rather than an embarrassment”.
The educators became active co-learners alongside children, rejecting the traditional perception of teachers as the source of all knowledge. To make the most of STEM opportunities in nature play, educators must understand their role as curious “scientists in action”. They problem-solve, investigate and discover alongside children.
Read more: Let them play! Kids need freedom from play restrictions to develop
Our research identified environmental science concepts as the area of scientific learning participants most often engaged with through nature play. This means environmental science, as a discipline of teaching and learning within STEM, has an important contribution to make to children’s scientific learning.
Like all STEM disciplines, environmental science emerges in the early years and will build in complexity throughout a child’s life. The educators in this study embraced nine distinct nature play practices and lessons:
- place/Country-responsive play — such as bushwalks and other excursions on Country and learning from and with local Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Elders
- non-human play — deep observation of plants, clouds, natural objects and other species
- slow play — giving children the time and freedom for sustained, unhurried, uninterrupted play, including child-directed free play and artmaking
- sensorial play — stimulating children’s senses and an awareness of the body through noticing, paying attention, foraging, smelling, feeling, touching and deepening connection
- risky play — climbing trees, hanging upside down, balancing, rope swings, navigating creeks, building campfires, using tools, wrestling and exploring without adult supervision
- imaginative play — also known as make-believe play, fantasy play, symbolic play, pretend play and dramatic play. Children often role-play as a way of exploring and making sense of the world
- construction/creative play — whittling, sawing wood, building tunnels and bridges, painting, drawing, dancing, singing, drumming, nature journaling, nature collage, weaving, felting, sculpting, and clay work
- discovery play — using a digital microscope, experimenting with natural resources, exploring shadows and light, floating and sinking, and watching insect and animal behaviour, as a way to think deeply about the world and learn how it works
- death play — observing dead animals decomposing over time, role-playing death/dying and learning about life cycles to explore death, dying or grief.
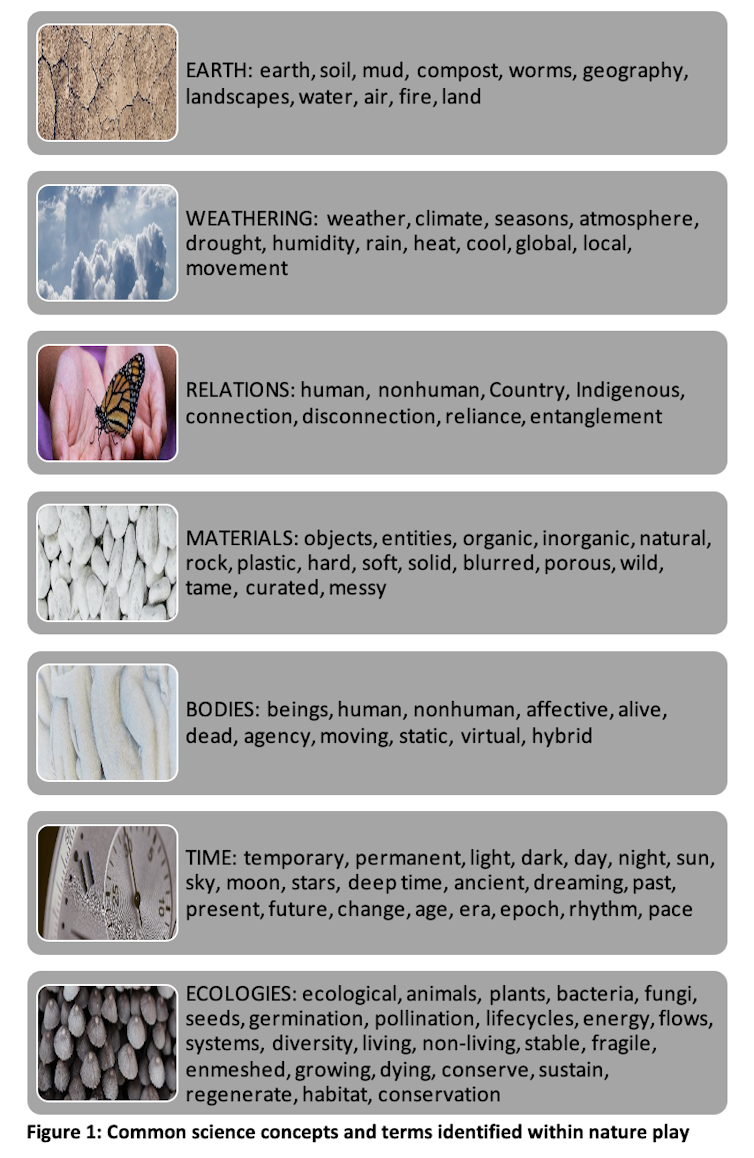
The project uncovered a vast number of key scientific concepts and terms explored through nature play. These were organised under the key areas of earth, ecologies, relations, materials, bodies, time and weathering.
This is not a prescriptive list, nor are these the only scientific concepts nature play enables. Rather, they are starting points to activate discussion and help children learn. When STEM concepts are inspired by the children’s interests, curiosities and questions, learning is more powerful, engaging and enduring.
Read more: Should I let my kid climb trees? We asked five experts
Authors: Amy Cutter-Mackenzie-Knowles, Executive Dean, Faculty of Education, Southern Cross University



















