the paradigm now shaping our world's data cities
- Written by Davina Jackson, Honorary Academic, School of Architecture, University of Kent
Today’s smart cities rely on networks: squillions of semiconductor devices that constantly pulse electromagnetic waves (light and radio frequencies) through telecommunications satellites.
 Data Cities, by the author.
Lund Humphries (2018), Author provided
Data Cities, by the author.
Lund Humphries (2018), Author provided
Another genre of satellites, equipped especially for Earth observations, is accelerating a more advanced form of urbanism: data cities. These realms are not only “smart and connected” but also increasingly responsive to electronic evidence revealing real situations and challenges.
In various publications and a new book, Data Cities: How satellites are transforming architecture and design, I explain how this century’s Earth observation science paradigm is destined to transform traditional practices among built environment professionals. That includes land surveyors, architects, engineers, landscape designers, property developers, builders and urban planners.
How do all the satellite data affect urban design?
In essence, much more detailed and accurate information about local environmental conditions will be supplied to development teams before new building concepts are designed. This should be more informative and less time-wasting than current routines. At present, planning authorities determine building proposals based on environmental impact assessment reports prepared after the design phase.
Architects and engineers already share the on-screen construction of building information models. They should benefit from obtaining more site-specific information earlier than is now usual. This would allow them to calculate more useful parameters, and receive more accurate performance predictions, for their virtual buildings and landscapes.
Earth observation satellites carry sensor and scanner systems that bounce different signals to and from the Earth. These systems constantly monitor and display many environmental conditions that normally are invisible to humans.
Some innovations in sat-imaging include: the patterns of street lighting that reliably map different cities at night; thermo-imaging (infrared) of the surface temperatures and energy losses of buildings; and high-res overviews of areas affected by drought, flooding, fires, chemical spills, eruptions, wars and other disasters.
 Earth observation has come a long way since this first photograph taken from space, on October 24 1946.
White Sands Missile Range/Applied Physics Laboratory
Earth observation has come a long way since this first photograph taken from space, on October 24 1946.
White Sands Missile Range/Applied Physics Laboratory
Earth observation satellites are not new. In 1946, a camera aboard a V-2 (aka A-4) missile launched from New Mexico took the first picture of Earth from space. The first satellite weather map was broadcast through small black-and-white television screens in 1960.
Today, more than 650 Earth observation satellites operate beyond the Earth’s atmosphere. Some orbit the planet to allow scanning in swathes. Others hold geostationary positions above specific places.
These satellites also operate at different distances from the Earth. And they carry different types of scanning and sensing equipment. As a result, they produce a diverse range of image resolutions, styles and scales of ground coverage.
The satellites record various kinds of environmental information, depending on which waves of the electromagnetic spectrum are used. These data are analysed and processed using precise algorithms.
A common example is data visualisations – often 2D or 3D video maps recorded over time. Typically, bright colours are applied to highlight contrasting conditions. For example, temperature data are colourised to show heat islands in cities. The same thing is done with aerosol data to depict patterns of carbon pollution.
What’s Australia’s role in this?
Australia does not fly satellites yet. But in July 2018 it launched the Australian Space Agency (ASA). Headed by former CSIRO director Megan Clark, it has an initial budget of A$300 million.
Read more: Ten essential reads to catch up on Australian Space Agency news
The ASA is working with Geoscience Australia (GA) on a A$225 million program to improve data positioning accuracy – to 3cm in cities with mobile coverage. Another A$37 million is going into developing the Digital Earth Australia program for environmental data simulations.
Digital Earth, a term Al Gore coined in his 1992 book, Earth in the Balance, is an international science agenda to use Earth observation systems to update the ancient cartography ambition to “present the known world as one and continuous”.
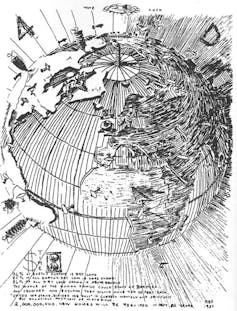 Buckminster Fuller’s 1927 vision of a ‘4D Interconnected, Unified World’.
Biography of R. Buckminster Fuller
Buckminster Fuller’s 1927 vision of a ‘4D Interconnected, Unified World’.
Biography of R. Buckminster Fuller
This dream was championed most influentially in the 20th century by US scientist Richard Buckminster Fuller, with his evolving concepts for an Air-Ocean World Town Plan (1928), Dymaxion map (1943), Geoscope (a giant electronic space-frame globe, 1962) and his book, Operating Manual for Spaceship Earth (1969).
In the early 2000s, NASA (World Wind) and Google (Google Earth) launched the first internet-enabled “virtual globes”.
In 2005, major nations established the Group on Earth Observations (GEO) secretariat in Geneva to develop a globally networked administration and online access system for geospatial data. These data are mainly from satellites at this stage.
The Global Earth Observations System of Systems (GEOSS) program now involves more than 200 national governments, United Nations data agencies, and global science and non-government organisations.
Australia’s representative on GEO is Geoscience Australia’s environmental division chief, Stuart Minchin. Working with Minchin, a GA team led by Adam Lewis produced the world-leading Data Cube system for rapidly analysing time-series stacks of American Landsat images covering Australia’s 40-plus zones of latitude and longitude.
European scientists are now using this method to compile a data-layered map of human settlements around the world.
Another notable advance in urban modelling comes from a public-private partnership between the Australian government’s data-marketing company, PSMA, and two global corporations: US satellite imagery supplier DigitalGlobe and business software vendor Pitney Bowes Australia. They offer information-rich online aerial imagery of Australian suburbs. Multispectral and shortwave infrared sensors aboard DigitalGlobe’s WorldView satellites are used to create these images.
Menu options enable users to clarify footprints and heights of buildings and trees, roof materials, and locations of swimming pools and solar panels. PSMA adds cadastral and other government land data, including plot areas and street addresses. This covers more than 15 million buildings over 7.6 million square kilometres.
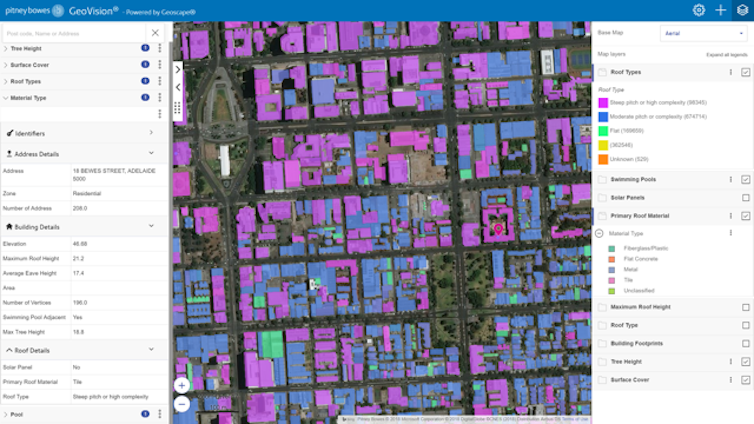 Mapping of building and roof materials in an Australian suburb, using GeoVision tools by Pitney Bowes derived from PSMA’s Geoscape data system, with imagery from shortwave infrared and multispectral sensors aboard DigitalGlobe’s WorldView 3 satellite.
Pitney Bowes Australia courtesy PSMA, Author provided
Mapping of building and roof materials in an Australian suburb, using GeoVision tools by Pitney Bowes derived from PSMA’s Geoscape data system, with imagery from shortwave infrared and multispectral sensors aboard DigitalGlobe’s WorldView 3 satellite.
Pitney Bowes Australia courtesy PSMA, Author provided
So where do people fit into this world?
As Al Gore noted in 1992:
… no one yet knows how to cope with the enormous volumes of data that will be routinely beamed down from orbit.
But he cited the importance of machines learning to improve their methods and a global infrastructure of massive parallelism — using dispersed chips and computers to process information at faster speeds.
Where do people step into this auto-piloting system? That remains moot.
Authors: Davina Jackson, Honorary Academic, School of Architecture, University of Kent
Read more http://theconversation.com/digital-earth-the-paradigm-now-shaping-our-worlds-data-cities-104938



















