what is surveillance capitalism and how does it shape our economy?
- Written by Donell Holloway, Senior research fellow, Edith Cowan University
I recently purchased a bedroom bundle (mattress, bed base, pillows and sheets) from a well known Australian startup for my son, who has flown the nest. Now I’m swamped with Google and Facebook ads for beds and bedding. The week before it was puffer jackets.
Ever wonder why and how this happens? The answer is surveillance capitalism.
Surveillance capitalism describes a market driven process where the commodity for sale is your personal data, and the capture and production of this data relies on mass surveillance of the internet. This activity is often carried out by companies that provide us with free online services, such as search engines (Google) and social media platforms (Facebook).
These companies collect and scrutinise our online behaviours (likes, dislikes, searches, social networks, purchases) to produce data that can be further used for commercial purposes. And it’s often done without us understanding the full extent of the surveillance.
The term surveillance capitalism was coined by academic Shoshana Zuboff in 2014. She suggests that surveillance capitalism depends on:
…the global architecture of computer mediation […] [which] produces a distributed and mostly uncontested new expression of power that I christen: “Big Other”.
Read more: Is it time to regulate targeted ads and the web giants that profit from them?
The big data economy
The late 20th century has seen our economy move away from mass production lines in factories to become progressively more reliant on knowledge. Surveillance capitalism, on the other hand, uses a business model based on the digital world, and is reliant on “big data” to make money.
The data used in this process is often collected from the same groups of people who will ultimately be its targets. For instance, Google collects personal online data to target us with ads, and Facebook is likely selling our data to organisations who want us to vote for them or to vaccinate our babies.
Third-party data brokers, as opposed to companies that hold the data like Google or Facebook, are also on-selling our data. These companies buy data from a variety of sources, collate information about individuals or groups of individuals, then sell it.
Smaller companies are also cashing in on this. Last year, HealthEngine, a medical appointment booking app, was found to be sharing clients’ personal information with Perth lawyers particularly interested in workplace injuries or vehicle accidents.
Cambridge Analytica was a wake-up call
Last year’s Cambridge Analytica revelations highlighted the extent to which internet companies surveil online activity. Cambridge Analytica’s actions broke Facebook’s own rules by collecting and on-selling data under the pretence of academic research. Their dealings may have violated election law in the United States.
Despite the questionable nature of Cambridge Analytics actions, the bigger players and leading actors in surveillance capitalism, Facebook and Google, are still legally amassing as much information as they can. That includes information about their users, their users’ online friends, and even their users’ offline friends (known as shadow profiling). A shadow profile is a profile created about someone who hasn’t signed up to particular social platform, but might have some data stored about them because they have interacted with someone who has. Platforms make huge profits from this.
In this sense, Cambridge Analytica was small player in the big data economy.
Read more: Big brother is watching: how new technologies are changing police surveillance
Where surveillance capitalism came from
Surveillance capitalism practices were first consolidated at Google. They used data extraction procedures and packaged users’ data to create new markets for this commodity.
Currently, the biggest “Big Other” actors are Google, Amazon, Facebook and Apple. Together, they collect and control unparalleled quantities of data about our behaviours, which they turn into products and services.
This has resulted in astonishing business growth for these companies. Indeed, Amazon, Microsoft, Alphabet (Google), Apple and Facebook are now ranked in the top six of the world’s biggest companies by market capitalisation.
Google, for instance, processes an average of 40 searches per second, 3.5 billion per day and 1.2 trillion per year. Its parent company, Alphabet, was recently valued at US$822 billion.
Sources of data are increasing
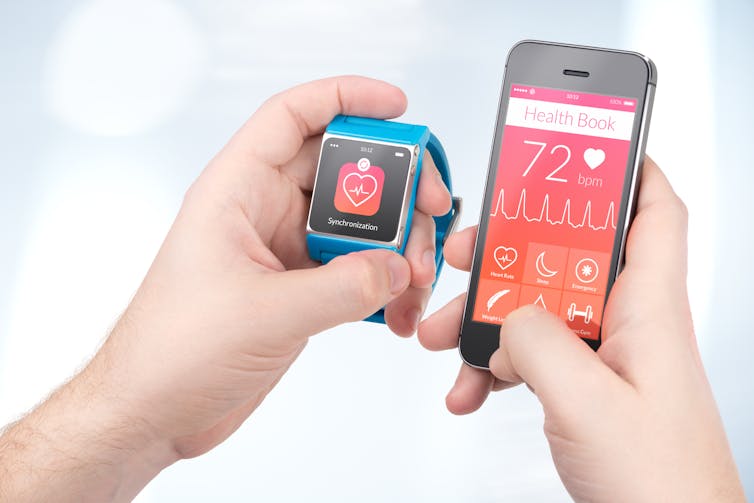
Newly available data sources have dramatically increased the quantity and variety of data available. Our expanding sensor-based society now includes wearables, smart home devices, drones, connected toys and automated travel. Sensors such as microphones, cameras, accelerometers, and temperature and motion sensors add to an ever expanding list of our activities (data) that can be collected and commodified.
Commonly used wearables like smart watches and fitness trackers, for example, are becoming part of everyday health care practices. Our activities and biometric data can be stored and used to interpret our health and fitness status.
 Shutterstock
Read more:
How artificial intelligence systems could threaten democracy
This same data is of great value to health insurance providers. In the US, some insurance providers require a data feed from the policyholder’s device in order to qualify for insurance cover.
Connected toys are another rapidly growing market niche associated with surveillance capitalism. There are educational benefits from children playing with these toys, as well as the possibility of drawing children away from screens towards more physical, interactive and social play. But major data breaches around these toys have already occurred, marking childrens’ data as another valuable commodity.
In her latest book, The Age of Surveillance Capitalism, Zubboff suggests that our emerging sensor based society will make surveillance capitalism more embedded and pervasive in our lives.
Shutterstock
Read more:
How artificial intelligence systems could threaten democracy
This same data is of great value to health insurance providers. In the US, some insurance providers require a data feed from the policyholder’s device in order to qualify for insurance cover.
Connected toys are another rapidly growing market niche associated with surveillance capitalism. There are educational benefits from children playing with these toys, as well as the possibility of drawing children away from screens towards more physical, interactive and social play. But major data breaches around these toys have already occurred, marking childrens’ data as another valuable commodity.
In her latest book, The Age of Surveillance Capitalism, Zubboff suggests that our emerging sensor based society will make surveillance capitalism more embedded and pervasive in our lives.
Authors: Donell Holloway, Senior research fellow, Edith Cowan University