Another stolen generation looms unless Indigenous women fleeing violence can find safe housing
- Written by Kyllie Cripps, Scientia Felllow and Senior Lecturer, Faculty of Law UNSW Sydney, UNSW
In Western Australia more than half the children placed in state care are Aboriginal. The state government committed this month to reducing this over-representation, in a move that parallels the Closing the Gap Refresh draft target nationally. Despite concerns about another stolen generation, Australia has yet to act on a root cause – the difficulty Indigenous women escaping family violence face in finding safe housing.
Read more: Why controversial child protection reforms in NSW could lead to another Stolen Generation
Our research shows domestic violence and housing are linked as a cause of child removal.
Every year governments spend millions addressing Indigenous intergenerational trauma. Child removal is an important cause of this trauma.
Care for children is a cornerstone of Aboriginal cultures. Child removal often has severe mental and physical health effects, with risks of substance use, homelessness and incarceration.
Read more: Aboriginal mothers are incarcerated at alarming rates – and their mental and physical health suffers
Consequences are similar for children, who also suffer from cultural dislocation. Yet Indigenous children are admitted to out-of-home care at 11 times the rate for non-Indigenous children. Far from declining, rates are increasing – by 21% between 2012 and 2017.
This issue is not primarily one of isolated remote communities. The rate of Indigenous children in out-of-home care is highest in our major cities.
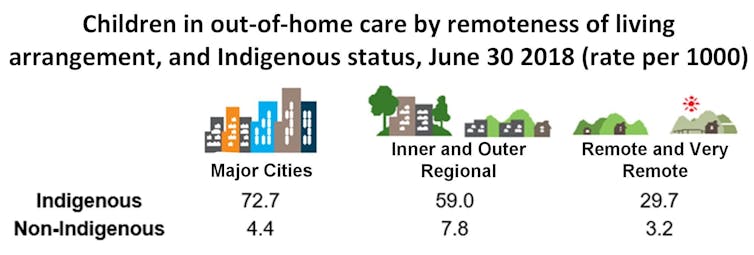 Child protection Australia 2017-18, AIHW (2019), Author provided
Why are children removed?
Contrary to public discourse, sexual abuse accounts for only a tiny percentage of substantiated notifications. Proportions are below those for non-Indigenous children (see chart below).
Emotional abuse, which includes the child’s exposure to family violence, accounts for most notifications. The second-most-common type is neglect. This occurs at more than double the non-Indigenous rate and includes inadequate, insecure or unsafe housing.
Child protection Australia 2017-18, AIHW (2019), Author provided
Why are children removed?
Contrary to public discourse, sexual abuse accounts for only a tiny percentage of substantiated notifications. Proportions are below those for non-Indigenous children (see chart below).
Emotional abuse, which includes the child’s exposure to family violence, accounts for most notifications. The second-most-common type is neglect. This occurs at more than double the non-Indigenous rate and includes inadequate, insecure or unsafe housing.
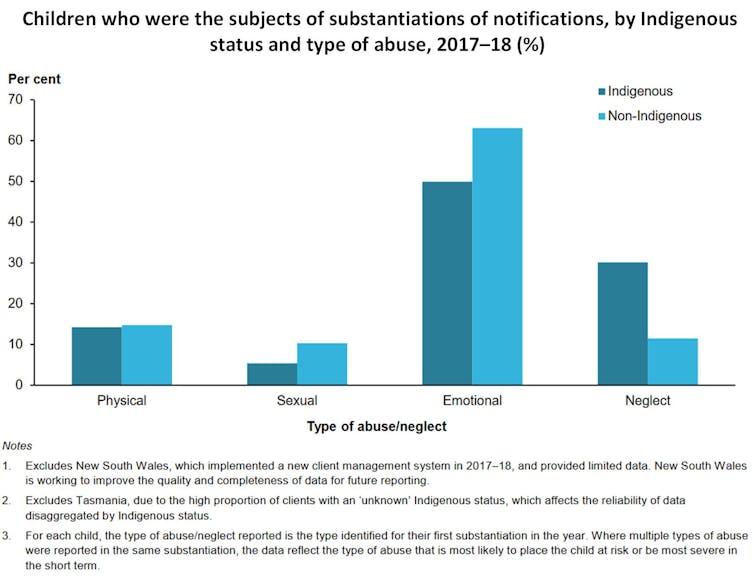 AIHW 2019, Author provided
Read more:
Child protection report lacks crucial national detail on abuse in out-of-home care
Mothers have nowhere to go
In situations of family violence many Aboriginal woman face an impossible situation when trying to protect their children. If they stay with the perpetrator they risk notification for emotional abuse. If they leave but cannot find suitable housing, they risk allegations of neglect.
This dilemma applies to all low-income women, but it is most acute for Aboriginal women. The combination of discrimination and low income means few find private rental housing. Crisis services are often full. The bottlenecks in the homelessness system result in long waits for transitional accommodation.
Waiting times for scarce public housing are long. Many also face delays in being added to priority wait lists due to housing debt – even though this is often a result of their partner’s financial abuse.
These women are often trapped in a revolving door between crisis centres, homelessness and returning to an unsafe home. This is a factor in their high rates of injury and early death.
Delays in being appropriately housed can prevent children from ever being returned to their parents. Child protection timelines generally allow only 12 months before removal can become permanent.
AIHW 2019, Author provided
Read more:
Child protection report lacks crucial national detail on abuse in out-of-home care
Mothers have nowhere to go
In situations of family violence many Aboriginal woman face an impossible situation when trying to protect their children. If they stay with the perpetrator they risk notification for emotional abuse. If they leave but cannot find suitable housing, they risk allegations of neglect.
This dilemma applies to all low-income women, but it is most acute for Aboriginal women. The combination of discrimination and low income means few find private rental housing. Crisis services are often full. The bottlenecks in the homelessness system result in long waits for transitional accommodation.
Waiting times for scarce public housing are long. Many also face delays in being added to priority wait lists due to housing debt – even though this is often a result of their partner’s financial abuse.
These women are often trapped in a revolving door between crisis centres, homelessness and returning to an unsafe home. This is a factor in their high rates of injury and early death.
Delays in being appropriately housed can prevent children from ever being returned to their parents. Child protection timelines generally allow only 12 months before removal can become permanent.
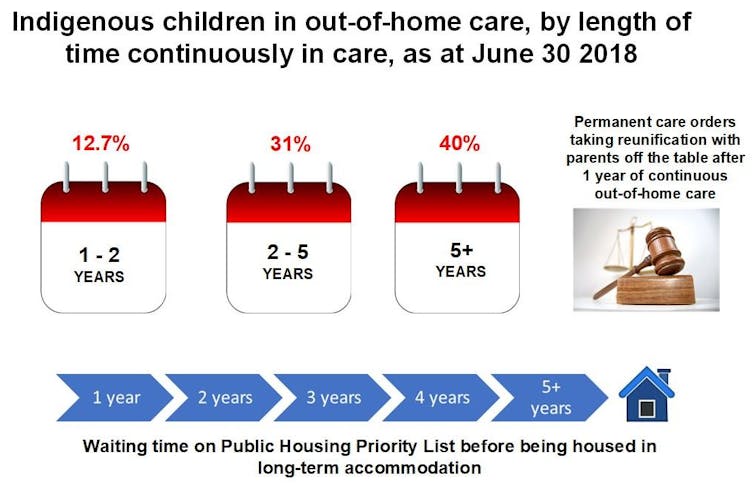 Data sourced from Child protection Australia 2017–18, AIHW (2019)
Cripps and Habibis (2019), Author provided
A policy blind spot
Housing’s critical role at the intersection of child protection and domestic violence has yet to be recognised in public policy. The national Fourth Action Plan to reduce violence against women and their children refers to “inadequate housing and overcrowding” as a factor in Aboriginal family violence. Despite this, it offers no specific guidelines or strategies to overcome these problems.
Read more:
The latest action plan to tackle violence against women isn’t perfect, but it takes a much-needed holistic approach
The Closing the Gap policy focus on housing is limited to reducing overcrowding. While critical, this misses the relationship between housing shortages and family violence and its impact on mums being separated from their children. And the Refresh targets are uncertain and underdeveloped.
Without specific housing targets, it is hard to see how the other targets to reduce violence and overrepresentation in out-of-home care will be met.
As Indigenous policy is realigned under the Closing The Gap Refresh the Australian government must act on this missing link. It should increase the number of crisis beds and consider targets to reduce the numbers of Aboriginal women and children turned away from crisis accommodation.
Programs should support timely access to secure housing. This is especially important for women seeking to reunify with children in state care.
Within the Safe at Home program, special funds should be made available for housing safety upgrades so Aboriginal women can remain in their own homes.
Beyond this, what’s needed are holistic solutions that work with the whole family, including the perpetrator. These solutions need to be developed and delivered in partnership with Aboriginal people, communities and services, building on the strengths of individuals and communities to overcome the impacts of violence and intergenerational trauma.
The short-term nature of funding is also a problem. Investment needs to go beyond political cycles. Current short-term funding arrangements undermine trust in services and greatly reduce their capacity and potential effectiveness.
Given the long-term intergenerational costs of child removal and domestic violence, such measures should prove cost-effective. More importantly, they would reduce violence against women and the over-representation of Aboriginal children in out-of-home care.
Data sourced from Child protection Australia 2017–18, AIHW (2019)
Cripps and Habibis (2019), Author provided
A policy blind spot
Housing’s critical role at the intersection of child protection and domestic violence has yet to be recognised in public policy. The national Fourth Action Plan to reduce violence against women and their children refers to “inadequate housing and overcrowding” as a factor in Aboriginal family violence. Despite this, it offers no specific guidelines or strategies to overcome these problems.
Read more:
The latest action plan to tackle violence against women isn’t perfect, but it takes a much-needed holistic approach
The Closing the Gap policy focus on housing is limited to reducing overcrowding. While critical, this misses the relationship between housing shortages and family violence and its impact on mums being separated from their children. And the Refresh targets are uncertain and underdeveloped.
Without specific housing targets, it is hard to see how the other targets to reduce violence and overrepresentation in out-of-home care will be met.
As Indigenous policy is realigned under the Closing The Gap Refresh the Australian government must act on this missing link. It should increase the number of crisis beds and consider targets to reduce the numbers of Aboriginal women and children turned away from crisis accommodation.
Programs should support timely access to secure housing. This is especially important for women seeking to reunify with children in state care.
Within the Safe at Home program, special funds should be made available for housing safety upgrades so Aboriginal women can remain in their own homes.
Beyond this, what’s needed are holistic solutions that work with the whole family, including the perpetrator. These solutions need to be developed and delivered in partnership with Aboriginal people, communities and services, building on the strengths of individuals and communities to overcome the impacts of violence and intergenerational trauma.
The short-term nature of funding is also a problem. Investment needs to go beyond political cycles. Current short-term funding arrangements undermine trust in services and greatly reduce their capacity and potential effectiveness.
Given the long-term intergenerational costs of child removal and domestic violence, such measures should prove cost-effective. More importantly, they would reduce violence against women and the over-representation of Aboriginal children in out-of-home care.
Authors: Kyllie Cripps, Scientia Felllow and Senior Lecturer, Faculty of Law UNSW Sydney, UNSW


















