New report shows the world is awash with fossil fuels. It's time to cut off supply
- Written by Peter Christoff, Associate Professor, School of Geography, University of Melbourne
A new United Nations report shows the world’s major fossil fuel producing countries, including Australia, plan to dig up far more coal, oil and gas than can be burned if the world is to prevent serious harm from climate change.
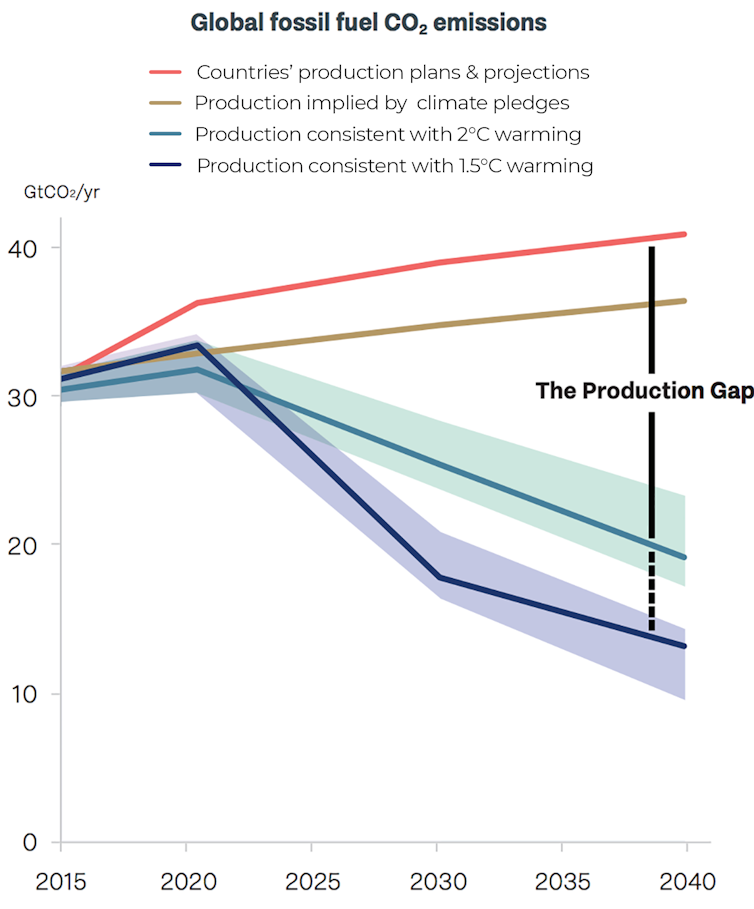
The report found fossil fuel production in 2030 is on track to be 50% more than is consistent with the 2℃ warming limit agreed under the Paris climate agreement. Production is set to be 120% more than is consistent with holding warming to 1.5℃ – the ambitious end of the Paris goals.
Australia is strongly implicated in these findings. In the same decade we are supposed to be cutting emissions under the Paris goals, our coal production is set to increase by 34%. This trend is undercutting our success in renewables deployment and mitigation elsewhere.
 productiongap.org
Mind the production gap
The United Nations Environment Program’s Production Gap report, to which I contributed, is the first to assess whether current and projected fossil fuel extraction is consistent with meeting the Paris goals.
It reviewed seven top fossil fuel producers (China, the United States, Russia, India, Australia, Indonesia, and Canada) and three significant producers with strong climate ambitions (Germany, Norway, and the UK).
Read more:
Drought and climate change were the kindling, and now the east coast is ablaze
The production gap is largest for coal, of which Australia is the world’s biggest exporter. By 2030, countries plan to produce 150% more coal than is consistent with a 2℃ pathway, and 280% more than is consistent with a 1.5℃ pathway.
The gap is also substantial for oil and gas. Countries are projected to produce 43% more oil and 47% more gas by 2040 than is consistent with a 2℃ pathway.
productiongap.org
Mind the production gap
The United Nations Environment Program’s Production Gap report, to which I contributed, is the first to assess whether current and projected fossil fuel extraction is consistent with meeting the Paris goals.
It reviewed seven top fossil fuel producers (China, the United States, Russia, India, Australia, Indonesia, and Canada) and three significant producers with strong climate ambitions (Germany, Norway, and the UK).
Read more:
Drought and climate change were the kindling, and now the east coast is ablaze
The production gap is largest for coal, of which Australia is the world’s biggest exporter. By 2030, countries plan to produce 150% more coal than is consistent with a 2℃ pathway, and 280% more than is consistent with a 1.5℃ pathway.
The gap is also substantial for oil and gas. Countries are projected to produce 43% more oil and 47% more gas by 2040 than is consistent with a 2℃ pathway.
 productiongap.org
Keeping bad company
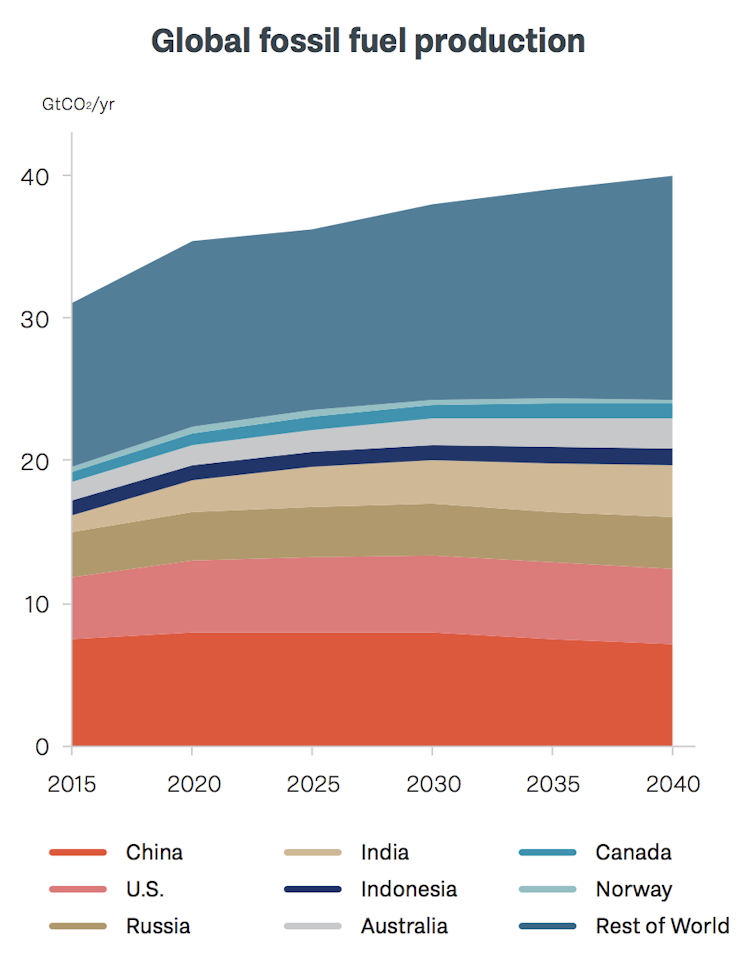
Nine countries, including Australia, are responsible for more than two-thirds of fossil fuel carbon emissions – a calculation based on how much fuel nations extract, regardless of where it is burned.
China is the world’s largest coal producer, accounting for nearly half of global production in 2017. The US produces more oil and gas than any other country and is the second-largest producer of coal.
Australia is the sixth-largest extractor of fossil fuels , the world’s leading exporter of coal, and the second-largest exporter of liquefied natural gas.
Read more:
The good, the bad and the ugly: the nations leading and failing on climate action
Prospects for improvement are poor. As countries continue to invest in fossil fuel infrastructure, this “locks in” future coal, oil and gas use.
US oil and gas production are each projected to increase by 30% to 2030, as is Canada’s oil production.
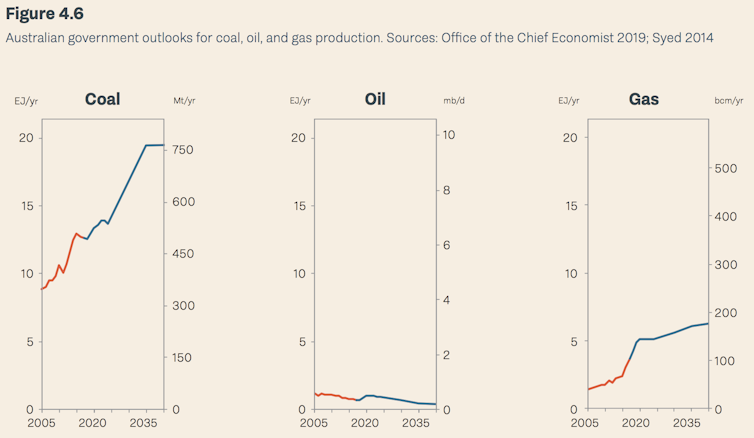
Australia’s coal production is projected to jump by 34%, the report says. Proposed large coal mines and ports, if completed, would represent one of the world’s largest fossil fuel expansions - around 300 megatonnes of extra coal capacity each year.
productiongap.org
Keeping bad company
Nine countries, including Australia, are responsible for more than two-thirds of fossil fuel carbon emissions – a calculation based on how much fuel nations extract, regardless of where it is burned.
China is the world’s largest coal producer, accounting for nearly half of global production in 2017. The US produces more oil and gas than any other country and is the second-largest producer of coal.
Australia is the sixth-largest extractor of fossil fuels , the world’s leading exporter of coal, and the second-largest exporter of liquefied natural gas.
Read more:
The good, the bad and the ugly: the nations leading and failing on climate action
Prospects for improvement are poor. As countries continue to invest in fossil fuel infrastructure, this “locks in” future coal, oil and gas use.
US oil and gas production are each projected to increase by 30% to 2030, as is Canada’s oil production.
Australia’s coal production is projected to jump by 34%, the report says. Proposed large coal mines and ports, if completed, would represent one of the world’s largest fossil fuel expansions - around 300 megatonnes of extra coal capacity each year.
 productiongap.org
The expansion is underpinned by a combination of ambitious national plans, government subsidies to producers and other public finance.
In Australia, tax-based fossil fuel subsidies total more than A$12 billion each year. Governments also encourage coal production by fast-tracking approvals, constructing roads and reducing royalty requirements, such as for Adani’s recently approved Carmichael coal mine in the Galilee Basin.
Ongoing global production loads the energy market with cheap fossil fuels – often artificially cheapened by government subsidies. This greatly slows the transition to renewables by distorting markets, locking in investment and deepening community dependency on related employment.
In Australia, this policy failure is driven by deliberate political avoidance of our national responsibilities for the harm caused by our exports. There are good grounds for arguing this breaches our moral and legal obligations under the United Nations climate treaty.
productiongap.org
The expansion is underpinned by a combination of ambitious national plans, government subsidies to producers and other public finance.
In Australia, tax-based fossil fuel subsidies total more than A$12 billion each year. Governments also encourage coal production by fast-tracking approvals, constructing roads and reducing royalty requirements, such as for Adani’s recently approved Carmichael coal mine in the Galilee Basin.
Ongoing global production loads the energy market with cheap fossil fuels – often artificially cheapened by government subsidies. This greatly slows the transition to renewables by distorting markets, locking in investment and deepening community dependency on related employment.
In Australia, this policy failure is driven by deliberate political avoidance of our national responsibilities for the harm caused by our exports. There are good grounds for arguing this breaches our moral and legal obligations under the United Nations climate treaty.
 Protestors locked themselves to heavy machinery to protest the Adani coal mine in central Queensland.
Frontline Action on Coal
Cutting off supply
So what to do about it? As our report states, governments frequently recognise that simultaneously tackling supply and demand for a product is the best way to limit its use.
For decades, efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have focused almost solely on decreasing demand for fossil fuels, and their consumption – through energy efficiency, deployment of renewable technologies and carbon pricing – rather than slowing supply.
While the emphasis on demand is important, policies and actions to reduce fossil fuels use have not been sufficient.
It is now essential we address supply, by introducing measures to avoid carbon lock-in, limit financial risks to lenders and governments, promote policy coherence and end government dependency on fossil fuel-related revenues.
Policy options include ending fossil fuel subsidies and taxing production and export. Government can use regulation to limit extraction and set goals to wind it down, while offering support for workers and communities in the transition.
Read more:
Australia could fall apart under climate change. But there's a way to avoid it
Several governments have already restricted fossil fuel production. France, Denmark and New Zealand have partially or totally banned or suspended oil and gas exploration and extraction, and Germany and Spain are phasing out coal mining.
Australia is clearly a major contributor in the world’s fossil fuel supply problem. We must urgently set targets, and take actions, that align our future fossil fuel production with global climate goals.
Protestors locked themselves to heavy machinery to protest the Adani coal mine in central Queensland.
Frontline Action on Coal
Cutting off supply
So what to do about it? As our report states, governments frequently recognise that simultaneously tackling supply and demand for a product is the best way to limit its use.
For decades, efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have focused almost solely on decreasing demand for fossil fuels, and their consumption – through energy efficiency, deployment of renewable technologies and carbon pricing – rather than slowing supply.
While the emphasis on demand is important, policies and actions to reduce fossil fuels use have not been sufficient.
It is now essential we address supply, by introducing measures to avoid carbon lock-in, limit financial risks to lenders and governments, promote policy coherence and end government dependency on fossil fuel-related revenues.
Policy options include ending fossil fuel subsidies and taxing production and export. Government can use regulation to limit extraction and set goals to wind it down, while offering support for workers and communities in the transition.
Read more:
Australia could fall apart under climate change. But there's a way to avoid it
Several governments have already restricted fossil fuel production. France, Denmark and New Zealand have partially or totally banned or suspended oil and gas exploration and extraction, and Germany and Spain are phasing out coal mining.
Australia is clearly a major contributor in the world’s fossil fuel supply problem. We must urgently set targets, and take actions, that align our future fossil fuel production with global climate goals.
Authors: Peter Christoff, Associate Professor, School of Geography, University of Melbourne


















