Portable Storage: An Affordable and Flexible Storage Solution
- Written by NewsServices.com
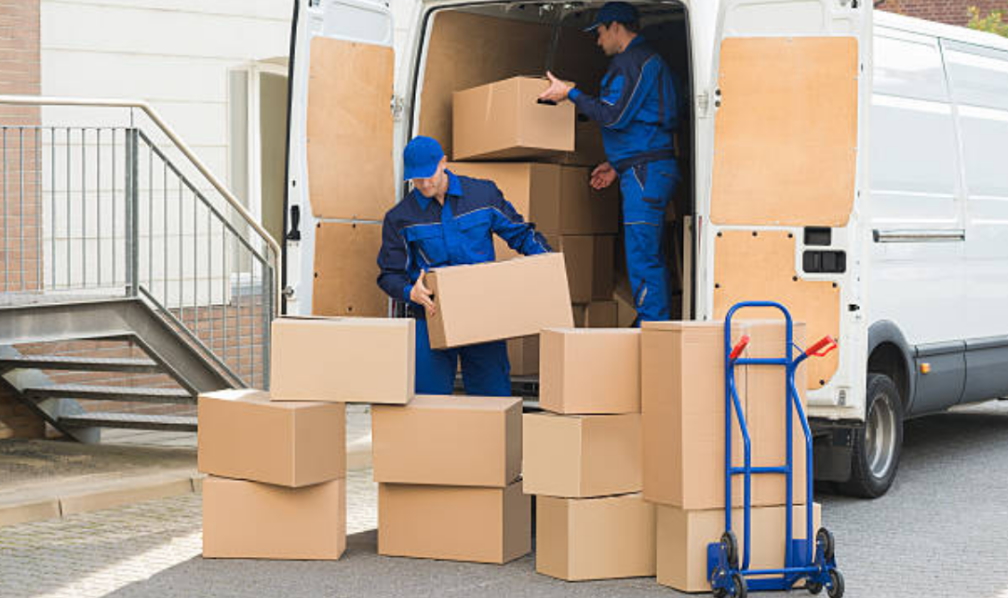

Portable storage is an affordable and flexible storage solution that can be used for a variety of purposes. It is perfect for those who need extra storage space but don't have room for a permanent storage unit. Portable storage units can be rented every month, and they can be delivered to your home or business.
Portable Storage Is an Affordable and Flexible solution
Portable storage is becoming an increasingly popular solution for those who need storage but don't have the space or the budget for a traditional storage unit. Here are some of the benefits of using portable storage:
- - It's more affordable than a traditional storage unit
- - It's more flexible- you can take it with you when you move
- - It's convenient- you can access your belongings whenever you need to
If you're looking for a storage solution that won't break the bank and is also convenient and flexible, portable storage is the perfect solution for you.
Portable Storage Is Easy to Find
Nowadays, people are looking for more convenient and affordable ways to store their belongings. They want something easy to access and can be transported without much hassle. This is where portable storage comes in.
Many companies offer this type of storage, so it is easy to find one that suits your needs. Most of these companies have an online presence, so you can easily compare prices and services.
Portable storage is a great solution for people who need extra storage space but do not want to deal with the hassle of renting a storage unit. It is also a convenient option for those who are moving and need to store their belongings temporarily.
Great Solution for Temporary Storage
As the weather begins to warm up and we start to think about all the projects we want to tackle around the house, we may find ourselves in need of some extra storage. Whether we're decluttering the garage or trying to make more space in the basement, portable storage is a great solution for temporary storage.
1800westoreit is a company that provides portable storage units that can be delivered to your home and stored on your property. You can pack and load the unit at your own pace, and then they will come and pick it up when you're ready. They will store the unit in their climate-controlled warehouse until you're ready to have it delivered to your new home or office.
Portable Storage for Big Appliances or Furniture
There's nothing quite like the feeling of a decluttered home. But sometimes, getting rid of big appliances or bulky furniture can be a challenge. Portable storage is the perfect solution for those items that you're not quite ready to part with but doesn't have the space for.
Portable storage units is convenient and easy to use. You can simply load up your items and call for a pick-up when you're ready. And the best part is that you can keep your belongings stored for as long as you need. So, whether you're downsizing your home or just need a little extra space, portable storage is the perfect solution.