Marine life is fleeing the equator to cooler waters. History tells us this could trigger a mass extinction event
- Written by Anthony Richardson, Professor, The University of Queensland
The tropical water at the equator is renowned for having the richest diversity of marine life on Earth, with vibrant coral reefs and large aggregations of tunas, sea turtles, manta rays and whale sharks. The number of marine species naturally tapers off as you head towards the poles.
Ecologists have assumed this global pattern has remained stable over recent centuries — until now. Our recent study found the ocean around the equator has already become too hot for many species to survive, and that global warming is responsible.
In other words, the global pattern is rapidly changing. And as species flee to cooler water towards the poles, it’s likely to have profound implications for marine ecosystems and human livelihoods. When the same thing happened 252 million years ago, 90% of all marine species died.
The bell curve is warping dangerously
This global pattern — where the number of species starts lower at the poles and peaks at the equator — results in a bell-shaped gradient of species richness. We looked at distribution records for nearly 50,000 marine species collected since 1955 and found a growing dip over time in this bell shape.
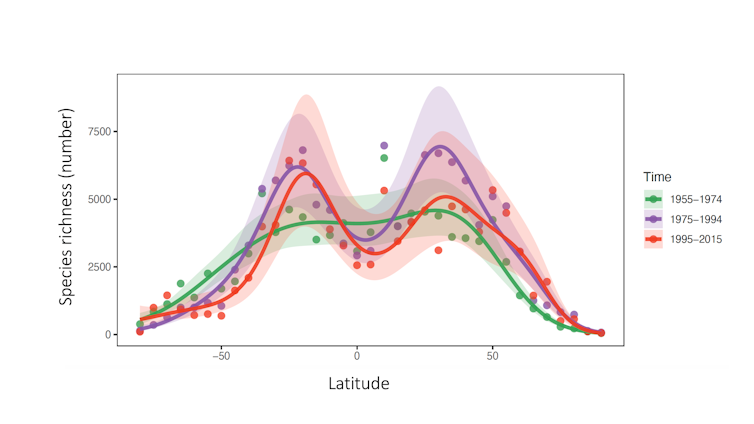 If you look at each line in this chart, you can see a slight dip in total species richness between 1955 and 1974. This deepens substantially in the following decades.
Anthony Richardson, Author provided
If you look at each line in this chart, you can see a slight dip in total species richness between 1955 and 1974. This deepens substantially in the following decades.
Anthony Richardson, Author provided
So, as our oceans warm, species have tracked their preferred temperatures by moving towards the poles. Although the warming at the equator of 0.6℃ over the past 50 years is relatively modest compared with warming at higher latitudes, tropical species have to move further to remain in their thermal niche compared with species elsewhere.
As ocean warming has accelerated over recent decades due to climate change, the dip around at the equator has deepened.
We predicted such a change five years ago using a modelling approach, and now we have observational evidence.
Read more: The ocean is becoming more stable – here's why that might not be a good thing
For each of the 10 major groups of species we studied (including pelagic fish, reef fish and molluscs) that live in the water or on the seafloor, their richness either plateaued or declined slightly at latitudes with mean annual sea-surface temperatures above 20℃.
Today, species richness is greatest in the northern hemisphere in latitudes around 30°N (off southern China and Mexico) and in the south around 20°S (off northern Australia and southern Brazil).
 The tropical water at the equator is renowned for having the richest diversity of marine life, including large aggregations of tuna fish.
Shutterstock
The tropical water at the equator is renowned for having the richest diversity of marine life, including large aggregations of tuna fish.
Shutterstock
This has happened before
We shouldn’t be surprised global biodiversity has responded so rapidly to global warming. This has happened before, and with dramatic consequences.
252 million years ago…
At the end of the Permian geological period about 252 million years ago, global temperatures warmed by 10℃ over 30,000-60,000 years as a result of greenhouse gas emissions from volcano eruptions in Siberia.
A 2020 study of the fossils from that time shows the pronounced peak in biodiversity at the equator flattened and spread. During this mammoth rearranging of global biodiversity, 90% of all marine species were killed.
125,000 years ago…
A 2012 study showed that more recently, during the rapid warming around 125,000 years ago, there was a similar swift movement of reef corals away from the tropics, as documented in the fossil record. The result was a pattern similar to the one we describe, although there was no associated mass extinction.
Authors of the study suggested their results might foreshadow the effects of our current global warming, ominously warning there could be mass extinctions in the near future as species move into the subtropics, where they might struggle to compete and adapt.
Today…
During the last ice age, which ended around 15,000 years ago, the richness of forams (a type of hard-shelled, single-celled plankton) peaked at the equator and has been dropping there ever since. This is significant as plankton is a keystone species in the foodweb.
Our study shows that decline has accelerated in recent decades due to human-driven climate change.
The profound implications
Losing species in tropical ecosystems means ecological resilience to environmental changes is reduced, potentially compromising ecosystem persistence.
In subtropical ecosystems, species richness is increasing. This means there’ll be species invaders, novel predator-prey interactions, and new competitive relationships. For example, tropical fish moving into Sydney Harbour compete with temperate species for food and habitat.
This could result in ecosystem collapse — as was seen at the boundary between the Permian and Triassic periods — in which species go extinct and ecosystem services (such as food supplies) are permanently altered.
 In Indonesia, the fishing industry is one of the largest contributors to the economy.
EPA/HOTLI SIMANJUNTAK
In Indonesia, the fishing industry is one of the largest contributors to the economy.
EPA/HOTLI SIMANJUNTAK
The changes we describe will also have profound implications for human livelihoods. For example, many tropical island nations depend on the revenue from tuna fishing fleets through the selling of licenses in their territorial waters. Highly mobile tuna species are likely to move rapidly toward the subtropics, potentially beyond sovereign waters of island nations.
Read more: Tropical fisheries: does limiting international trade protect local people and marine life?
Similarly, many reef species important for artisanal fishers — and highly mobile megafauna such as whale sharks, manta rays and sea turtles that support tourism — are also likely to move toward the subtropics.
The movement of commercial and artisanal fish and marine megafauna could compromise the ability of tropical nations to meet the Sustainable Development Goals concerning zero hunger and marine life.
Is there anything we can do?
One pathway is laid out in the Paris Climate Accords and involves aggressively reducing our emissions. Other opportunities are also emerging that could help safeguard biodiversity and hopefully minimise the worst impacts of it shifting away from the equator.
Currently 2.7% of the ocean is conserved in fully or highly protected reserves. This is well short of the 10% target by 2020 under the UN Convention on Biological Diversity.
 Manta rays and other marine megafauna leaving the equator will have a huge impact on tourism.
Shutterstock
Manta rays and other marine megafauna leaving the equator will have a huge impact on tourism.
Shutterstock
But a group of 41 nations is pushing to set a new target of protecting 30% of the ocean by 2030.
This “30 by 30” target could ban seafloor mining and remove fishing in reserves that can destroy habitats and release as much carbon dioxide as global aviation. These measures would remove pressures on biodiversity and promote ecological resilience.
Designing climate-smart reserves could further protect biodiversity from future changes. For example, reserves for marine life could be placed in refugia where the climate will be stable over the foreseeable future.
We now have evidence that climate change is impacting the best-known and strongest global pattern in ecology. We should not delay actions to try to mitigate this.
 This story is part of Oceans 21
Our series on the global ocean opened with five in-depth profiles. Look out for new articles on the state of our oceans in the lead-up to the UN’s next climate conference, COP26. The series is brought to you by The Conversation’s international network.
Read more:
Australia's marine (un)protected areas: government zoning bias has left marine life in peril since 2012
This story is part of Oceans 21
Our series on the global ocean opened with five in-depth profiles. Look out for new articles on the state of our oceans in the lead-up to the UN’s next climate conference, COP26. The series is brought to you by The Conversation’s international network.
Read more:
Australia's marine (un)protected areas: government zoning bias has left marine life in peril since 2012
Authors: Anthony Richardson, Professor, The University of Queensland