World-first study decodes the DNA structure of a 52,000-year-old woolly mammoth sample
- Written by Parwinder Kaur, Associate Professor | Director, DNA Zoo Australia, The University of Western Australia
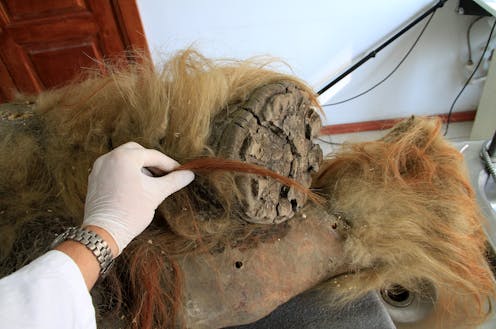
In a world-first study, we have revealed and analysed remarkably preserved fragments of ancient DNA from the skin of a woolly mammoth.
For the first time, we’ve been able to understand how the genetic instructions for this extinct species were organised inside its cells. This is known as genome architecture – the three-dimensional arrangement of DNA in the cell’s nucleus.
The research, published today in Cell, was a mammoth international effort, including teams from the United States, Australia, Denmark, Spain, Sweden, Russia and Norway. The discovery greatly enhances our understanding of a lost species.
By examining the genome architecture of the woolly mammoth, we can uncover the secrets of its survival in harsh environments – and its eventual extinction around 10,000 years ago. Our discovery also brings unprecedented insights into ancient DNA and opens up new avenues for research in this field.
A new look at an extinct species
Genome architecture influences how genes are turned on or off. This impacts everything from development to disease. In modern species, scientists study genome architecture to understand how the genes are regulated, and how the cells of the organism function.
When applied to ancient DNA, it can illuminate the biological and environmental history of an extinct species – such as the woolly mammoth.
Along with some proteins, the DNA within cells is stashed in what’s known as chromatin. It packages the long DNA molecules into a more compact, dense shape. This allows them to fit inside the cell nucleus.
The chromatin we found in our woolly mammoth sample from Siberia was remarkably well preserved, despite the animal having died 52,000 years ago.
The mammoth would have rapidly frozen after death. Its tissue was transformed due to the cold, dry and stable conditions. Although typically DNA degrades over time, in our sample we found it preserved in a glass-like state.
At the nanoscale, it’s akin to a bumper-to-bumper traffic jam where individual particles – in this case ancient DNA fragments – are immobilised and unable to move far from each other, even over thousands of years.
Usually, the study of ancient genome architecture is particularly challenging because DNA falls apart relatively quickly. However, we adapted a genomic analysis technique that maps chromatin interactions, allowing us to delve into the ancient DNA structures we found in the sample.
We could count the individual chromosomes and learn that mammoths had 28 – just like their closest living relatives, elephants. Then, we dug deeper.
A strikingly familiar pattern
When we compared the genome architecture of the mammoth and the Asian elephant living today, we found a striking similarity. This suggests the ancient DNA sample still shows useful biological information.
The sample was so detailed, not only could we see which genes were activated in the mammoth genome, but also why. One key discovery was what we call “mammoth altered regions”. These were changes in gene activity specific to the species.
For instance, we found that genes involved in hair development and immune response showed different activity patterns in mammoths compared to elephants.
The woolly mammoth had several unique physical traits adapted for cold environments. These included a thick, shaggy coat of fur and large tusks curving upwards.
They also had relatively small ears to minimise heat loss, and a specialised fat layer under the skin for insulation. These adaptations helped them thrive in ice age conditions.
A groundbreaking step forward
Our detailed work on the woolly mammoth’s genome architecture has provided a window into the past. By comparing them to their living relatives, we’ve found that crucial chromatin structures and gene regulation mechanisms have been preserved for more than 50,000 years.
This shows just how resilient genomic architecture can be on a grand evolutionary scale. The methods we developed to peer at the chromatin structures now open up new avenues of research.
As we continue to explore these ancient blueprints, we may uncover further secrets of how this extinct species adapted and thrived in its environment.
Our discovery may spark thoughts of resurrecting the woolly mammoth. However, our insights from studying ancient DNA might actually help the conservation of existing species.
What happened to the woolly mammoth in the Siberian permafrost was essentially natural biobanking – preservation and storage of genetic material. If we do this proactively for currently endangered species, we can safeguard their genetic diversity for future generations.
This would also provide a crucial resource for scientific research and conservation efforts. Just as the frozen mammoths have yielded knowledge about their adaptations and evolutionary pathways, modern biobanking efforts can offer insights into species’ resilience to environmental changes, disease resistance, and other critical traits.
This knowledge is vital for informing conservation strategies. It will help us ensure the long-term survival of biodiversity in a rapidly changing world.
Authors: Parwinder Kaur, Associate Professor | Director, DNA Zoo Australia, The University of Western Australia