what they are, how they work and why it's hard to make more
- Written by Berto Pandolfo, Senior Lecturer Product Design, University of Technology Sydney
Around the world, people are racing to design and manufacture much-needed ventilators to address a global lack of supply. One New York hospital has reportedly attempted treating two patients per ventilator out of desperation.
On March 26, a joint statement published by the American Society of Anaesthesiologists advised in regards to COVID-19 patients that:
… sharing mechanical ventilators should not be attempted because it cannot be done safely with current equipment.
Ventilators help a patient breathe by assisting the lungs to inhale and exhale air. These machines are used to treat patients suffering from conditions including pneumonia, brain injury and stroke.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus (which causes the COVID-19 disease) attacks the respiratory system. When infected, a patient’s ability to breathe is compromised. In mild cases, breathing or respiratory support can be provided using noninvasive means, such as delivering oxygen-rich air through a face mask.
In more severe cases, when a patient suffers acute respiratory distress, an invasive form of respiratory support is required. This is provided through an artificial airway. A tube attached to a ventilator is inserted into the patient’s mouth or nose (and down the windpipe), or via a surgically-made hole in the neck.
Read more: What steps hospitals can take if coronavirus leads to a shortage of beds
Breathe in, breathe out
The principal function of a ventilator is to pump or blow oxygen-rich air into the lungs; this is referred to as “oxygenation”. Ventilators also assist in the removal of carbon dioxide from the lungs, and this is referred to as “ventilation”.
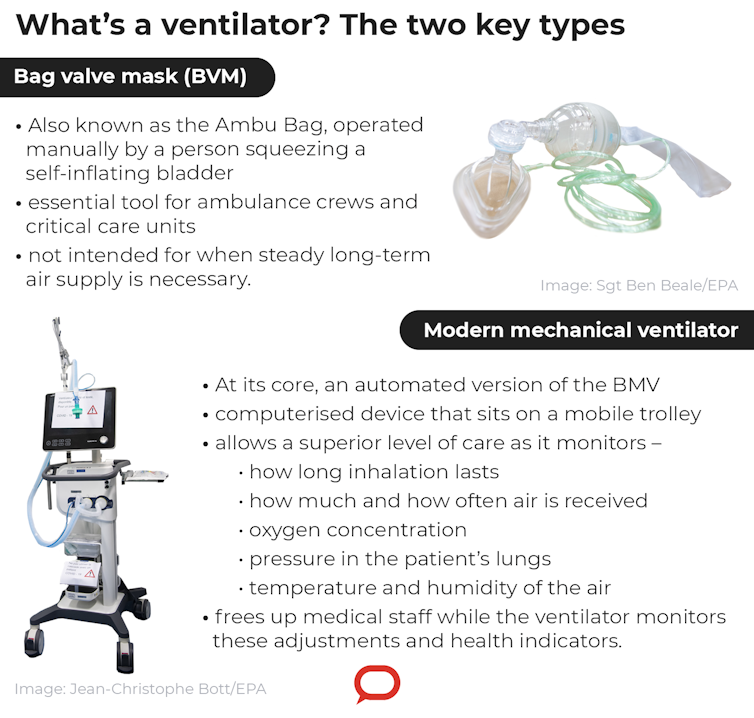
One basic type of ventilator is the Bag Valve Mask (BVM). The BVM, also known as the Ambu Bag, is operated manually by a person squeezing a self-inflating bladder. This is an essential tool for ambulance crews, first responders and critical care units. It is light, compact and easy to use.
However, in situations where a steady and controlled air exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out) is needed, mechanical ventilators are required. These look like a quintessential medical product.
 The Conversation/EPA/AAP
A mechanical ventilator comprises a computerised box that sits on top of a mobile trolley. There is an array of screens, dials, data cables, power cords and gas tubes. Modern mechanical ventilators are highly complex and sophisticated pieces of equipment. Their increased complexity in comparison with the Ambu Bag allows a superior level of care.
The extra features and control measures of mechanical ventilators allow adjustments such as:
how long inhalation for a patient lasts
how much air is received
how often air is received
the concentration of oxygen within the air (air is about 21% oxygen, but in some cases the percentage of oxygen is increased)
how much pressure the patient’s lungs are inflated to
the temperature and humidity of the air.
Ventilators – a DIY project?
Making a mechanical ventilator requires considerable expertise in research, design and manufacturing. To make a commercial mechanical ventilator means ensuring reliability, serviceability and adherence to strict regulatory standards.
All of this is vital, as mechanical ventilators are often used in life and death situations. And this is why, like other specialist medical devices, they are not cheap. One mechanical ventilator can cost up to US$50,000 (about A$82,000).
Read more:
How are the most serious COVID-19 cases treated, and does the coronavirus cause lasting damage?
Responding to a global need in mechanical ventilators, various groups from around the world have emerged with alternative ventilator designs, each claiming their design works and can be manufactured quickly and cheaply.
A number of these DIY mechanical ventilators are based on the Ambu Bag design, including open lung ventilation and proposals from Triple 8 Racing, Richard Branson’s aerospace company Virgin Orbit and British home and garden appliance company Gtech.
However, instead of relying on manual activation like the Ambu Bag bladder, these designs use mechanical automation to press and release the bladder at desired intervals. Some basic controls are available, but the most significant advantage is their inherent simplicity.
Big players join the race
More complex ventilator proposals have also appeared. The Mechanical Ventilator Milano (MVM) was inspired by a 1960s design and uses the pressurised medical oxygen available in hospitals to drive the ventilator. This simplifies the unit considerably, as it doesn’t need a motor.
The MVM was designed by more than one hundred academics and researchers from around the world. It even features a control system enabled through wifi connectivity.
One proposal that more closely mirrors existing ventilators was developed by Dyson, following an urgent request from British Prime Minister Boris Johnson, who was moved to ICU last night as he battles COVID-19. The Dyson ventilator, unsurprisingly, incorporates a motor from one of its iconic vacuum cleaners.
Read more:
Who needs to be in an ICU? It's hard for doctors to tell
Dyson is an internationally recognised design and manufacturing company. Pivoting its resources to a mechanical ventilator is not as difficult as it would be for other companies. After all, managing the movement of air is a core function of Dyson’s products (mainly vacuum cleaners, fans and hair dryers).
Importantly, Dyson will only release its ventilator once it meets British health authority specifications.
But while the race to design and manufacture much-needed ventilators continues, health workers on the front lines must make do with what they have. Let’s hope these collective efforts can soon alleviate some of their stress.
The Conversation/EPA/AAP
A mechanical ventilator comprises a computerised box that sits on top of a mobile trolley. There is an array of screens, dials, data cables, power cords and gas tubes. Modern mechanical ventilators are highly complex and sophisticated pieces of equipment. Their increased complexity in comparison with the Ambu Bag allows a superior level of care.
The extra features and control measures of mechanical ventilators allow adjustments such as:
how long inhalation for a patient lasts
how much air is received
how often air is received
the concentration of oxygen within the air (air is about 21% oxygen, but in some cases the percentage of oxygen is increased)
how much pressure the patient’s lungs are inflated to
the temperature and humidity of the air.
Ventilators – a DIY project?
Making a mechanical ventilator requires considerable expertise in research, design and manufacturing. To make a commercial mechanical ventilator means ensuring reliability, serviceability and adherence to strict regulatory standards.
All of this is vital, as mechanical ventilators are often used in life and death situations. And this is why, like other specialist medical devices, they are not cheap. One mechanical ventilator can cost up to US$50,000 (about A$82,000).
Read more:
How are the most serious COVID-19 cases treated, and does the coronavirus cause lasting damage?
Responding to a global need in mechanical ventilators, various groups from around the world have emerged with alternative ventilator designs, each claiming their design works and can be manufactured quickly and cheaply.
A number of these DIY mechanical ventilators are based on the Ambu Bag design, including open lung ventilation and proposals from Triple 8 Racing, Richard Branson’s aerospace company Virgin Orbit and British home and garden appliance company Gtech.
However, instead of relying on manual activation like the Ambu Bag bladder, these designs use mechanical automation to press and release the bladder at desired intervals. Some basic controls are available, but the most significant advantage is their inherent simplicity.
Big players join the race
More complex ventilator proposals have also appeared. The Mechanical Ventilator Milano (MVM) was inspired by a 1960s design and uses the pressurised medical oxygen available in hospitals to drive the ventilator. This simplifies the unit considerably, as it doesn’t need a motor.
The MVM was designed by more than one hundred academics and researchers from around the world. It even features a control system enabled through wifi connectivity.
One proposal that more closely mirrors existing ventilators was developed by Dyson, following an urgent request from British Prime Minister Boris Johnson, who was moved to ICU last night as he battles COVID-19. The Dyson ventilator, unsurprisingly, incorporates a motor from one of its iconic vacuum cleaners.
Read more:
Who needs to be in an ICU? It's hard for doctors to tell
Dyson is an internationally recognised design and manufacturing company. Pivoting its resources to a mechanical ventilator is not as difficult as it would be for other companies. After all, managing the movement of air is a core function of Dyson’s products (mainly vacuum cleaners, fans and hair dryers).
Importantly, Dyson will only release its ventilator once it meets British health authority specifications.
But while the race to design and manufacture much-needed ventilators continues, health workers on the front lines must make do with what they have. Let’s hope these collective efforts can soon alleviate some of their stress.
Authors: Berto Pandolfo, Senior Lecturer Product Design, University of Technology Sydney