HKU Biomedical Engineering team develops a novel injectable hydrogel that can revolutionise regenerative medicine
HONG KONG SAR - Media OutReach - 31 August 2023 - Researchers from the University of Hong Kong (HKU), the HKU-Shenzhen Hospital and the Princeton University, collaborated to achieve a breakthrough in the development of injectable hydrogels, a highly effective method of administering medicine.
Their innovative product, Fibro-Gel, offers numerous advantages over existing hydrogels and has promising applications in wound healing. 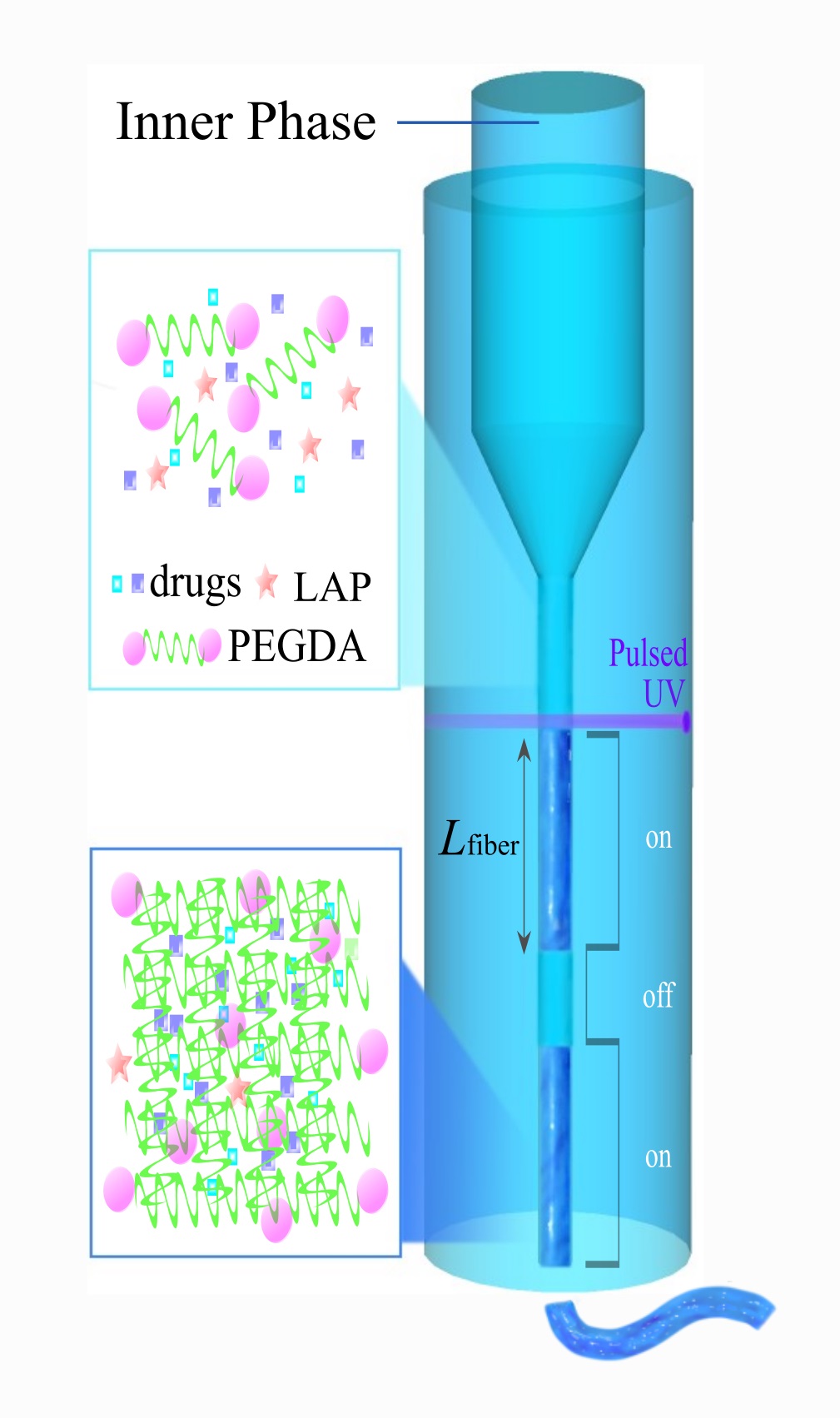
Injectable hydrogel delivery is a highly effective method of administering medicine. A drug is incorporated into a soft gel which is then injected directly where it is required. Another advantage of this method is that the gel releases the drug gradually, allowing for better, more precise control of drug dosage.
Injectable hydrogels have a number of applications – from cancer therapy where they can deliver drugs directly to the tumours, to treating diabetes, regenerating human tissues, and chronic pain management. They are especially suitable for treating wounds, including burns and surgical sites. Hydrogels can deliver growth factors, antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory drugs directly to the wound, aiding the healing process.
However, there have been challenges in hydrogel development, such as the high cost of production, difficulty in scaling up, and the potential for adverse reactions in patients. The Fibro-Gel, created by the research team led by Professor Anderson Ho Cheung Shum from HKU's Department of Mechanical Engineering, together with two groups of collaborators - Professor Michael To's team from The University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital, and the group of Professor Howard Stone and Dr Janine Nunes from the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at Princeton University, addresses these issues.
Fibro-Gel is made by squeezing out a polymer, that contains the molecules of the required drug, through a narrow channel (not unlike toothpaste squeezed out of a tube), and snapping off the microfibres by using a pulse of ultra-violet light.
What sets aside Fibro-Gel from the existing hydrogels is that it is solely aqueous-based, without using oils – which makes it more biocompatible, stable and cheaper to make. In addition, Fibro-Gel is biomimetic – it replicates the properties of biological materials, such as the tissues it is injected into, which prevents adverse reactions. As the result, Fibro-Gel heals wounds faster as it promotes vascularisation – formation of new blood vessels, which plays a crucial role in wound healing.
A revolutionary feature of Fibro-Gel is that it allows the use of different drugs within the same gel, thus enabling controlling and tuning the time of their release. This is very important because the processes of healing and tissue regeneration consist of a sequence of different stages which require administration of specific growth factors and drugs.
Finally, the production of Fibro-Gel production is not costly and can be easily scaled up to manufacturing levels.
The crucial breakthrough was made by PhD student Yanting Shen and postdoctoral fellow Dr Yuan Liu of HKU's Department of Mechanical Engineering – the researchers realised that the release of the drugs from the gel can be controlled and tailored by setting the length of microfibres that the gel consists of.
Longer microfibres become very entangled, resulting in a stiffer, less fluid gel, and it takes longer for the molecules of the drug to be released from it. Conversely, Fibro-Gel with shorter microfibers has lower stiffness and is more fluid fluid-like, resulting in faster rates of drug release.
Leveraging this feature, the researchers designed a multiple drug release system – a gel consisting of multiple layers with different length of microfibres and containing different drugs. These multiple drugs are released from the gel at different times, in sequence, addressing the drawbacks of existing hydrogel systems.
Laboratory testing on mice showed that, compared to commercially available gels, Fibro-Gel regenerates tissues significantly faster, with new tissue forming sooner. Furthermore, using a two-layer Fibro-Gel model, the researchers demonstrated that the release of distinct drugs at different rates enhanced wound healing.
One such potential application of Fibro-Gel is regeneration of brain tissue in people suffering from Parkinson's or Alzheimer's.
Professor Shum emphasised that multidisciplinary collaboration was key in producing Fibre-Gel, "Our collaboration has enabled us to address the topic of wound healing from multiple perspectives. This novel hydrogel has immense potential to address critical medical needs that require more versatile and compatible soft materials."
The successful partnership between HKU and Princeton University, supported by the Research Impact Fund by the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong, exemplifies the power of cross-border collaboration and highlights the significance of pooling expertise to drive groundbreaking research in the field of regenerative medicine.
Their work was published in Advanced Materials in an article "Fibro-Gel: An All-Aqueous Hydrogel Consisting of Microfibers with Tunable Release Profile and its Application in Wound Healing".
Link to the paper: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202211637.
Hashtag: #HKU
The issuer is solely responsible for the content of this announcement.


















