Aftershocks hit Papua New Guinea as it recovers from a remote major earthquake
- Written by Sabin Zahirovic, Postdoctoral Research Associate, University of Sydney
Another powerful aftershock hit Papua New Guinea this weekend as the recovery effort continues following February’s deadly magnitude 7.5 earthquake, with many thousands of people dependent on humanitarian aid.
Aid organisations such as CARE Australia and UNICEF are still seeking donations. The Australian government has sent medical staff and other support to help.
Some have criticised the PNG government’s efforts as “too slow”.
Read more: The science of landslides, and why they're so devastating in PNG
But the earthquake highlights the challenge for emerging economies like PNG in deploying relief efforts into remote areas to deal with natural disasters.
And the same geological features that make PNG a rich source of mineral deposits are also part of its earthquake problem.
The earthquake hits
The February earthquake struck the western Highlands provinces of the Pacific island nation, and a series of aftershocks, including several of magnitude 6 or more, continued to shake the region during the following weeks.
Although parts of PNG are particularly earthquake-prone (especially in the north and the islands, along the plate boundary), February’s earthquake was quite exceptional.
It occurred in a usually less active part of the plate boundary and was remarkably powerful when compared with the short (modern) instrumental earthquake record. The strength and frequency of the aftershocks has posed an additional threat to local populations and key economic infrastructure.
On average 10-20 major earthquakes (magnitudes 7 and greater) occur on Earth every year. Most of them occur far from densely populated regions, such that only a few draw media attention.
The mountainous regions of New Guinea, known as the fold and thrust belt, have been geologically active for millions of years. But the long recurrence interval of major earthquakes (every few centuries) combined with the short period of the instrument records (just a few decades) gives us the false impression that seismicity is uncommon in this region.
The February earthquake occurred due to the activation of a major fault system in the forested foothills, between the Papuan highlands to the north and the Fly River lowlands to the south.
Australia collides
The Papuan highlands have risen due to the collision between the Australian and Caroline/Pacific tectonic plates over the past five million years.
An animation of Australia’s tectonic journey as it broke away from Gondwana more than 100 million years ago. (Credit: Sabin Zahirovic)Despite this collision, the Australian plate continues to move at about 7 cm a year to the northeast, in geological terms a quite remarkable speed, leading to a build-up of strain in the continental crust.
Much of this strain is released at the plate boundary along northern New Guinea, usually with more frequent but less powerful swarms of earthquakes. It is this motion, driven by the churning interior of our planet, that leads to major adjustments to the GPS datum and reference coordinates for the entire Australian continent.
But few people are aware that this very motion of the Australian continent is what causes the seismic and volcanic activity in New Guinea and parts of Southeast Asia.
As Australia moves northward, the entire New Guinea margin acts as a bulldozer, collecting Pacific islands, seamounts and other topographic features. New Guinea represents the leading edge of the advancing Australian continent, which causes continental crust to fold and crumple over a broad region.
This is a well-known process in plate tectonics, where the oceanic plates are known to behave quite rigidly, whereas the continental regions tend to deform over broader diffuse boundaries that resemble plasticine over geological timeframes.
When continents are squeezed during tectonic collisions, the crust crumples and folds over geological timescales. (Credit: Romain Beucher)But the continental deformation process results in poorly defined (often due to the thick tropical vegetation cover) and intermittently active fault systems in the continent.
Over the duration of mountain building in the past five million years, the areas of highest deformation have shifted across the range. Today most of the deformation in PNG takes place north of the mountainous area, where it generates a lot of earthquakes.
Underground riches at risk
Some substantial crumpling of the continental crust still occurs across the southern foothills. The folding and thrusting has generated geologically young folds, within which a large part of PNG’s gas and oil wealth has accumulated.
The intense tectonic activity has also led to the enrichment of mineral resources, including mines sourcing gold, copper, silver, nickel, cobalt and a suite of other ore types.
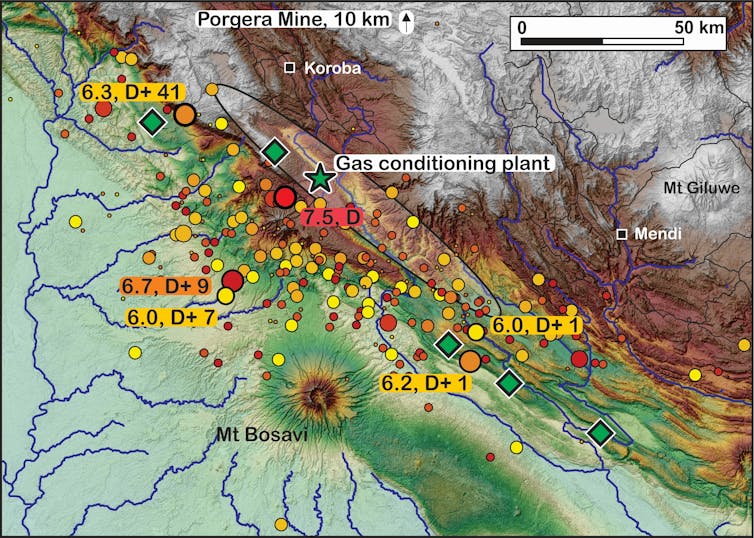 Distribution of the aftershocks magnitude 4+ since the main quake (as of April 9, 2018). The size and colour (small to large, yellow to red) indicate aftershock magnitude and D+ the number of days after main shock. The white shaded ellipse represents the area of greatest slip during the main shock. Green diamonds represent the main gas fields.
USGS/Gilles Brocard, Author provided
Distribution of the aftershocks magnitude 4+ since the main quake (as of April 9, 2018). The size and colour (small to large, yellow to red) indicate aftershock magnitude and D+ the number of days after main shock. The white shaded ellipse represents the area of greatest slip during the main shock. Green diamonds represent the main gas fields.
USGS/Gilles Brocard, Author provided
It is this tectonic activity that determines the delicate interplay of economic benefits from raw materials, and the often-devastating and usually-unpredictable effects of natural disasters on society.
Although the February earthquake occurred at the very heart of one of the largest and newest gas fields in the country, the industrial installations, at the highest international standards, have not suffered major damage from the tremors.
But the ongoing disaster triggered a temporary halt in gas extraction, as the facilities require inspections and repairs. Unfortunately, and unusually, the earthquakes have struck in some of the most remote parts of the country.
Coping with disaster
Hela province is one of the poorest in PNG and its people are unprepared and ill-equipped to deal with a disaster of this scale. As many as half a million people were reported to be affected by the earthquake. At least 145 people reported killed.
Read more: Five active volcanoes on my Asia Pacific 'Ring of Fire' watch-list right now
The Highlands Highway, the one real road into the region, was badly damaged and this is the major source of food and medicines. Many feeder roads have gone.
Papua New Guineans are resilient but it is likely that more external assistance will be needed to ensure that a physical disaster does not become a greater human tragedy.
Even so the full extent of the disaster has still to be revealed, while aftershocks continue to trigger secondary hazards including major landslides that have isolated a large number of communities.
Not only are local communities facing the immediate hazards of further earthquakes and landslides, they face a protracted and costly recovery ahead.
Authors: Sabin Zahirovic, Postdoctoral Research Associate, University of Sydney


















