How will they make internet speeds faster? And will the regions miss out?
- Written by Thas Ampalavanapillai Nirmalathas, Group Head - Electronic and Photonic Systems Group and Professor of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Melbourne

The federal government has announced a A$3.5 billion upgrade to the National Broadband Network (NBN) that will grant two million households on-demand access to faster fibre-to-the-node (FTTN) internet by 2023.
Reports from the ABC suggest the plan would go as far as to upgrade the FTTN services to fibre-to-the-premises (FTTP) – although this wasn’t explicitly said in Minister for Communications Paul Fletcher’s announcement.
The minister said the upgrade would involve expanding current FTTN connections to run along more streets across the country, giving people the option to connect to broadband speeds of up to one gigabit per second. Improvements have also been promised for the hybrid fibre coaxial (HFC) and fibre-to-the-curb (FTTC) systems.
Altogether the upgrade is expected to give about six million households access to internet speeds of up to one gigabit per second. But how will the existing infrastructure be boosted? And who will miss out?
Getting ahead of the terminology
Let’s first understand the various terms used to describe aspects of the NBN network.
Fibre to the Premises (FTTP)
FTTP refers to households with an optical fibre connection running from a device on a wall of the house directly to the network. This provides reliable high-speed internet.
The “network” simply refers to the exchange point from which households’ broadband connections are passed to service providers, such as Telstra, who help them get connected.
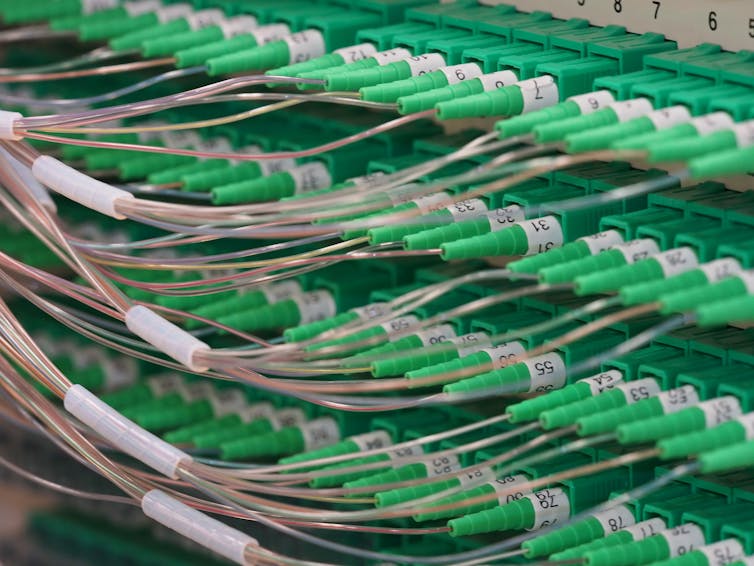 In an FTTP network, fibre optic connectors in the back of distribution hub panels connect homes to broadband services. Shutterstock
In an FTTP network, fibre optic connectors in the back of distribution hub panels connect homes to broadband services. Shutterstock
Fibre to the Node (FTTN)
The FTTN system serves about 4.7 million premises in Australia, out of a total 11.5 million covered under the NBN.
With FTTN, households are connected via a copper line to a “node” in their neighbourhood. This node is further connected to the network with fibre optic cables that transfer data much faster than copper cables can.
With FTTN systems, the quality of the broadband service depends on the length of the copper cable and the choice of technology used to support data transmission via this cable.
It’s technically possible to offer high internet speeds when copper cables are very short and the latest data transmission technologies are used.
In reality, however, Australia’s FTTN speeds using a fibre/copper mix have been slow. An FTTN connection’s reliability also depends on network conditions, such as the age of the copper cabling and whether any of the signal is leaking due to degradation.
 Fibre optic cables use pulses of light for high-speed data transmission across long distances. Shutterstock
Fibre optic cables use pulses of light for high-speed data transmission across long distances. Shutterstock
Fibre to the Curb (FTTC)
The limitations of FTTN mentioned above can be sidestepped by extending fibre cables from the network right up to a curbside “distribution point unit” nearer to households. This unit then becomes the “node” of the network.
FTTC allows significantly faster data transmission. This is because it services relatively fewer households (allowing better signal transmission to each one) and reduces the length of copper cable relied upon.
Hybrid Fibre Coaxial (HFC)
In many areas, the NBN uses coaxial cables instead of copper cables. These were first installed by Optus and Telstra in the 1990s to deliver cable broadband and television. They’ve since been modernised for use in the NBN’s fibre network.
In theory, HFC systems should be able to offer internet speeds of more than 100 megabits per second. But many households have been unable to achieve this due to the poor condition of cabling infrastructure in some parts, as well as large numbers of households sharing a single coaxial cable.
Coaxial cables are the most limiting part of the HFC system. So expanding the length of fibre cabling (and shortening the coaxial cables being used) would allow faster internet speeds. The NBN’s 2020 corporate plan identifies doing this as a priority.
Minister Fletcher today said the planned upgrades would ensure all customers serviced by HFC would have access to speeds of up to one gigabit per second. Currently, only 7% of HFC customers do.
Mixing things up isn’t always a good idea
Under the original NBN plan, the Labor government in 2009 promised optical fibre connections for 93% of all Australian households.
Successive reviews led to the use of multiple technologies in the network, rather than the full-fibre network Labor envisioned. Many households are not able to upgrade their connection because of limitations to the technology available in their neighbourhood.
Read more: The NBN: how a national infrastructure dream fell short
Also, many businesses currently served by FTTN can’t access internet speeds that meet their requirements and need to reach out to external providers for business grade internet solutions. To avoid internet speeds hindering their work, many businesses need a minimum speed between 100 megabits and 1 gigabit per second, depending on their scale.
Currently, no FTTN services and few HFC services can support such speeds.
Moreover, the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission’s NBN monitoring report published in May (during the pandemic) found in about 95% of cases, NBN plans only delivered 83-91% of the maximum advertised speed.
The report also showed 10% of the monitored services were underperforming – and 95% of these were FTTN services. This makes a strong case for the need to upgrade FTTN.
Who will benefit?
While the NBN’s most recent corporate plan identifies work to be done across its various offerings (FTTN, FTTC, HFC, fixed wireless), it’s unclear exactly how much each system stands to gain from today’s announcements.
Ideally, urban and regional households that can’t access 100 megabits per second speeds would be prioritised for fibre expansion. The expanded FTTN network should also cover those struggling to access reliable broadband in regional Australia.
Bringing fibre cabling to households in remote areas would be difficult. One option, however, could be to extend fibre connections to an expanded network of base stations in regional Australia, thereby improving the NBN’s fixed wireless connectivity capacity.
These base stations “beam” signals to nearby premises. Installing more stations would mean fewer premises covered by each (and therefore better connectivity for each).
Regardless, it’s important the upgrades happen quickly. Many NBN customers now working and studying from home will be waiting eagerly for a much-needed boost to their internet speed.
Read more: How to boost your internet speed when everyone is working from home
Authors: Thas Ampalavanapillai Nirmalathas, Group Head - Electronic and Photonic Systems Group and Professor of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Melbourne



















