As holidaymakers arrive, what does COVID-19 mean for rural health services?
- Written by Timothy Baker, Associate Professor and Director, Centre for Rural Emergency Medicine, Deakin University
At the start of the pandemic, health services in regional cities and small towns braced for a tsunami of cases. Many worried the patient transport system between hospitals would fail, and each hospital would be left to fend for itself. Small hospitals planned makeshift intensive care departments with improvised long-term ventilators. And health-care teams drilled themselves in how they would manage a COVID-positive patient who was deteriorating.
Fortunately, in Australia, these dire predictions were wrong (at least for now). But they could have been right. Rural areas are not immune to COVID-19. In the United States, the current rural infection rate is higher than has ever been recorded in metropolitan areas. A Louisiana hospital described exactly the makeshift intensive care scenario we feared in Australia. Rural patients are more vulnerable too, as the community is older with more chronic health problems.
Read more: Rural America is more vulnerable to COVID-19 than cities are, and it's starting to show
In rural Australia, dealing with the pandemic has been more like whack-a-mole than an overwhelming wave. Outbreaks occurred around meatworks, local hospitals, and super-spreaders travelling from hotspots.
So, what have we learned so far about the impact of COVID-19 on rural health, and how can we maintain effective rural health care as tourism ramps up?
We must work together
A pandemic lays bare pre-existing structural problems. It exposes the lack of formal channels for rural clinicians to communicate across disciplines and across regions. It reveals the barriers between clinicians in the hospitals and bureaucrats in regional and city offices.
But it also provides an opportunity to connect these groups. During the pandemic, health services across different regions and states shared local solutions. Public health, hospital, community care and inter-hospital services created joint protocols. New communication channels must be maintained and ready for activation if cases increase.
Local knowledge remains important. Embedding local health workers in contact-tracing teams is a strength of NSW’s pandemic defences.
As the Victorian town of Shepparton discovered last week, local outbreaks cause an immediate and massive demand for testing. Using local media to keep rural communities up to date enhances the remarkable support already shown for quarantine measures.
Teleconferencing between clinicians has expanded, as it has between clinicians and patients. It is best and most geographically equitable when it adds to face-to-face local care.
But it may also detract from enabling the best care when it replaces clinicians on the ground. One possible example is that of a woman who died in the emergency department of a regional NSW hospital in September. No doctors were present in person, having been replaced by telehealth treatment outside business hours.
Read more: Where did Victoria go so wrong with contact tracing and have they fixed it?
Self-reliance and silent hypoxia are a bad combination
Identifying patients before they become critically ill is crucial to rural acute care. This is true for COVID-19. The disease has a reasonably predictable path of early fever, improvement, and then a sometimes rapid deterioration in the second week. For all but large regional centres, this means COVID-19 is managed in the community. Deteriorating patients need to be transferred early.
Unfortunately, COVID-19 has a horrible trick. It can cause extremely low levels of blood oxygen without a patient feeling unwell or breathless, or realising their oxygen levels are critically low. This is called silent hypoxia.
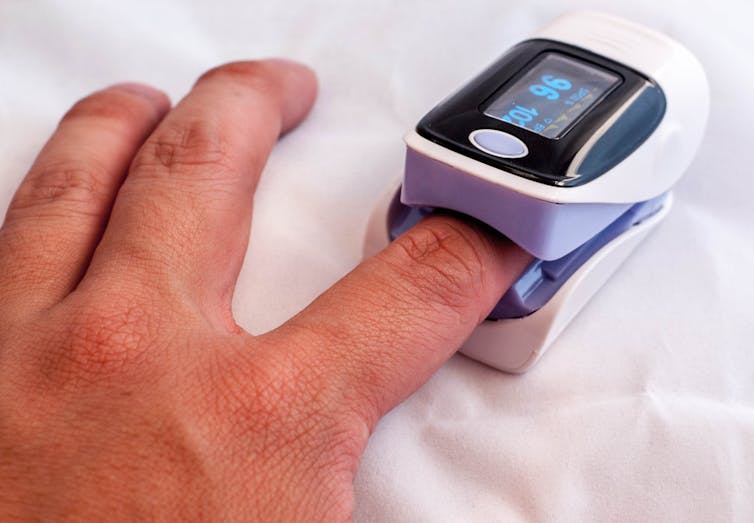 Many rural health services have used remote oxygen monitoring tools so clinicians can check in on patients recovering at home.
Shutterstock
Many rural health services have used remote oxygen monitoring tools so clinicians can check in on patients recovering at home.
Shutterstock
It’s a problem everywhere, but it may be worse in rural areas. Patients often visit regional hospitals at a later stage of their illness due to self-reliance, distance to care, and a poorer understanding of the health system. By the time a rural COVID-19 patient thinks they are unwell enough to attend, they may already be close to dying.
Rural health services have had to adopt policies of regular local and remote checking-in for COVID-19 patients, especially in the second week. Telephone and internet connections are not always enough, so many hospitals have bought oxygen-monitoring tools for patients to use at home.
Maintaining normal services is difficult
COVID-19 need only infect a few staff at regional hospitals to make service delivery impossible. In northwest Tasmania, Australian Defence Force members had to replace infected and quarantining staff in mid-April.
Even without an outbreak, COVID makes it difficult to maintain normal operations. Health services relying on fly-in fly-out staff have struggled when staff can no longer travel freely across quarantine lines from the city or across state borders. Exemptions were given but the approval process was slow and many staff still had to do periods of self-quarantine, meaning many staff found it too difficult. Mechanisms to replace or increase staff may still be needed for regions with outbreaks.
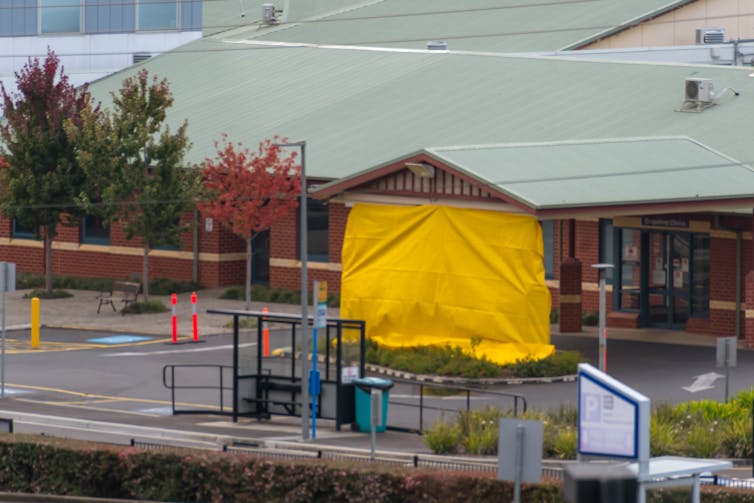 Two hospitals in northwest Tasmania were forced to temporarily close in mid-April due to coronavirus outbreaks, as more than 1,000 health-care workers went into quarantine.
Simon Sturzaker/AAP
Two hospitals in northwest Tasmania were forced to temporarily close in mid-April due to coronavirus outbreaks, as more than 1,000 health-care workers went into quarantine.
Simon Sturzaker/AAP
Although rural hospitals have been spared the overwhelming numbers of COVID-19 seen in Melbourne hospitals, the extra precautions required to manage patients who could potentially have COVID-19 are draining. Maintaining services reliant on supplies at the end of the supply and logistics chain is slower and challenging. Like metropolitan staff, rural staff are feeling fatigued and requiring extra mental health support.
This is a problem as people move to rural areas for holidays and business. Even in normal years, health services in coastal and other tourist towns are busiest when the population swells in summer. With bookings of holiday accommodation booming in many areas, rural health services may be facing their busiest and most tiring part of the pandemic. If holidaymakers feel leaving the city means leaving behind the risk of infection and the need to socially distance, the results in some rural towns may be catastrophic.
Authors: Timothy Baker, Associate Professor and Director, Centre for Rural Emergency Medicine, Deakin University