Australia's waste export ban becomes law, but the crisis is far from over
- Written by Jenni Downes, Research Fellow, BehaviourWorks Australia (Monash Sustainable Development Institute), Monash University
Last week, Australia took an important step towards addressing the ongoing effects of the 2018 waste crisis. The federal parliament passed legislation banning the export of unprocessed waste overseas via the Recycling and Waste Reduction Act 2020.
The new law provides an impetus to reconfigure local infrastructure to reprocess and re-manufacture recyclables onshore. It should create local demand to reuse these recovered materials in infrastructure, packaging and products as part of a move towards a circular economy.
It’s encouraging to see the federal government finally providing clear policy direction for the waste industry and making Australia more responsible for how our waste is recovered. But it’s far from enough to temper the waste crisis.
Is exporting waste ‘bad’?
The total amount of waste generated in 2018-19 went up 10% from just two years earlier — and only half of that was recycled. Meanwhile, opportunities to export material for overseas recycling have been drying up.
In 2019, Australia exported an estimated 7% of all waste generated. The proportion is much higher for the household commingled recycling bin, where around one-third of all paper and plastics were exported to overseas trading partners, particularly in Asia.
Exporting material recovered from waste isn’t “bad” per se, particularly when you consider Australia imports more manufactured goods than we make locally. Currently, our economy remains structured around exporting virgin (new) and recyclable materials, which are made into products offshore and then re-imported.
So, when we export well-sorted, quality, recyclable material, it’s no different than exporting, say, iron ore.
However, just dumping “rubbish” on other countries is not acceptable. And even exporting potentially recyclable material without taking responsibility for how the material will be recovered overseas leads to a greater risk of it being dumped or burned.
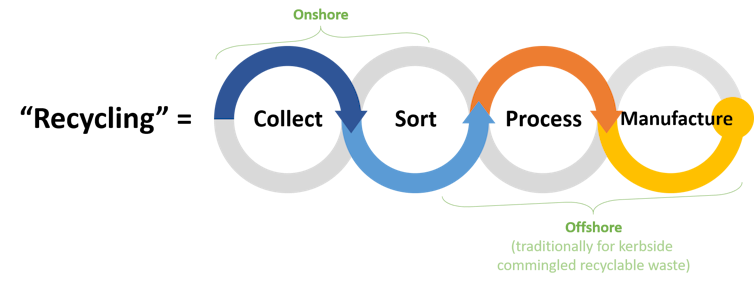 Stages of recycling Australia’s mixed kerbside wastes.
Downes, J. (2020)
Stages of recycling Australia’s mixed kerbside wastes.
Downes, J. (2020)
Such an economic structure makes us reliant on international markets and the policy priorities of those countries.
This was highlighted in 2018 when China banned waste imports of all but the highest purity, with other countries in Asia following suit. This shocked Australia’s (and the world’s) recycling industry, and led to plummeting prices for certain waste materials and increased stockpiling and short-term landfilling.
Read more: China's recycling 'ban' throws Australia into a very messy waste crisis
What’s more, when developing countries import too much waste or low-quality material, their infrastructure and markets can become overwhelmed. The waste then ends up “leaking” into the environment, including the ocean, as litter.
A ban on Australia’s waste export was first announced in August 2019 to help address our responsibility for ocean plastics. The ban could localise much of Australia’s reprocessing — and possibly, manufacturing — activity.
What does the ban involve?
The new law passed last week will complement and extend existing laws on hazardous waste and product stewardship.
Effectively, the ban prohibits the export of specific raw (unprocessed) materials collected for recycling: plastic, paper, glass and tires. Any materials that have been re-processed and turned into other “value-added” materials (those ready for further use) can still be exported under the law. For example, a single type of plastic cleaned and shredded into “flakes”, or cleaned packaging glass crushed into “cullet”.
The law is accompanied by commitments from the federal and state governments to help address some of the critical systemic barriers to onshore processing, such as the lack of existing infrastructure and domestic markets for reprocessed material.
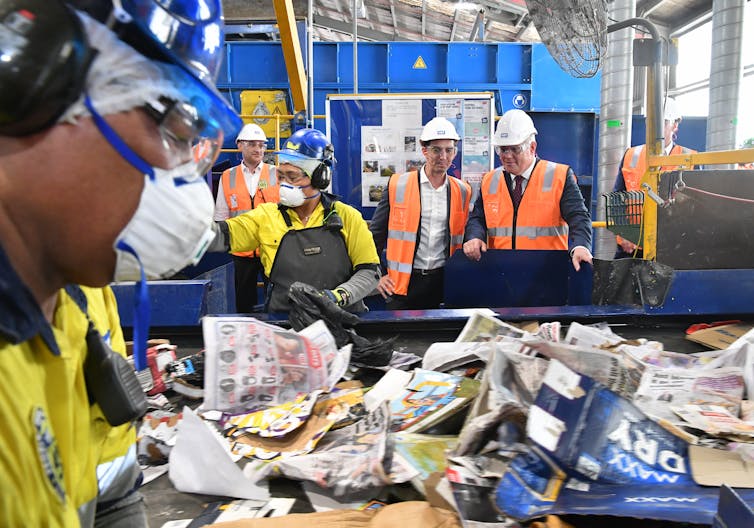 Prime Minister Scott Morrison announced in the budget that recycling will get a $250 million boost in a plan to stop more than 600,000 tonnes of waste ending up in landfill.
AAP Image/Darren England
Prime Minister Scott Morrison announced in the budget that recycling will get a $250 million boost in a plan to stop more than 600,000 tonnes of waste ending up in landfill.
AAP Image/Darren England
No room for error
Without sufficient transition measures, it’s possible the ban could lead to more waste ending up in landfills, stockpiling or illegal dumping.
For the ban to be effective, a lot of things need to go right. This includes:
Getting the transition right will be critical for Western Australia, South Australia, Queensland and the Northern Territory, which are particularly lacking in proper infrastructure.
Read more: Can we safely burn waste to make fuel like they do in Denmark? Well, it’s complicated
It’s also important for NSW and Victoria because of the high proportion of banned materials they currently export. For example, over 80% of Australia’s exported plastic was from NSW and Victoria, while 90% of exported glass was from Victoria.
 Ultimately, it’s far better for the environment to reduce the generation of waste in the first place.
Shutterstock
Ultimately, it’s far better for the environment to reduce the generation of waste in the first place.
Shutterstock
Increasing momentum
Given exports are only a part of overall waste material flows, it’s great to see the ban is part of a suite of responses. This includes the Recycling Modernisation Fund, and the recent $10 million National Product Stewardship Investment Fund and Product Stewardship Centre of Excellence.
Still, we shouldn’t lose sight of the fact these are predominantly “end-of-pipe” solutions.
While there are promising efforts from industry and government to minimise waste by improving the design of Australian-made products and packaging, more should be done.
Options include minimum design standards and extended producer responsibility, which would make manufacturers and retailers financially responsible for ensuring their products are recycled. This would incentivise better “up the chain” (design) choices.
Read more: Four bins might help, but to solve our waste crisis we need a strong market for recycled products
And as a major importer of manufactured products, Australia also needs to manage what’s coming into the country through improved standards, such as minimum requirements for recyclability and durability, or prohibiting problematic materials in inferior products that will quickly become waste.
Ultimately, it’s far better for the environment to reduce the generation of waste in the first place. Together with better design, this will move us towards a more circular economy.
If Australia’s new waste and recycling law represents increasing momentum towards a circular economy in Australia, rather than a pinnacle on which we rest, it will be an excellent step forward.
Authors: Jenni Downes, Research Fellow, BehaviourWorks Australia (Monash Sustainable Development Institute), Monash University