A staggering 1.8 million hectares burned in 'high-severity' fires during Australia's Black Summer
- Written by Ross Bradstock, Emeritus professor, University of Wollongong
In the aftermath of Australia’s devastating Black Summer fires, research has begun to clarify the role of climate change.
We already know climate change contributed to the record-breaking drought and fire weather conditions, leading to the bushfires’ unprecedented range across Australia.
Our new research looks at whether bushfires are becoming more “severe” (an indicator of how intensely the vegetation burned) as a result of climate change.
Our findings were unexpected, as we learned the proportion of high-severity fires generally hasn’t increased in recent decades. However, the sheer breadth of the Black Summer fires meant an unprecedented 1.8 million hectares across southeast Australia were exposed to high-severity fires. This has dire consequences for the people and wildlife who call the forests home.
What is fire severity?
Two measurements in fire science are pertinent to our research: fire severity and fire intensity.
Fire severity refers to how high the flames and the plume of hot air reach, as measured by the resulting damage to vegetation (vertical profile of scorch and consumption of leaves and twigs). Fire intensity refers to the energy released from the fire — how hot and destructive the flames are.
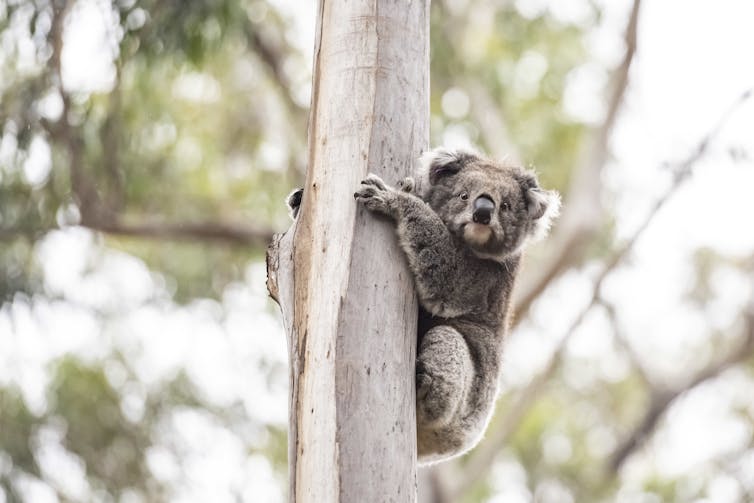 Animals that live in trees are at the greatest risk of high-severity fires.
AAP Image/Zoos Victoria
Animals that live in trees are at the greatest risk of high-severity fires.
AAP Image/Zoos Victoria
Scientists can estimate severity using using satellite imagery, by contrasting differences in the cover and condition of vegetation before and after fires.
In forests, “high-severity” fires occur when the crowns of dominant trees are fully burnt or scorched. High-severity fires are lethal to tree-dwelling mammals in forests, such as possums, gliders and koalas. They also pose a big risk to nearby homes and buildings.
“Low-severity” fires, on the other hand, may be confined to the leaf litter and ground cover plants beneath the forest canopy, and can even leave entirely unburnt patches in forests.
Are high severity fires becoming more common?
To determine if high-severity bushfires are becoming more common, we looked at satellite data for bushfires from 1988 to 2020. The data covered more than 130,000 square kilometres of forest, woodland and shrubland ecosystems in southeast Australia.
If fires were becoming more intense in recent decades, we would have expected the proportion of vegetation subjected to high-severity fire to have increased.
Instead, we found the average proportion of high-severity wildfire remained constant in dry forest — the dominant vegetation across this region. There was, however, evidence of an increase in the average proportion of high-severity fire in wet forests and rainforests, along with woodlands.
Read more: 5 remarkable stories of flora and fauna in the aftermath of Australia’s horror bushfire season
Nonetheless, the main conclusion was clear: across the bulk of the study area, the average proportion of high-severity fires has not changed in recent decades, despite an increase in the area burned during the Black Summer bushfires.
Why the Black Summer bushfires were exceptional
While the proportion of high-severity fires hasn’t changed, the enormous range of the 2019-2020 bushfires meant 44% of the total area burned by high-severity fire since 1988 occurred in that one summer alone.
This means 1.8 million hectares of the forest and woodland regions of southeastern Australia — an enormous proportion — was exposed to intense and severe fire. In this regard, the Black Summer bushfires were exceptional.
As Australians remember all too clearly, this had a devastating effect on the environment. An estimated three billion animals were killed or displaced, vulnerable rainforests burned and 3,000 homes were destroyed.
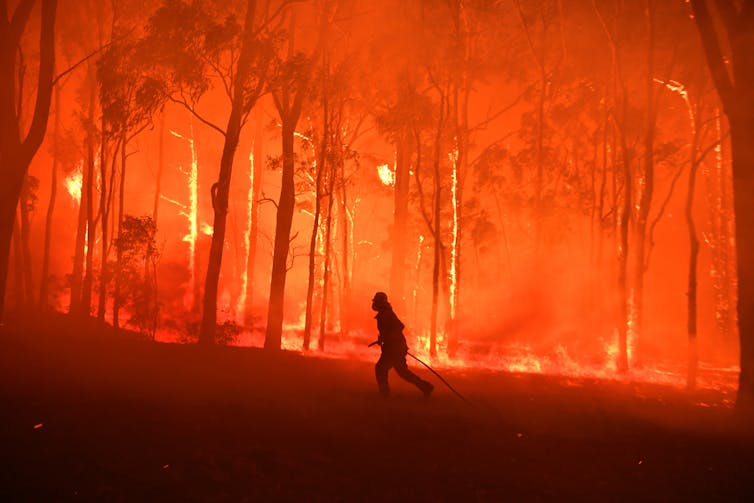 Firestorms could become more common under a changing climate.
AAP Image/Dean Lewins
Firestorms could become more common under a changing climate.
AAP Image/Dean Lewins
The 2019-20 fire season also involved a record number of “firestorms”, particularly during the latter part of the season in January and early February. This occurs when fires create their own weather.
These fires can burn at exceptional intensity. And research from 2019 indicates such firestorms could become more common under climate change.
This means we can’t rule out a future change in the proportion of bushfires that burn at the highest levels of intensity and severity.
Ecosystems in jeopardy
The results of our study underline one of the likely consequences of future climate change.
The sheer scale of the area burned in the 2019-20 fire season exceeded not only historical records for forested ecosystems of southern Australia, but also outstripped projections for the late 21st century under strong scenarios of climate change.
As bushfires become larger in the future, the area exposed to intense and severe fires is likely to increase commensurately. As a result, the future of our wetter forest types, which have not evolved to cope with frequent and severe fires, is in jeopardy.
So, as the area exposed to intense fires is likely to increase in the future, we’ll see major challenges to the long-term viability of our forested ecosystems, the services they provide and the people who reside in and around them.
Authors: Ross Bradstock, Emeritus professor, University of Wollongong