Demasi cleared, but images in science continue to attract intense scrutiny
- Written by Rachael Dunlop, Honorary Research Fellow, Macquarie University
Science reporter Maryanne Demasi was last month cleared of allegations of research misconduct in relation to her University of Adelaide PhD thesis published in 2004.
The allegations were investigated by an independent panel convened by the University of Adelaide’s Office of Research Ethics, Compliance and Integrity. It comprised a former justice of the Supreme Court of South Australia and three professors of medical science not linked with the University of Adelaide.
There were 17 allegations about images in Demasi’s thesis. The question before the panel was whether the images “had been duplicated and/or manipulated in a manner that deviated from the applicable standards at the relevant time”.
All of the impugned images depicted the results of experiments to detect proteins or RNA molecules. The techniques to do this are known as “western blot” and “northern blot”, respectively.
In 14 cases the panel found no image duplication had taken place. In the remaining three cases Demasi “admitted that she had duplicated or probably duplicated the relevant impugned images” – but the panel “could not be satisfied that the duplication constituted a deviation from the applicable standards at the relevant time”.
It’s not clear whether blot images are the focus of The Journal of Biological Chemistry’s expression of concern in 2017 regarding one of Demasi’s scientific papers published in 2003.
Demasi firmly denies any research misconduct in both her thesis and research papers. But what are western and northern blots? And why do they attract such scrutiny?
Read more: How we edit science part 1: the scientific method
Detecting proteins
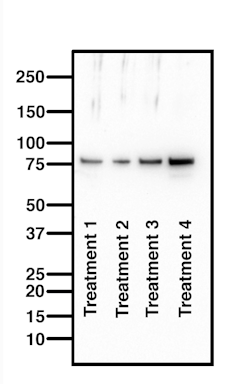 A good western blot will show the entire membrane, from 250 kilodaltons to 10 kilodaltons, and be clean except for the protein of interest. Each band represents a different sample so should be visually different.
Author's own western blot
A good western blot will show the entire membrane, from 250 kilodaltons to 10 kilodaltons, and be clean except for the protein of interest. Each band represents a different sample so should be visually different.
Author's own western blot
Westerns blots detect proteins, and are a commonly used and sensitive scientific technique. The image they produce may look like a nondescript smudge, but western blots are in fact a very useful way to home in on a specific protein in a complex mixture of biological materials, such as blood or tissue.
Western blots are used in the diagnosis of Lyme disease, for example. This is because infection with the bacterium that causes Lyme (Borrelia burgdorferi) leaves a unique fingerprint of proteins in a patient’s blood.
Western blots also enable researchers to determine changes in proteins in response to a drug regimen. In my own lab, I routinely run western blots to measure changes in protein profiles in response to a dietary supplement that we are trialling for the treatment of motor neuron disease.
Read more: What we know, don’t know and suspect about what causes motor neuron disease
Western, southern, northern
Western blots are named for the location of the American lab where they were first conducted. The choice of the term “western” is apparently in homage to the previously named Southern (named after Ed Southern) and northern blots, for detecting DNA and RNA, respectively.
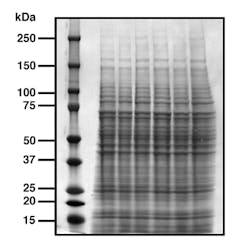 A mix of proteins are first separated by their molecular weight, with small ones moving faster and reaching the bottom of the gel sooner, to create a ladder-like appearance. A protein stain enables us to visualise the proteins, where each band represents a different population of proteins.
Author's own protein stain
A mix of proteins are first separated by their molecular weight, with small ones moving faster and reaching the bottom of the gel sooner, to create a ladder-like appearance. A protein stain enables us to visualise the proteins, where each band represents a different population of proteins.
Author's own protein stain
To run a western blot, a mix of proteins is loaded onto a gel made of polyacrylamide that allows separation of the proteins according to their molecular weights. Molecular weight is measured in kilodaltons, or kDa (the dalton or atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 the weight of the carbon-12 isotope, or approximately one hydrogen atom).
When an electrical current is applied, small proteins move relatively rapidly through the gel, and larger ones more slowly – the result is a ladder-like distribution of the proteins.
After this, the protein ladder is immersed in an antibody solution and incubated. When the excess antibody is washed away, you’re left with a “band” where your antibody has bound to your protein of interest.
Read more: Dr Google probably isn't the worst place to get your health advice
What to look for
Because a western blot is designed to detect one protein at a time, the image should be blank except for your band of interest.
Below is a bad western blot that I prepared earlier. By now, you should be able to identify what’s wrong with this one – it has multiple bands, meaning that the antibody is not specific. And while it’s tempting to crop out extra bands and extraneous artefacts, I really should be going back to the lab to optimise this.
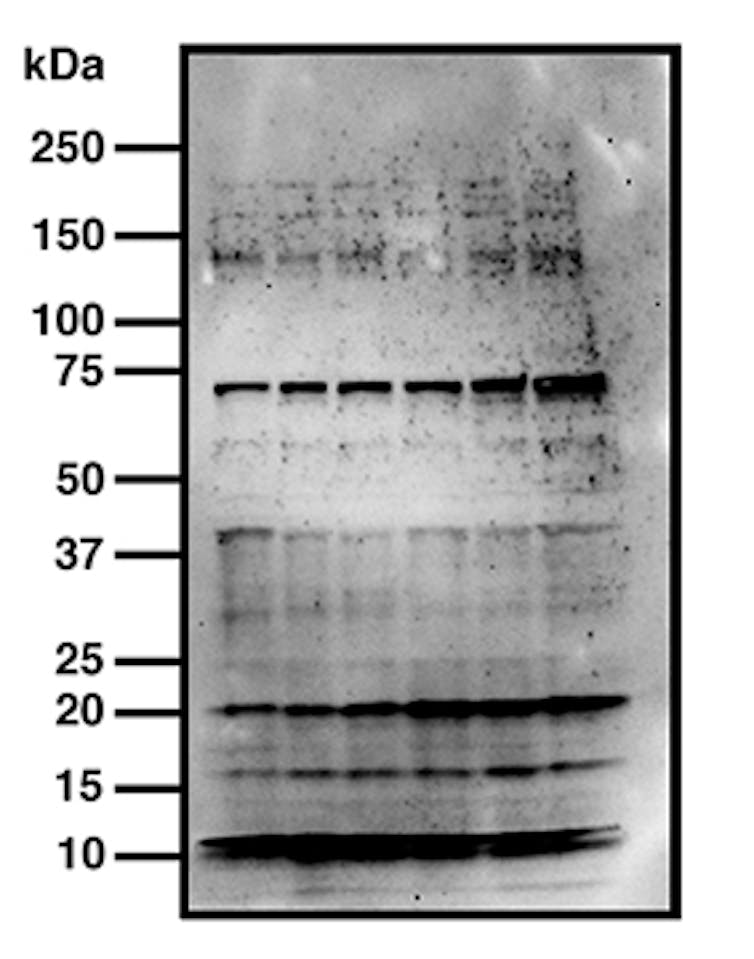 A bad western blot has multiple bands instead of one, meaning the antibody has recognised several proteins and is therefore not specific. It’s not uncommon for scientists to crop these images tight to remove offending artefacts. As a result, some journals now request authors submit the full, un-cropped image, for review.
Author's own bad western
A bad western blot has multiple bands instead of one, meaning the antibody has recognised several proteins and is therefore not specific. It’s not uncommon for scientists to crop these images tight to remove offending artefacts. As a result, some journals now request authors submit the full, un-cropped image, for review.
Author's own bad western
Importantly, each sample run on a western blot is unique, so each sample band should also look different.
A northern blot is a similar concept to the western blot, but commonly uses probes to detect RNA instead of ones to detect proteins. In the Southern blot technique, DNA is detected.
Increasing scrutiny
Since the advent of websites such as PubPeer, western blots are being increasingly scrutinised. Independent blog Retraction Watch cites dozens of papers that have allegedly been retracted for western blot manipulation.
Western blots can be manipulated in a number of ways – by duplicating protein bands, or by vertical or horizontal flipping to make re-used bands look unique. Duplication is typically done with the help of image manipulation software, where it is easier to conceal.
Manipulation can be spotted by looking for artefacts such as obvious splices, similar band shapes, or spots and scratches that carry over onto duplicated bands.
But manipulating images helps no one. Scientists are under intense pressure to publish or perish, where scientific publications are increasingly being treated like currency to be traded for promotions or tenure.
Manipulating images only contributes to a distrust of science, at a time when we increasingly need to defend it.
Authors: Rachael Dunlop, Honorary Research Fellow, Macquarie University