How a simple crystal could help pave the way to full-scale quantum computing
- Written by Jarryd Pla, Senior Lecturer in Quantum Engineering, UNSW
Vaccine and drug development, artificial intelligence, transport and logistics, climate science — these are all areas that stand to be transformed by the development of a full-scale quantum computer. And there has been explosive growth in quantum computing investment over the past decade.
Yet current quantum processors are relatively small in scale, with fewer than 100 qubits — the basic building blocks of a quantum computer. Bits are the smallest unit of information in computing, and the term qubits stems from “quantum bits”.
While early quantum processors have been crucial for demonstrating the potential of quantum computing, realising globally significant applications will likely require processors with upwards of a million qubits.
Our new research tackles a core problem at the heart of scaling up quantum computers: how do we go from controlling just a few qubits, to controlling millions? In research published today in Science Advances, we reveal a new technology that may offer a solution.
What exactly is a quantum computer?
Quantum computers use qubits to hold and process quantum information. Unlike the bits of information in classical computers, qubits make use of the quantum properties of nature, known as “superposition” and “entanglement”, to perform some calculations much faster than their classical counterparts.
Unlike a classical bit, which is represented by either 0 or 1, a qubit can exist in two states (that is, 0 and 1) at the same time. This is what we refer to as a superposition state.
Demonstrations by Google and others have shown even current, early-stage quantum computers can outperform the most powerful supercomputers on the planet for a highly specialised (albeit not particularly useful) task — reaching a milestone we call quantum supremacy.
Google’s quantum computer, built from superconducting electrical circuits, had just 53 qubits and was cooled to a temperature below -273℃ in a high-tech refrigerator. This extreme temperature is needed to remove heat, which can introduce errors to the fragile qubits. While such demonstrations are important, the challenge now is to build quantum processors with many more qubits.
Major efforts are underway at UNSW Sydney to make quantum computers from the same material used in everyday computer chips: silicon. A conventional silicon chip is thumbnail-sized and packs in several billion bits, so the prospect of using this technology to build a quantum computer is compelling.
Read more: Quantum computers could arrive sooner if we build them with traditional silicon technology
The control problem
In silicon quantum processors, information is stored in individual electrons, which are trapped beneath small electrodes at the chip’s surface. Specifically, the qubit is coded into the electron’s spin. It can be pictured as a small compass inside the electron. The needle of the compass can point north or south, which represents the 0 and 1 states.
To set a qubit in a superposition state (both 0 and 1), an operation that occurs in all quantum computations, a control signal must be directed to the desired qubit. For qubits in silicon, this control signal is in the form of a microwave field, much like the ones used to carry phone calls over a 5G network. The microwaves interact with the electron and cause its spin (compass needle) to rotate.
Currently, each qubit requires its own microwave control field. It is delivered to the quantum chip through a cable running from room temperature down to the bottom of the refrigerator at close to -273℃. Each cable brings heat with it, which must be removed before it reaches the quantum processor.
At around 50 qubits, which is state-of-the-art today, this is difficult but manageable. Current refrigerator technology can cope with the cable heat load. However, it represents a huge hurdle if we’re to use systems with a million qubits or more.
The solution is ‘global’ control
An elegant solution to the challenge of how to deliver control signals to millions of spin qubits was proposed in the late 1990s. The idea of “global control” was simple: broadcast a single microwave control field across the entire quantum processor.
Voltage pulses can be applied locally to qubit electrodes to make the individual qubits interact with the global field (and produce superposition states).
It’s much easier to generate such voltage pulses on-chip than it is to generate multiple microwave fields. The solution requires only a single control cable and removes obtrusive on-chip microwave control circuitry.
For more than two decades global control in quantum computers remained an idea. Researchers could not devise a suitable technology that could be integrated with a quantum chip and generate microwave fields at suitably low powers.
In our work we show that a component known as a dielectric resonator could finally allow this. The dielectric resonator is a small, transparent crystal which traps microwaves for a short period of time.
The trapping of microwaves, a phenomenon known as resonance, allows them to interact with the spin qubits longer and greatly reduces the power of microwaves needed to generate the control field. This was vital to operating the technology inside the refrigerator.
In our experiment, we used the dielectric resonator to generate a control field over an area that could contain up to four million qubits. The quantum chip used in this demonstration was a device with two qubits. We were able to show the microwaves produced by the crystal could flip the spin state of each one.
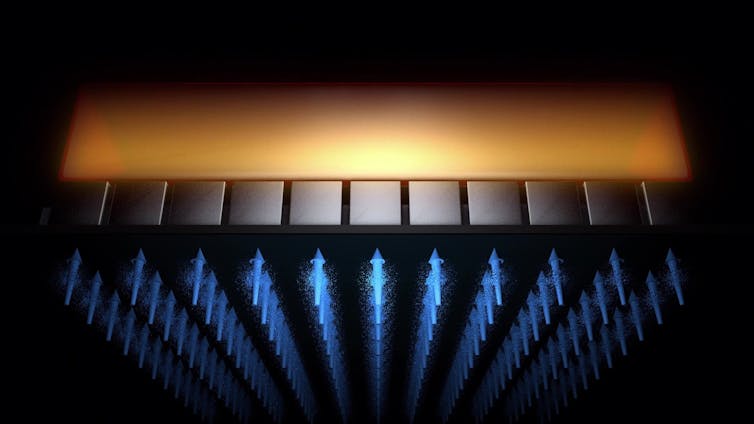 Illustration of a crystal dielectric resonator producing a global control field in a spin quantum processor.
Tony Melov
Illustration of a crystal dielectric resonator producing a global control field in a spin quantum processor.
Tony Melov
The path to a full-scale quantum computer
There is still work to be done before this technology is up to the task of controlling a million qubits. For our study, we managed to flip the state of the qubits, but not yet produce arbitrary superposition states.
Experiments are ongoing to demonstrate this critical capability. We’ll also need to further study the impact of the dielectric resonator on other aspects of the quantum processor.
That said, we believe these engineering challenges will ultimately be surmountable — clearing one of the greatest hurdles to realising a large-scale spin-based quantum computer.
Read more: Error correcting the things that go wrong at the quantum computing scale
Authors: Jarryd Pla, Senior Lecturer in Quantum Engineering, UNSW


















