After nearly 70 years, the death penalty again becomes a real prospect in Papua New Guinea
- Written by Mai Sato, Associate Professor, Director of Eleos Justice, Faculty of Law, Monash University
On July 30 2021, the Supreme Court of Papua New Guinea (PNG) quashed the National Court’s temporary stay of executions for all people sentenced to death.
The judgment has cleared a major obstacle to carrying out death sentences for the first time in nearly 70 years. It makes execution a real possibility for 15 individuals who are on death row.
From the PNG government’s perspective, there remain rather brutal administrative considerations: regulations authorising officers to carry out executions, and nominating the “most possible” of the approved methods of execution under law.
The then Australian administration abolished the death penalty in PNG in 1970. The PNG government reintroduced it in 1991.
Despite its reintroduction in law, PNG has not carried out any executions since 1954. Even so, the death penalty, or at least the threat of its implementation, has been used as a form of social control and has remained part of PNG’s criminal justice system. As of August 2021, there are 15 prisoners on death row.
In the past ten years, the death penalty has been part of the domestic political debate in PNG. In 2013, the parliament expanded the scope of the death penalty. Sorcery-related murder, aggravated rape, and robbery all became punishable by death under the Criminal Code (Amendment) Act 2013.
In 2015, the PNG cabinet endorsed guidelines for execution by approving three modes of execution: hanging, lethal injection and firing squad. It also determined the location for the execution.
Three years later, the judiciary applied the revised criminal code by sentencing eight men to death for sorcery-related murder.
By 2020 it had become such a part of political discussion that the government promised a nationwide consultation to examine the level of public support for the death penalty.
On the international stage, PNG has so far resisted the trend towards abolition of the death penalty. At its most recent UN Universal Periodic Review(2016), PNG did not accept recommendations to move away from the death penalty.
Since 2007, PNG has voted against, or abstained from voting on, the UN General Assembly resolution calling for a moratorium on the death penalty.
Indeed, in 2020, PNG actively opposed the resolution, appearing to commit itself to a position in direct tension with the abolitionist majority of the international community.
PNG’s justification for retaining the death penalty has centred on it being an effective deterrent to heinous crimes. In 2013, the then prime minister, Peter O’Neill, proposed the expanded use of the death penalty to tackle violent crimes. He claimed the “majority of our people are demanding it”. The then opposition leader, Belden Namah, also supported these measures, viewing it as an effective deterrent.
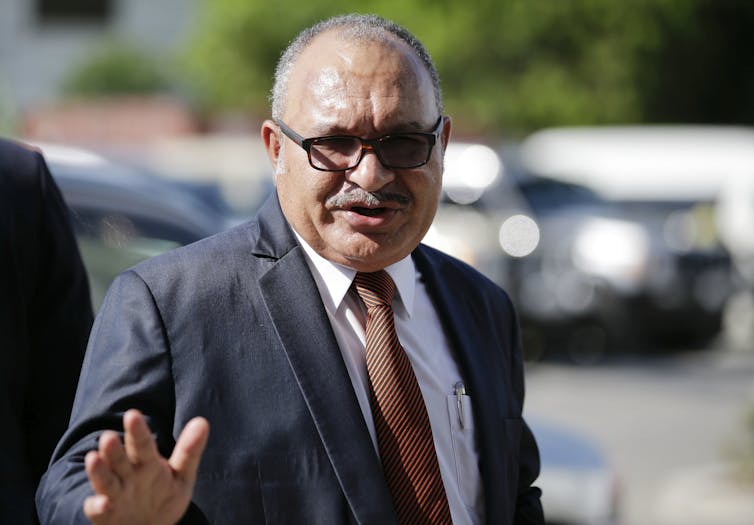 As prime minister, Peter O'Neill proposed expanding the use of the death penalty to tackle violent crimes.
Aaron Favila/AP/AAP
As prime minister, Peter O'Neill proposed expanding the use of the death penalty to tackle violent crimes.
Aaron Favila/AP/AAP
Resorting to increasing the severity of punishment to tackle serious crime has achieved little across different jurisdictions. These include the US, the UK and, more recently, Australia. In this sense, there is nothing new in PNG attempting to solve problems of violence through the use of harsher criminal punishments. But a consequence of PNG’s punitive turn could be dire.
There is no doubt PNG experiences a severe range of violent crime, including tribal fighting and sorcery-related deaths. In violence related to sorcery accusations, many of the victims are women who have been gang-raped and sometimes beaten or burnt to death. But victims are reluctant to report these crimes to police for fear of being targeted again or of their family being attacked. Unless beliefs about sorcery change, it is unlikely any criminal punishment will serve to curtail violent incidents, especially if the community does not trust the police to intervene and offer protection to the victims.
Furthermore, there is no scientific evidence that proves the death penalty is an effective deterrent compared to other sentences such as life imprisonment.
Two-thirds of countries have abolished the death penalty or have not executed anyone for ten years or more. While Asia lags behind this global trend, the Pacific Island countries are at the forefront of the abolitionist movement.
Every Pacific Island state apart from PNG and Tonga has abolished the death penalty for ordinary crimes. If PNG was to resume executions, it would entrench itself as an outlier among Pacific Island states.
PNG is not bound to proceed with executions. In the Supreme Court’s judgment, Justice Manuhu’s dissent is particularly instructive. He endorsed the National Court’s finding that
[…] it is now too late to execute any of these prisoners, as their right of protection against inhuman punishment has been infringed.
Indeed, of the 15 on death row in PNG, 13 have been in prison for more than five years. Some have been there for more than 17 years.
PNG is next scheduled to participate in the UN’s Universal Periodic Review in October 2021. It will be an opportunity for a direct and meaningful diplomatic exchange with abolitionist states.
Read more: 'A dam has been breached': a COVID crisis on our doorstep shows how little we pay attention to PNG
Taking steps towards the abolition of the death penalty at law would not constitute a substantial change for the PNG community, given its moratorium for nearly 70 years.
Authors: Mai Sato, Associate Professor, Director of Eleos Justice, Faculty of Law, Monash University