3 ways 'algorithmic management' makes work more stressful and less satisfying
- Written by Sharon Kaye Parker, Australian Research Council Laureate Fellow, Curtin University
If you think your manager treats you unfairly, the thought might have crossed your mind that replacing said boss with an unbiased machine that rewards performance based on objective data is a path to workplace happiness.
But as appealing as that may sound, you’d be wrong. Our review of 45 studies on machines as managers shows we hate being slaves to algorithms (perhaps even more than we hate being slaves to annoying people).
Algorithmic management — in which decisions about assigning tasks to workers are automated — is most often associated with the gig economy.
Platforms such as Uber were built on technology that used real-time data collection and surveillance, ratings systems and “nudges” to manage workers. Amazon has been another enthusiastic adopter, using software and surveillance to direct human workers in its massive warehouses.
As algorithms become ever more sophisticated, we’re seeing them in more workplaces, taking over tasks once the province of human bosses.
Read more: Algorithms workers can't see are increasingly pulling the management strings
To get a better sense of what this will mean for the quality of people’s work and well-being, we analysed published research studies from across the world that have investigated the impact of algorithmic management on work.
We identified six management functions that algorithms are currently able to perform: monitoring, goal setting, performance management, scheduling, compensation, and job termination. We then looked at how these affected workers, drawing on decades of psychological research showing what aspects of work are important to people.
Just four of the 45 studies showed mixed effects on work (some positive and some negative). The rest highlighted consistently negative effects on workers. In this article we’re going to look at three main impacts:
- Less task variety and skill use
- Reduced job autonomy
- Greater uncertainty and insecurity
1. Reduced task variety and skill use
A great example of the way algorithmic management can reduce task variety and skill use is demonstrated by a 2017 study on the use of electronic monitoring to pay British nurses providing home care to elderly and disabled people.
The system under which the nurses worked was meant to improve their efficiency. They had to use an app to “tag” their care activities. They were paid only for the tasks that could be tagged. Nothing else was recognised. The result was they focused on the urgent and technical care tasks — such as changing bandages or giving medication — and gave up spending time talking to their patients. This reduced both the quality of care as well as the nurses’ sense of doing significant and worthwhile work.
Research suggests increasing use of algorithms to monitor and manage workers will reduce task variety and skill us. Call centres, for example, already use technology to assess a customers’ mood and instruct the call centre worker on exactly how to respond, from what emotions they should deeply to how fast they should speak.
2. Reduced job autonomy
Gig workers refer to as the “fallacy of autonomy” that arises from the apparent ability to choose when and how long they work, when the reality is that platform algorithms use things like acceptance rates to calculate performance scores and to determine future assignments.
This loss of general autonomy is underlined by a 2019 study that interviewed 30 gig workers using the “piecework” platforms Amazon Mechanical Turk, MobileWorks and CloudFactory. In theory workers could choose how long they worked. In practice they felt they needed to constantly be on call to secure the best paying tasks.
This isn’t just the experience of gig workers. A detailed 2013 study of the US truck driving industry showed the downside of algorithms dictating what routes drivers should take, and when they should stop, based on weather and traffic conditions. As one driver in the study put it: “A computer does not know when we are tired, fatigued, or anything else […] I am also a professional and I do not need a [computer] telling me when to stop driving.”
3. Increased intensity and insecurity
Algorithmic management can heighten work intensity in a number of ways. It can dictate the pace directly, as with Amazon’s use of timers for “pickers” in its fulfilment centres.
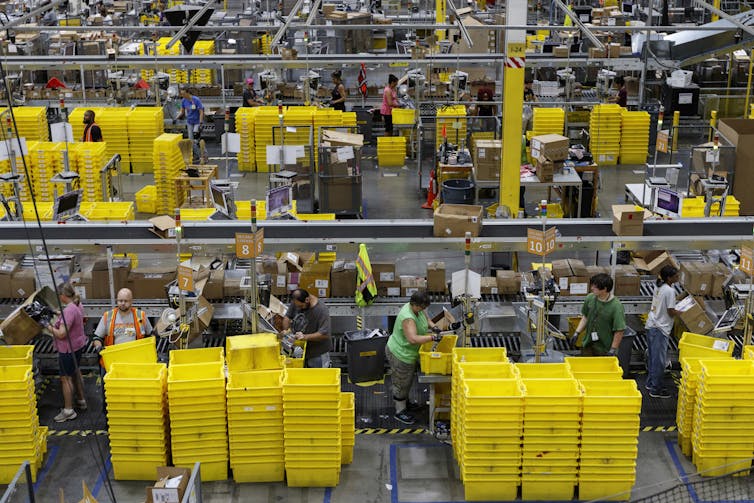 An Amazon warehouse in Chattanooga, Tennessee.
Doug Strickland/Chattanooga Times Free Press/AP
An Amazon warehouse in Chattanooga, Tennessee.
Doug Strickland/Chattanooga Times Free Press/AP
But perhaps more pernicious is its ability to ramp up the work pressure indirectly. Workers who don’t really understand how an algorithm makes its decisions feel more uncertain and insecure about their performance. They worry about every aspect of affecting how the machine rates and ranks them.
For example, in a 2020 study of the experience of 25 food couriers in Edinburgh, the riders spoke about feeling anxious and being “on edge” to accept and complete jobs lest their performance statistics be affected. This led them to take risks such as riding through red lights or through busy traffic in heavy rain. They felt pressure to take all assignments and complete them as quickly as possible so as to be assigned more jobs.
Avoiding a tsunami of unhealthy work
The overwhelming extent to which studies show negative psychological outcomes from algorithmic management suggests we face a tsunami of unhealthy work as the use of such technology accelerates.
Read more: Worker-protection laws aren't ready for an automated future
Currently the design and use of algorithmic management systems is driven by “efficiency” for the employer. A more considered approach is needed to ensure these systems can coexist with dignified, meaningful work.
Transparency and accountability is key to ensuring workers (and their representatives) understand what is being monitored, and why, and that they can appeal those decisions to a higher, human, power.
Authors: Sharon Kaye Parker, Australian Research Council Laureate Fellow, Curtin University