Biomining the elements of the future
- Written by Marcos Voutsinos, PhD Candidate, Geomicrobiology, University of Melbourne
Biomining is the kind of technique promised by science fiction: a vast tank filled with microorganisms that leach metal from ore, old mobile phones and hard drives.
It sounds futuristic, but it’s currently used to produce about 5% of the world’s gold and 20% of the world’s copper. It’s also used to a lesser extent to extract nickel, zinc, cobalt and rare earth elements. But perhaps it’s most exciting potential is extracting rare earth elements, which are crucial in everything from mobile phones to renewable energy technology.
Read more: Will rare earth elements power our clean energy future?
The Mary Kathleen mine, an exhausted uranium mine in northwest Queensland, contains an estimated A$4 billion in rare earth elements. Biomining offers a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option for getting it out.
Biomining is so versatile that it can be used on other planetary bodies. Bioleaching studies on the international space station have shown microorganisms from extreme environments on Earth can leach a large variety of important minerals and metals from rocks when exposed to the cold, heat, radiation and vacuum of space.
Some scientists even believe we cannot colonise other planets without the help of biomining technologies.
How does it work?
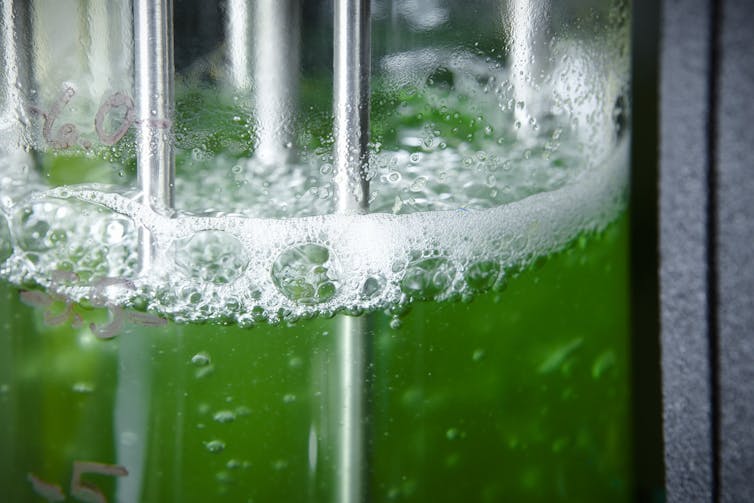 Microorgaisms in tanks leach the minerals from any source material. Courtesy of Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
Microorgaisms in tanks leach the minerals from any source material. Courtesy of Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
Biomining takes place within large, closed, stirred-tank reactors (bioreactors). These devices generally contain water, microorganisms (bacteria, archaea, or fungi), ore material, and a source of energy for the microbes.
The source of energy required depends on the specific microbe necessary for the job. For example, gold and copper are biologically “leached” from sulfidic ores using microorganisms that can derive energy from inorganic sources, via the oxidation of sulfur and iron.
However, rare earth elements are bioleached from non-sulfidic ores using microorganisms that require an organic carbon source, because these ores do not contain a usable energy source. In this case, sugars are added to allow the microbes to grow.
All living organisms need metals to carry out basic enzyme reactions. Humans get their metals from the trace concentrations in their food. Microbes, however, obtain metals by dissolving them from the minerals in their environment. They do this by producing organic acids and metal-binding compounds. Scientists exploit these traits by mixing microbes in solution with ores and collecting the metal as it floats to the top.
The temperature, sugars, the rate at which the tank is stirred, acidity, carbon dioxide and oxygen levels all need to be monitored and fine-tuned to provide optimal working conditions
The benefits of biomining
Traditional mining methods require harsh chemicals, lots of energy and produce many pollutants. In contrast, biomining uses little energy and produces few microbial by-products such as organic acids and gases.
Because it’s cheap and simple, biomining can effectively exploit low grade sources of metals (such as mine tailings) that would otherwise be uneconomical using traditional methods.
Countries are increasingly turning to biomining such as Finland, Chile and Uganda. Chile has exhausted much of its copper rich ores and now utilises biomining, while Uganda has been extracting cobalt from copper mine tailings for over a decade.
Read more: Politically charged: do you know where your batteries come from?
Why do we need rare earth elements?
The rare earth elements include the group of 15 lanthanides near the bottom of the periodic table, plus scandium and yttrium. They are widely used in just about all electronics and are increasingly sought after by the electric vehicle and renewable energy industries.
The unique atomic properties of these elements make them useful as magnets and phosphors. They’re used as strong lightweight magnets in electric vehicles, wind turbines, hard disc drives, medical equipment and as phosphors in energy efficiency lighting and in the LEDs of mobile phones, televisions and laptops.
Despite their name, rare earth elements are not rare and some are in fact more abundant than copper, nickel and lead in the Earth’s crust. However, unlike these primary metals which form ores (a naturally occurring mineral or rock from which a useful substance can be easily extracted), rare earth elements are widely dispersed. Thus to be economically feasible they are generally mined as secondary products alongside primary metals such as iron and copper.
Over 90% of the world’s rare earth elements come from China where production monopolies, trade restrictions and illegal mining have caused prices to fluctuate dramatically over the years.
 Most renewable energy technologies depend on rare earth metals. Pixabay
Most renewable energy technologies depend on rare earth metals. Pixabay
Reports from the US Department of Energy, European Union, and the US intelligence commission have labelled several rare earth elements as critical materials, based on their importance to clean energy, high supply risk, and lack of substitutes.
These reports encourage research and development into alternative mining methods such as biomining as a potential mitigation strategy.
Heeding these calls, laboratories in Curtin, and Berkeley Universities have used microorganisms to dissolve common rare-earth-element-bearing minerals. These pilot scale studies have shown promising results, with extraction rates growing closer to those of conventional mining methods.
Read more: Curious Kids: How do scientists work out how old the Earth is?
Because most electronics have a notoriously short lifespan and poor recyclability, laboratories are experimenting with “urban” biomining. For example, bioleaching studies have seen success in extracting rare earth elements from the phosphor powder lining fluorescent globes, and the use of microorganisms to recycle rare earth elements from electronic wastes such as hard drive magnets.
The rare earth elements are critical for the future of our technology. Biomining offers a way to obtain these valuable resources in a way that is both environmentally sustainable and economically feasible.
Authors: Marcos Voutsinos, PhD Candidate, Geomicrobiology, University of Melbourne
Read more http://theconversation.com/biomining-the-elements-of-the-future-87621