Labor's 2% cap on private health insurance premium rises won't fix affordability
- Written by Peter Sivey, Associate Professor, School of Economics, Finance and Marketing, RMIT University
The promised cap is in response to consistently high premium increases of around 5% in recent years. In justifying the policy, Shorten said:
… the idea these big insurers are making record profits and yet the premiums keep going up and up, it can’t be sustained.
This announcement has already been greeted with scepticism and fury from the health insurance industry, with industry body Private Healthcare Australia branding the proposal “disastrous”.
Read more: INFOGRAPHIC: A snapshot of private health insurance in Australia
As the proposal explicitly targets their profit margins, their response is predictable. However, in this case, they are right to complain. The premium cap policy is a crude measure that is unlikely to improve long-term affordability and may further distort the market in the short term.
Unintended consequences
Price controls introduced by governments usually have good intentions, but often have unintended consequences.
Consider, for example, the proposal to introduce caps on rent increases in the United Kingdom. Rent controls are among the most well-understood policies in economics: they reduce the quality and quantity of housing, leaving renters facing long search times to find housing and poorly maintained properties.

Private health insurers drop their cover for certain treatments and procedures to save money. Look for a therapist near me.
In health insurance, the most likely immediate response to the cap would be for insurers to increase the amount of exclusions – procedures and treatments that aren’t funded – and co-payments associated with policies.
So, while prices are kept low by the cap, consumers are effectively getting less coverage for their money. This would enable insurers to maintain their profit margins, but produce no gain, and further confusion, for consumers.
We already know the number of policies with exclusions, such as hip replacements and childbirth, has grown substantially. Labor’s proposal will probably accelerate the trend.
Read more: Confused about your private health insurance coverage? You're not alone
Long-term pain
Alternatively, as this proposed cap is time-limited, insurers may just put up with the pain of lower margins for a couple of years, with the timeline too short for significant changes to exclusions.
However, there may still be negative long-term impacts. We can look back in history for a clue about the long-term effects of a temporary cap on premiums. In 2000 and 2001, the Howard government implemented an effective “freeze” on private health insurance premium increases.
As can be seen in the graph, average premium increases were below 2% in 2000 (the largest insurer, Medibank Private, had a 0% increase in 2000), and were zero in 2001.
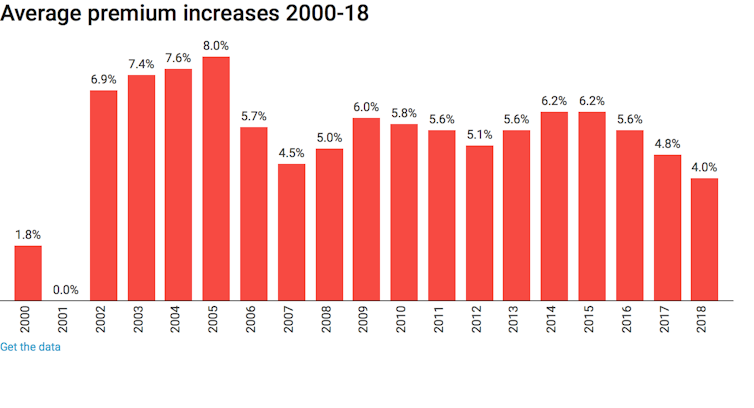 Average private health insurance premium increases in Australia from 2000 to 2018. Author
Average private health insurance premium increases in Australia from 2000 to 2018. Author
While consumers in 2000 and 2001 may have gained from lower real-terms premiums, we can see the long-term effects in the years from 2002 to 2005, when premium increases were between 7 and 8%. This is clearly an attempt by health insurance companies to “catch up” on the increases they missed in 2000 and 2001.
So, we may expect history to repeat itself if Labor wins the next election and introduces this policy: premiums will just rise faster in the years following the cap, negating any short-term benefit to consumers.
Why costs are rising
The proposed Productivity Commission review is much more promising in tackling important issues in the market, including lack of competition, confusing exclusions in policies, and its interaction with public funding through Medicare and public hospitals.
However, there is no solution to premium rises way in excess of general inflation if recent trends in healthcare technology and use continue. The number of hospital visits funded by private health insurance is growing strongly, at an average of 5.5% per year over the past five years.
Growth is across all areas of health care, from elective surgery like cataracts (4.9% a year) and hip replacement (5.5% a year) to diagnostic procedures such as endoscopy (4.4% a year) and life-saving cancer treatments like chemotherapy (5.5% a year).
We are paying more for our health insurance because we are using it more. No crude, short-term measures to restrict premium growth will deal with this fact. And good luck to the Productivity Commission in trying to reverse a global trend for higher private health care expenditure.
Authors: Peter Sivey, Associate Professor, School of Economics, Finance and Marketing, RMIT University



















