Australia has led the way regulating gene technology for over 20 years. Here’s how it should apply that to AI
- Written by Julia Powles, Associate Professor of Law and Technology; Director, UWA Tech & Policy Lab, Law School, The University of Western Australia
Since 2019, the Australian Department for Industry, Science and Resources has been striving to make the nation a leader in “safe and responsible” artificial intelligence (AI). Key to this is a voluntary framework based on eight AI ethics principles, including “human-centred values”, “fairness” and “transparency and explainability”.
Every subsequent piece of national guidance on AI has spun off these eight principles, imploring business, government and schools to put them into practice. But these voluntary principles have no real hold on organisations that develop and deploy AI systems.
Last month, the Australian government started consulting on a proposal that struck a different tone. Acknowledging “voluntary compliance […] is no longer enough”, it spoke of “mandatory guardrails for AI in high-risk settings”.
But the core idea of self-regulation remains stubbornly baked in. For example, it’s up to AI developers to determine whether their AI system is high risk, by having regard to a set of risks that can only be described as endemic to large-scale AI systems.
If this high hurdle is met, what mandatory guardrails kick in? For the most part, companies simply need to demonstrate they have internal processes gesturing at the AI ethics principles. The proposal is most notable, then, for what it does not include. There is no oversight, no consequences, no refusal, no redress.
But there is a different, ready-to-hand model that Australia could adopt for AI. It comes from another critical technology in the national interest: gene technology.
A different model
Gene technology is what’s behind genetically modified organisms. Like AI, it raises concerns for more than 60% of the population.
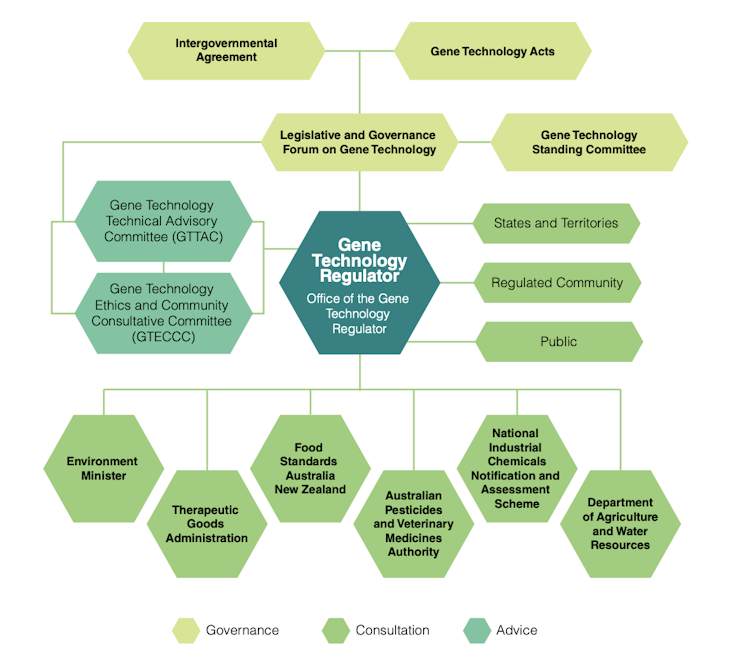
In Australia, it’s regulated by the Office of the Gene Technology Regulator. The regulator was established in 2001 to meet the biotech boom in agriculture and health. Since then, it’s become the exemplar of an expert-informed, highly transparent regulator focused on a specific technology with far-reaching consequences.
Three features have ensured the gene technology regulator’s national and international success.
First, it’s a single-mission body. It regulates dealings with genetically modified organisms:
to protect the health and safety of people, and to protect the environment, by identifying risks posed by or as a result of gene technology.
Second, it has a sophisticated decision-making structure. Thanks to it, the risk assessment of every application of gene technology in Australia is informed by sound expertise. It also insulates that assessment from political influence and corporate lobbying.
The regulator is informed by two integrated expert bodies: a Technical Advisory Committee and an Ethics and Community Consultative Committee. These bodies are complemented by Institutional Biosafety Committees supporting ongoing risk management at more than 200 research and commercial institutions accredited to use gene technology in Australia. This parallels best practice in food safety and drug safety.
Third, the regulator continuously integrates public input into its risk assessment process. It does so meaningfully and transparently. Every dealing with gene technology must be approved. Before a release into the wild, an exhaustive consultation process maximises review and oversight. This ensures a high threshold of public safety.
Regulating high-risk technologies
Together, these factors explain why Australia’s gene technology regulator has been so successful. They also highlight what’s missing in most emerging approaches to AI regulation.
The mandate of AI regulation typically involves an impossible compromise between protecting the public and supporting industry. As with gene regulation, it seeks to safeguard against risks. In the case of AI, those risks would be to health, the environment and human rights. But it also seeks to “maximise the opportunities that AI presents for our economy and society”.
Second, currently proposed AI regulation outsources risk assessment and management to commercial AI providers. Instead, it should develop a national evidence base, informed by cross-disciplinary scientific, socio-technical and civil society expertise.
The argument goes that AI is “out of the bag”, with potential applications too numerous and too mundane to regulate. Yet molecular biology methods are also well out of the bag. The gene tech regulator still maintains oversight of all uses of the technology, while continually working to categorise certain dealings as “exempt” or “low-risk” to facilitate research and development.
Third, the public has no meaningful opportunity to assent to dealings with AI. This is true regardless of whether it involves plundering the archives of our collective imaginations to build AI systems, or deploying them in ways that undercut dignity, autonomy and justice.
The lesson of more than two decades of gene regulation is that it doesn’t stop innovation to regulate a promising new technology until it can demonstrate a history of non-damaging use to people and the environment. In fact, it saves it.
Authors: Julia Powles, Associate Professor of Law and Technology; Director, UWA Tech & Policy Lab, Law School, The University of Western Australia



















