Uber might not take over the world, but it is still normalising job insecurity
- Written by Peter Fleming, Professor, University of Technology Sydney
The effective exclusion of Uber from London, one of the digital platform’s most lucrative markets, adds to a small but significant list of places putting up roadblocks to “uberisation”.
Governments in Bulgaria, China, Denmark, Hungary and Australia’s Northern Territory have all made conditions hostile to Uber. There are partial bans in Finland, France, Germany, Italy and the Netherlands.
Specific reasons for the bans differ. In the case of London it is thousands of cases of unauthorised, insured drivers using verified driver accounts to pick up passengers.
Behind safety concerns, though, is also a deep resentment towards Uber itself circumventing regulations. This has led, in 2016 and 2014, to thousands of drivers of London’s traditional black cabs jamming the city in protest.
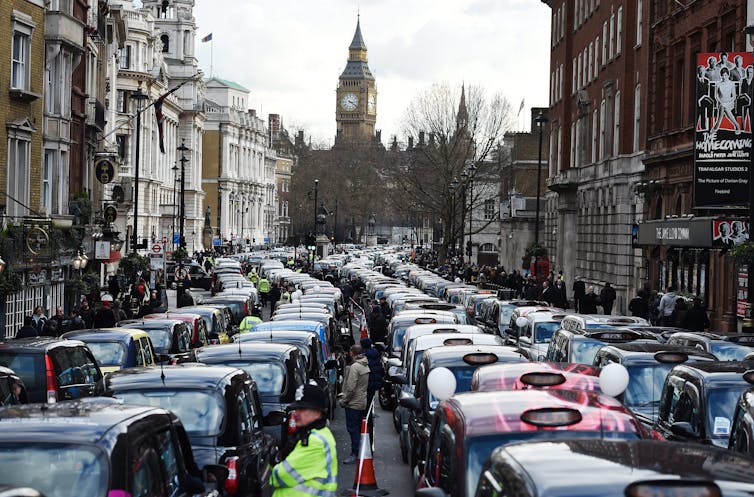 London cab drivers block Whitehall in central London in February 2016 to protest against Uber being allowed to operate.
Andy Rain/EPA
London cab drivers block Whitehall in central London in February 2016 to protest against Uber being allowed to operate.
Andy Rain/EPA
Uberisation refers to the use of a computing platform to facilitate transactions between service providers and customers, often bypassing a traditional organisational intermediary. Uber pioneered this in “ride-sharing” and has pushed aggressively into food delivery. Its most controversial bypass is the traditional employment relationship.
This is epitomised by the case of Amita Gupta, the Australian Uber Eats driver fired for being ten minutes late in delivering a food order. Gupta’s claim of unfair dismissal was rejected by Australia’s federal Fair Work Commission on the basis she was an independent contractor, not an employee, and therefore not covered by the protections of Australia’s Fair Work Act. (She is now appealing to the full bench of the Fair Work Commission.)
Read more: How to stop workers being exploited in the gig economy
The good news, as the London ban on Uber signals, is that uberisation is not an unstoppable force. For all its attractions to companies keen to hire labour while circumventing costly labour laws, it is destined to clash with the controls required to keep capitalism ticking over.
That’s no cause for complacency, though, because even if uberisation has its limits, we are seeing the apparent normalisation of all forms of precarious and insecure work.
The revolution that never happened
In 2015, with a crush of Uber-inspired startups rushing to market, a Huffington Post article predicted the combination of “realtime data, mobile payments, instant gratification and dynamic pricing” was the beginning of “an on-demand revolution that will ‘Uberize’ the entire economy.”
This hasn’t happened.
In the United States the percentage of workers in precarious employment – including agency temps, contract workers, independent contractors, freelancers and the like – rose from 10.7% in 2005 to 15.8% in 2015. Only an estimated 0.5% were involved with online intermediaries like Uber.
A 2018 report for Britain’s Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy estimated less than 1% of British workers relied on the gig economy for the majority of their income.
In Australia, our analysis of the data presented by Deloitte Access Economics for the NSW Department of Finance, Services and Innovation suggests 1.6% of the population earn money in the gig economy, often as supplement to other income.
The limits of capitalism’s logic
Uber and other labour-based digital platforms reveal the limits of the logic of contemporary capitalism: a logic based on the assumed value of deregulated markets that operate best with minimal interference by the state.
Their business models follow a textbook formula of unfettered capitalism. It eliminates employment obligations in favour of a spartan market-based economic exchange between capital and labour. Paid holidays, pension contributions, minimum wage, sick leave and protection from unfair dismissal – with a click on an app, all these hard-won rights disappear.
Read more: A new definition of 'worker' could protect many from exploitation
If this were to become the dominant economic model, it would undermine the system rather than help it flourish. More workers would find themselves among the “working poor”, unable to sustain themselves and their families. The burden on the welfare state would increase. Conflict and industrial unrest would escalate, as it has wherever Uber has set up shop, be it in New York, London, Paris, Madrid, Rome, Berlin, Nairobi, Johannesburg, Delhi, Jakarta or Melbourne.
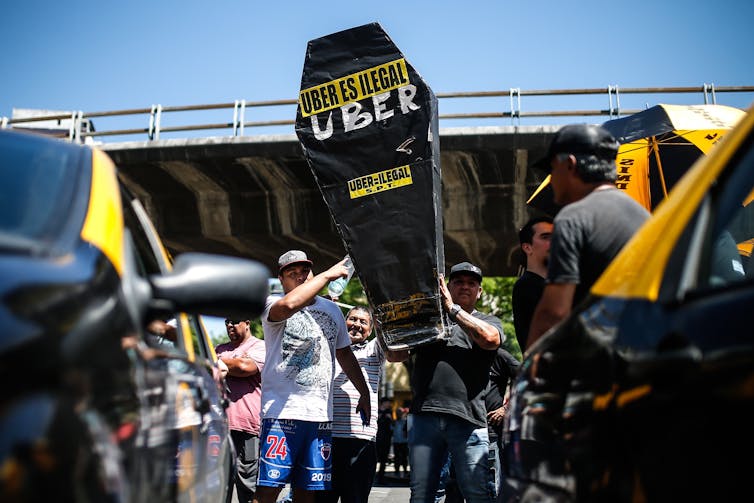 Drivers and taxi owners demonstrate against Uber and Cabify in Buenos Aires, Argentina, November 7 2019.
Juan Ignacio Roncoroni/EPA
Drivers and taxi owners demonstrate against Uber and Cabify in Buenos Aires, Argentina, November 7 2019.
Juan Ignacio Roncoroni/EPA
The business model is parasitical. It depends on the regular economy to subsidise it. And yet this is still not enough. To date Uber has never recorded a profit. When it listed on the New York Stock Exchange, its Initial Public Offering filing revealed its plan to further “reduce driver incentives to improve our financial performance”.
Normalising precarious work
While we can be relieved the gig economy hasn’t become more widespread, it is a concern that these platforms’ high profiles and extensive marketing have helped normalise and sanitise business models with parasitical employment practices.
Celebrities to have fronted Uber Eats advertisements in Australia, for example, include Boy George, Sophie Monk, Naomi Watts, Nic Naitanui, Ryan Moloney, Peter FitzSimons, Rebel Wilson, Ruby Rose, Lee Lin Chin and Ray Martin. Its most recent campaign features Jimmy Barnes, John Farnham and Anh Do.
Such endorsements have arguably helped to make Uber Eats and all forms of precarious work more acceptable.
Read more: The costs of a casual job are now outweighing any pay benefits
In Australia, some research suggests the number of workers who feel insecure in their jobs has been relatively stable for the past two decades, as have casualisation and self-employment. But Australia also tops the OECD in its levels of casual and contract work. Given stagnant wage growth, widening inequality, falling housing affordability, a mounting wage theft crisis and growing corporate power, it is clear that feelings of insecurity and precariousness about work are painfully real for many.
So even without Uber taking over the world, we might all end up damagingly closer to the situation workers like Amita Gupta have found themselve in.
Authors: Peter Fleming, Professor, University of Technology Sydney