Non-native species should count in conservation – even in Australia
- Written by Arian Wallach, Lecturer, Centre for Compassionate Conservation, University of Technology Sydney
As the world struggles to keep tabs on biodiversity decline, conservation largely relies on a single international database to track life on Earth. It is a mammoth and impressive undertaking – but a glaring omission from the list may be frustrating conservation efforts.
Read more: In defence of invasive alien species
The International Union for the Conservation of Nature’s Red List aims to be a “complete barometer of life”. But non-native wildlife is excluded from the list.
Our study, published today in the journal Conservation Biology, questions the wisdom of this omission. It means, for example, vulnerable species facing existential threats in their “home country” may be exterminated freely in another. Excluding these animals, such as wild camels in Australia, and rare Australian frogs living overseas, distorts conservation science.
What counts as ‘native’?
The concept of “native” draws a sharp line between species that count and those that don’t. It is essentially an ethical choice, and a disputed one at that. Regardless of whether one defends or disputes the concept, it is problematic to use a moral term to filter a critical source of scientific data.
 Trash Animals: How We Live with Nature’s Filthy, Feral, Invasive, and Unwanted Species.
Trash Animals: How We Live with Nature’s Filthy, Feral, Invasive, and Unwanted Species.
The invisible components of biodiversity – those populations excluded from conservation’s definition of life – can be found in trash lists, where they are described as invasive, aliens, pests, and feral.
So what does the world look like if we include all wildlife in biodiversity assessments? We rummaged around in the “trash piles” to find out.
When all life counts
By focusing on Australian non-native vertebrate species – amphibians, birds, fishes, mammals, and reptiles – we did something many conservationists would find unthinkable. We added unloved species such as feral cats, cane toads, the Indian myna, and carp to Australia’s biodiversity counts.
We created maps showing the range of 87 species whose ancestors were introduced into Australia, and 47 species native to Australia that were introduced elsewhere, since European colonisation.
Many of these so-called invasive species are at risk of extinction in their native ranges; 32% are assessed as threatened or decreasing in the Red List. For 15 of them, non-native ranges provide a lifeline.
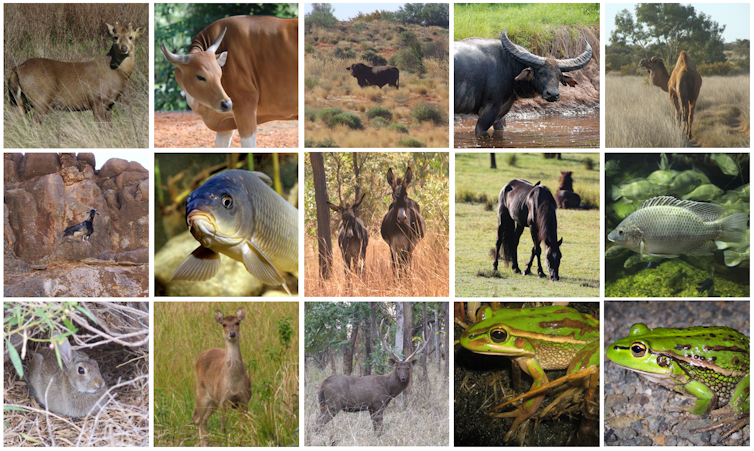 Australia’s vertebrate species that are threatened or near threatened in their native ranges with significant populations overseas. From left-to-right: Indian hog deer, banteng, wild cattle, wild water buffalo, wild camel; wild goat, carp, wild donkey, brumby, Mozambique tilapia; European rabbit, Javan rusa, sambar deer, and (emigrants) green and golden bell frog, growling grass frog.
Arian Wallach et al
Australia’s vertebrate species that are threatened or near threatened in their native ranges with significant populations overseas. From left-to-right: Indian hog deer, banteng, wild cattle, wild water buffalo, wild camel; wild goat, carp, wild donkey, brumby, Mozambique tilapia; European rabbit, Javan rusa, sambar deer, and (emigrants) green and golden bell frog, growling grass frog.
Arian Wallach et al
Not only does Australia contribute to the survival and flourishing of these species, but immigrant vertebrates have also added 52 species to the number of vertebrate species in Australia (after accounting for extinctions).
This number in no way indicates that non-native species replace or make up for those that have been lost. And it does not exonerate humans of their role in causing extinctions. But the current data do not even allow us to acknowledge that these species exist.
Because they are not counted in conservation, these non-native populations are subjected to mass eradication programs. Paradoxically, in assessing how such programs are justified, we found conservation is the most frequently cited reason for killing these wild animals.
Dromedary camels were extinct in the wild for some 5,000 years until they “went feral” in Australia, where they are now endemic. Rather than celebrating what is arguably the most extraordinary rewilding event in the world, wild camels were declared a pest. Between 2009 and 2013, Australia spent A$19 million to gun down 160,000 individuals of a species found nowhere else on Earth in the wild.
Likewise, 89% of the global distribution of Javan rusa, a deer species vulnerable to extinction, is in Australia. As pest, they are culled and hunted for sport.
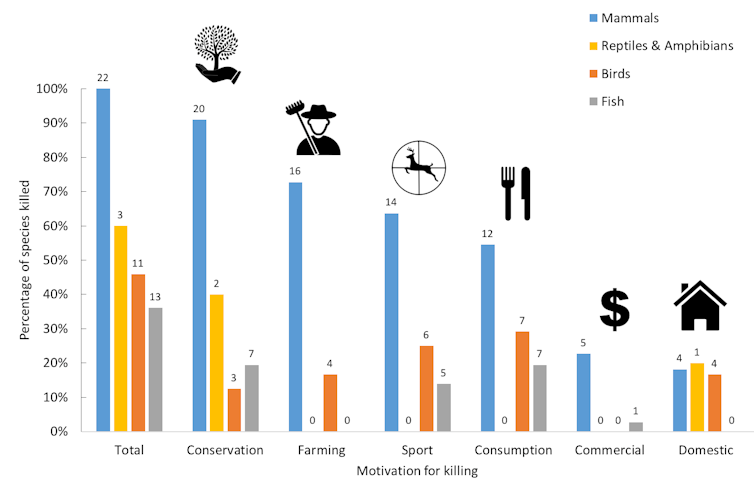 Stated motivations for killing Australia’s immigrant vertebrate wildlife, shown as percentages of species targeted per taxonomic group. Numbers above bars indicate absolute number of species targeted.
Stated motivations for killing Australia’s immigrant vertebrate wildlife, shown as percentages of species targeted per taxonomic group. Numbers above bars indicate absolute number of species targeted.
Nativism not only renders countless species invisible, along with their unique and fascinating ecologies; it also exposes them to unfettered, unscientific, unmonitored, and unlamented mass killing programs.
Read more: From feral camels to 'cocaine hippos', large animals are rewilding the world
Mass killing of non-native species, if questioned at all, is generally explained as protecting native species. But ecology is complex. But one cannot simply assume that all non-native populations, in all contexts, do nothing but harm.
Where non-native species do contribute to the loss of native species, humans need to confront the ethical complexities and shoulder real responsibility, rather than simply reach for a gun as a first solution.
In many situations changing harmful human behaviours, like persecuting apex predators such as dingoes, can solve problems that appear to be caused solely by non-native species.
Irrespective of whether we value non-native species or not, there is no scientific justification for expunging large swaths of the living world from conservation data. Smuggling ethically dubious distinctions into data harms conservation science, and has grave repercussions.
Read more: The toad we love to hate
Persisting with the assumption that we have the right to pick and choose which species “count” looks like playing God. By now, we should have learned we must not.
Authors: Arian Wallach, Lecturer, Centre for Compassionate Conservation, University of Technology Sydney
Read more http://theconversation.com/non-native-species-should-count-in-conservation-even-in-australia-127926



















