Bingeing Netflix under lockdown? Here's why streaming comes at a cost to the environment
- Written by Michael Fuhrer, Professor of Physics, Monash University

Coronavirus lockdowns have led to a massive reduction in global emissions, but there’s one area where energy usage is up – way up – during the pandemic: internet traffic.
Data-intensive video streaming, gaming and livestreaming for business, university and school classes, is chewing up energy.
Estimates can be notoriously difficult and depend on the electricity source, but six hours of streaming video may be the equivalent of burning one litre of petrol, due to emissions from the electricity used to power the data centres which deliver the video.
In fact, the energy associated with the global IT sector – from powering internet servers to charging smartphones – is estimated to have the same carbon footprint as the aviation industry’s fuel emissions (before planes were grounded).
But Australia is a global leader in research to lower the energy used in IT, which is vital for meeting the streaming demand without the environmental cost.
Where does the data come from?
Video requires huge amounts of data, and accounts for around 80% of the data transmitted on the internet. Much of the energy needed for streaming services is consumed by data centres, which deliver data to your computer or device. Increasingly housed in vast factory-sized buildings, these servers store, process and distribute internet traffic. The number of data centres all across the world supplied by the likes of 4D Data Centres and many other companies are increasing in size and numbers year after year, which isn't surprising considering the amount of data and number of webpages on the world wide web now.
 Data centres, in factory-sized buildings, send data to your device. Shutterstock
Data centres, in factory-sized buildings, send data to your device. Shutterstock
Research in 2015 found data centres may consume as much as 13% of the world’s electricity by 2030, accounting for about 6% of global carbon dioxide emissions. And the European Commission-funded Eureca project found data centres in EU countries consumed 25% more energy in 2017 compared with 2014.
Imagine what those figures will look like at the end of this year of home-bound internet use.
Read more: Where's your data? It's not actually in the cloud, it's sitting in a data centre
Meeting demands with Moore’s law
The growth in IT is often taken for granted. In contrast to the old days of dial-up internet, we now demand a three-hour movie, in high definition, to download immediately. We want phones that can take video like a pro.
None of this is free. Nor is it sustainable. Every year the number of computations, or transmission of information through space, done globally, increases by 60%, according to 2011 research.
All this computation uses “transistors”. These are tiny switches that amplify electrical signals, and are made using silicon-based technology.
For the past 40 years, our ever-increasing need for more computing was largely satisfied by incremental improvements in silicon-based computing technology – ever-smaller, ever-faster, ever-more efficient chips. We refer to this constant shrinking of silicon components as “Moore’s law”.
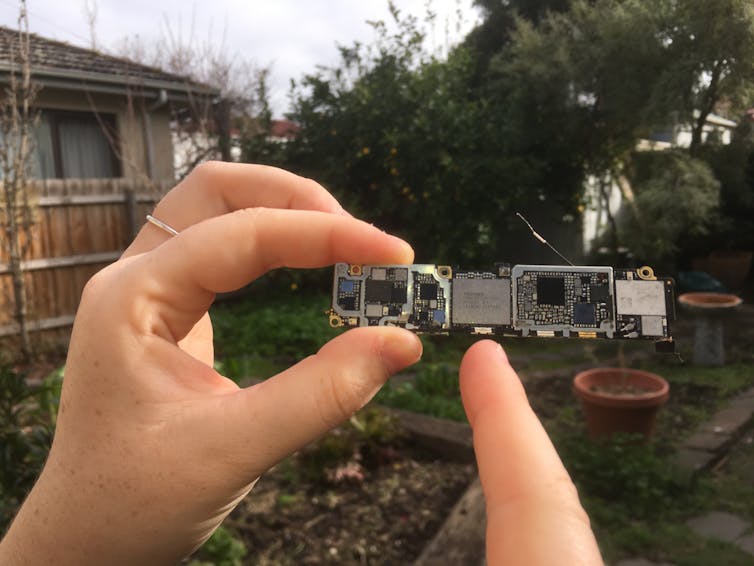 Pointing to the processor chip at the heart of an iPhone 6S, which came out in 2015. This chip measures 12mm by 15mm and contains over 2 billion transistors. At this point, the transistors were 19 nanometres. Errol Hunt, Author provided
Pointing to the processor chip at the heart of an iPhone 6S, which came out in 2015. This chip measures 12mm by 15mm and contains over 2 billion transistors. At this point, the transistors were 19 nanometres. Errol Hunt, Author provided
For example, since the late 1970s the length of transistors reduces by about 30%, and the area by about 50%, every two years. This shrinks the energy used in switching on and off each transistor by about 50%, which is better for the environment.
While each transistor uses only a tiny amount of energy, there are billions of transistors in a typical computer chip, each switching billions of time per second. This can add up to a vast amount of energy.
We need better chips
Recently it has become much harder (and much more expensive) to pursue such trends, and the number of companies pursuing smaller components is dropping off rapidly.
Globally, four companies manufactured chips with 14 nanometre (nm) transistors in 2014, but in recent years they’ve struggled to continue shrinking the size of silicon transistors. Global Foundries dropped out of this race altogether in 2018, and Intel experienced enormous problems with manufacturing at 10 nm. That leaves only two companies (Samsung and TSMC) making 7 nm transistors today.
So the answer isn’t to switch off Netflix. The answer is to create better computer chips.
But we’ve got everything we can out of silicon, so we need to use something else. If we want computing to continue to grow, we need new, energy-efficient computers.
Australia is a leader in low-energy solutions
Australia is leading the world in this new field to replace conventional electronics. The ARC Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies (FLEET) was established in 2017 to address exactly this challenge.
Michael Fuhrer explains topological materials and why they might change the world.Last year scientists at FLEET published research in Nature revealing the discovery that the “topological” material sodium-bismuthide could be the key to achieving ultra-low energy electronics.
These so-called topological insulators, which led to a 2016 Nobel Prize in Physics, conduct electricity only along their edges, and in one direction, without loss of energy due to resistance.
This discovery is a first step towards the development of a low-energy replacement for conventional silicon-based electronics.
Read more: Why are scientists so excited about a recently claimed quantum computing milestone?
Other top research centres in Australia are addressing different parts of this challenge. For example, one centre is working to reduce the energy used in ubiquitous communication of digital data. Another two are taking a different tack, developing an entirely new quantum technology for computing which promises to enormously speed up, and improve the efficiency of, certain difficult computing tasks.
Quantum computing expert Michelle Simmons explains why this research is so important.Other countries are equally focused on developing alternatives to the unsustainable need for better and faster electronics, since we cannot sustain the energy needed for these existing and future technologies.
All of these technologies are still confined to specialised laboratories and are probably at least a decade away from finding their way into everyday devices. But we don’t expect the demand for computing to go away, and the energy problem in IT will only become more urgent.
Authors: Michael Fuhrer, Professor of Physics, Monash University



















