Why the shipping industry's increased climate ambition spells the end for its fossil fuel use
- Written by Christiaan De Beukelaer, Senior Lecturer in Culture & Climate, The University of Melbourne
A revised strategy to reduce global shipping emissions has emerged from two weeks of intense talks in London. It marks a significant increase in the industry’s climate ambition.
The revised strategy has been criticised for not being ambitious enough. However, the forecast growth in global trade and the world’s shipping fleet means the reductions required of individual ships are much greater than the overall greenhouse gas emission targets.
The new targets for international shipping are:
- reductions of 20% (from a 2008 baseline), striving for 30%, by 2030
- reductions of 70%, striving for 80%, by 2040
- net-zero emissions “by or around, i.e. close to” 2050.
We calculate the strategy will require cuts in emissions per ship of up to 60% by 2030 and as much as 91% by 2040. This means the days of fossil-fuelled ships are numbered.
Edging closer to limiting warming to 1.5℃
Global shipping emissions rank within to the top 10 countries for emissions. The industry should do its fair share in keeping global warming below 1.5℃.
The revised strategy was negotiated at the London headquarters of the International Maritime Organization (IMO), the United Nations agency that regulates shipping. Backed by the Science-Based Targets initiative, several Pacific Island states, New Zealand, the US, the UK and Canada had proposed emission cuts of at least 37% by 2030, 96% by 2040 and to absolute zero by 2050. (An initial strategy adopted in 2018 aimed to reduce shipping emissions by at least 50% by 2050.)
The revised strategy’s targets are not as high as those called for by the science and the most ambitious governments. However, they are still very stringent at a ship level.
Shipping volumes have grown by more than 50% since 2008, with further growth expected. Increasing numbers of ships mean average emission reductions per ship will need to be 54-60% by 2030 and 86-91% by 2040.
Before the revised strategy, IMO policy focused on improving the energy efficiency and carbon intensity of new and existing ships. These tools failed to rein in shipping emissions.
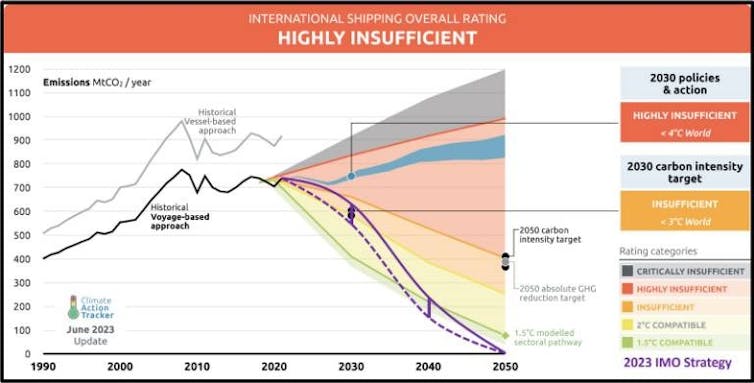
Climate Action Tracker’s most recent analysis concluded the “highly insufficient” initial strategy put shipping on a pathway consistent with 3-4℃ of warming. To estimate how the new targets compare – assuming the strategy’s measures that are yet to be adopted will be effective – they can be superimposed on this assessment’s current trajectories.
This shows the revised strategy still does not align global shipping with the emission-reduction pathway needed to avoid more than 1.5℃ of warming. But it does mark the beginning of the end for fossil fuels.
What are the strategy’s key elements?
The revised strategy calls for “net-zero” GHG emissions “by or around, i.e. close to 2050”. The term “net” leaves an unfortunate loophole for future use of emission offsets. It’s big enough for the giant container ship Ever Given to steam through. This ambiguity has been left for future negotiations to resolve.
Importantly, though, IMO member states agreed to set targets for emissions on a “well-to-wake” basis, covering emissions from both fuel production and combustion. Including “upstream” emissions ensures shipping decarbonisation does not shift emissions ashore. Being required to achieve these reductions will fundamentally and rapidly change the sector’s technology and energy supply chains.
Decarbonisation will drive up shipping costs. Developing countries fear the impacts will be much greater for them than for developed countries.
Small island developing states and least developed countries bear almost no historical responsibility for the climate crisis. They have called for a “just and equitable transition”. So too have countries with large numbers of maritime workers, like the Philippines, as well as the International Transport Workers’ Federation representing these workers.
Read more: To reach net zero, we must decarbonise shipping. But two big problems are getting in the way
To deliver a policy that both reduces emissions and supports a just and equitable transition, the revised strategy includes a commitment to finalise a “basket of candidate measures”, both technical and economic.
The technical measure is a fuel standard that ratchets down the permissible emission intensity of fuels over time. This proved uncontroversial.
The “candidate” economic measures to price emissions did not all get broad support. For example, a mandatory universal emissions levy – proposed by the Marshall Islands and the Solomon Islands – was strongly opposed by countries like China, Brazil and Argentina for fear it might harm their exports.
Many “small island developing states” and “least developed countries” backed a levy. They see it as the most environmentally effective companion to a fuel standard. A price on emissions will speed up the transition, while revenues from the levy can be used to support a just and equitable transition.
As a result of these political differences, more work needs to be done to resolve the specifics of the emissions pricing mechanism.
Read more: Marshall Islands, a nation at the heart of global shipping, fights for climate justice
Strategy is still a work in progress
The message to industry is crystal clear: the commercial competitiveness of fossil-fuel-driven ships, and demand for them, will dwindle rapidly with almost a full phasing out by the 2040s. During this rapid transition, shipping firms will have to very carefully manage the liabilities and risks of existing investments and formulate ways to maximise opportunities and market share.
Pressure from Pacific Island states and increased public scrutiny forced IMO member states to commit to higher levels of ambition than many had wanted to accept. Continued pressure will be needed, though, to ensure the measures adopted deliver on the ambition of the IMO strategy.
Before member states adopt any of these measures, the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) will model the expected impacts on states. Some countries may then fight hard to block or reduce the effect of measures that have “disproportionate negative impacts”.
The final “basket of measures” won’t be adopted until 2025 when their details are finalised. They will become legally binding when the strategy comes into force in 2027.
In sum, the revised strategy is a modest win, but the battle is far from over.
Authors: Christiaan De Beukelaer, Senior Lecturer in Culture & Climate, The University of Melbourne



















