Our land is burning, and western science does not have all the answers
- Written by David Bowman, Professor of Pyrogeography and Fire Science, University of Tasmania
Last week’s catastrophic fires on Australia’s east coast – and warnings of more soon to come – will become all too common as climate change gathers pace. And as the challenges of modern hazard reduction become clear, there is much to learn from the ancient Aboriginal practice of burning country.
Indigenous people learnt to use fire skillfully and to their advantage, including to moderate bushfires. Most of the fires were small and set at dry times of the year, resulting in a fine-scale mosaic of different vegetation types and fuel ages. This made intense bushfires uncommon and made plant and animal foods more abundant.
Read more: A surprising answer to a hot question: controlled burns often fail to slow a bushfire
Contemporary fire managers also attempt to lower bushfire risk by reducing fuel loads through hazard reduction burning. To minimise costs, this is often achieved by dropping incendiaries from aircraft.
Concern is growing that such methods exacerbate biodiversity declines and often do not prevent a subsequent bushfire. As climate change makes bushfires more ferocious and extreme, now is the time to better understand how our First Peoples used fire.
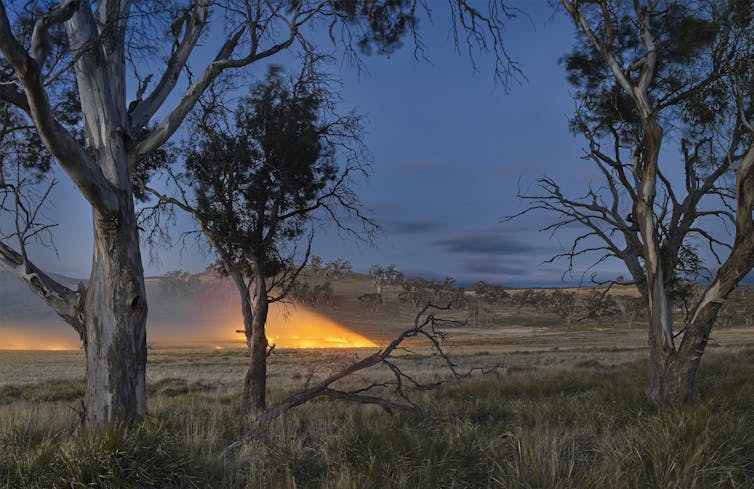 Patch burning in the Midlands region of Tasmania. The technique draws on traditional Aboriginal knowledge and can help in modern fire management.
Alan McFetridge
Patch burning in the Midlands region of Tasmania. The technique draws on traditional Aboriginal knowledge and can help in modern fire management.
Alan McFetridge
A slow, ancient craft
Traditional Aboriginal fire practices are based on local knowledge and spiritual connection to country.
Before white settlement, Aboriginal people were a constant presence in the landscape, and traditionally burnt country by walking the land. This meant they could control the timing and spread of fire, as well as its ecological effects.
By contrast, most modern fire programs are far less flexible and responsive. They usually take place on weekdays in specific seasons and weather conditions. Many fires are ignited from the air – especially those in remote areas where vast areas of burning is desired. This technique results in bigger, more intense fires than those conducted by Aboriginal people.
Read more: Grattan on Friday: When the firies call him out on climate change, Scott Morrison should listen
Contemporary fire managers do reduce fuel in small areas, through ground crews working on foot. These crews often work in specific weather windows such as fog, and at cooler times of day such as the evening, to keep fires controlled and protect sensitive areas.
This method is reminiscent of Aboriginal fire practice and leads to smaller, less intense fires than aerial ignition. But it also differs from traditional techniques. Modern ground crews use “drip torches” – hand-held devices filled with fuel – and burn in a box pattern. By contrast, Indigenous people use a slower technique such as dragging a smouldering stick through the bush, and burn in spiral or strip patterns to achieve a mosaic effect.
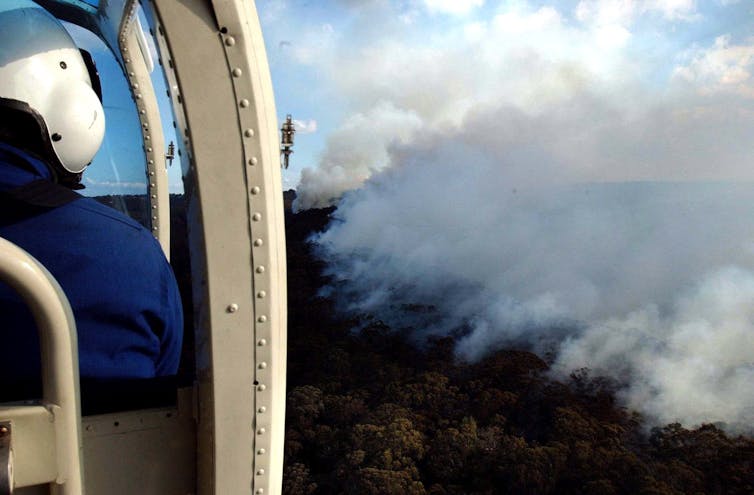 A hazard reduction operation conducted by the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Services in the Blue Mountains. About 120 hectares were burnt.
Mick Tsikas/AAP
A hazard reduction operation conducted by the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Services in the Blue Mountains. About 120 hectares were burnt.
Mick Tsikas/AAP
Taking lessons from the past
Aboriginal fire practice across Australia was severely disrupted by European invasion. The practice is being reinvigorated through initiatives such as the Firesticks Alliance, an Indigenous-led network involving training, on-ground works and scientific monitoring to better understand the ecological effects of cultural burning.
But there is a huge opportunity to further develop traditional fire management alongside western science. Our project on a farm in Tasmania offers a good example. Since 2017, University of Tasmania scientists have worked with a farmer and the Aboriginal community to reintroduce Indigenous burning to native grasslands (see video below).
This project began as straightforward research into fire management in an endangered eucalypt woodland community. It took a novel turn when the landowner asked that the Tasmanian Aboriginal community be involved. We then employed Aboriginal rangers to burn experimental plots.
Importantly, this research does not take the old-school anthropological approach of solely studying Aboriginal burning practices. Instead, it is a true collaboration where all parties learn from each other.
As a consequence, the project design changed in the course of the experiment. For example its original “efficient” approach involved burning predetermined units of a set size. But in the second year, Aboriginal rangers selected the areas burnt, resulting in a patchy and varied burning pattern.
Read more: Bushfires can make kids scared and anxious: here are 5 steps to help them cope
The project is still being monitored and results are not finalised. However it has already achieved an important goal: stronger cross-cultural partnerships.
Such initiatives should not be rushed. Genuine engagement of the Aboriginal community requires time, allowing trust to build between groups that don’t have a long history of working together.
The project took place on private property, at the request of a landowner who took responsibility for approvals and compliance. Such small-scale projects are excellent for building skills and allowing Aboriginal people to reconnect with country. Upscaling such projects to public lands such as national parks requires more complex negotiation and agreement, but this will be easier if a record of successful smaller programs exists.
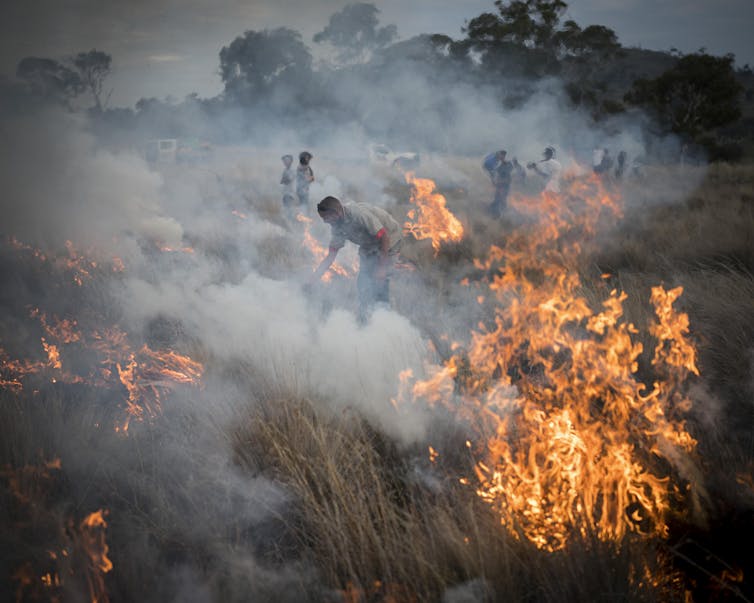 Indigenous-led burning at a project site in Tasmania.
Matthew Newton/RUMMIN Productions
Indigenous-led burning at a project site in Tasmania.
Matthew Newton/RUMMIN Productions
Looking to the future
There are profound cultural differences between traditional and modern fire management, stemming from different understanding of belonging, place, history, values and metaphysics.
The growing fire crisis means it’s vital western science and Aboriginal knowledge are brought together to make communities as fire-safe as possible.
This includes a sustainable funding model for Indigenous-led fire management programs, as well as cross-cultural training for both Indigenous and non-Indigenous fire managers to better work together.
Authors: David Bowman, Professor of Pyrogeography and Fire Science, University of Tasmania