How our red blood cells keep evolving to fight malaria
- Written by Sant-Rayn Pasricha, Laboratory Head, Population Health and Immunity/ Infection and Immunity, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute
Ever since humans first evolved from our primitive ancestors, we have been locked in a battle with our greatest infectious foe – malaria. This life-threatening disease, caused by the Plasmodium parasite and transmitted through mosquito bites, kills one child every two minutes. There were an estimated 216 million cases of malaria in 91 countries (most in sub-Saharan Africa) in 2016, which is 5 million more than the previous year.
For most of history, humans lived without antimalarial drugs, bed nets or even the basic understanding of how malaria is caused. But still our bodies fought against it. In the intense human-malaria war, one way humans could survive would be to make ourselves less hospitable to the pathogen. And that’s exactly what happened.
Over thousands of years, randomly occurring differences in our genetic code that inadvertently reduced malarial risk and provided a survival advantage have been “selected” – meaning these genetic differences become more prominent in the population. Today, human populations in specific parts of the world carry heavy genetic marks from our ancient war with malaria. And it is the red blood cell (erythrocyte) that mostly bears the scars.
Read more: What 115 years of data tells us about Africa's battle with malaria past and present
The red blood cell
The erythrocyte is a remarkable cell. It ships oxygen, bound to iron in the red haemoglobin molecule, from the lungs and heart to every tissue in the body. Its unique shape – a biconcave disc – allows it to deform and reshape itself. This helps it squeeze into the smallest of blood vessels to deliver its payload of oxygen.
 The red blood cell’s unique shape helps it get into difficult places to deliver oxygen.
from shutterstock.com
The red blood cell’s unique shape helps it get into difficult places to deliver oxygen.
from shutterstock.com
But red cells can also be homes to malaria parasites. These parasites grow, replicate and then burst from the cells during an infection, damaging not just the infected red cell but also uninfected bystanders. Damaged red cells are removed from circulation and the reduction causes anaemia (low levels of haemoglobin), which makes people feel weak, tired and lethargic. In severe cases, it can kill.
Malaria has provoked humans to modify the red cell to protect itself from infection. Almost every part of the red cell – from its membrane to the globin genes that confer its role in oxygen transport – harbour common genetic changes in a desperate effort to help our species survive the onslaught of malaria.
Read more: Explainer: what's actually in our blood?
Genetic changes and sickle cells
Perhaps the most important changes have happened to the haemoglobin molecule itself. Haemoglobin comprises two key components: haem, which contains iron and binds oxygen, and globin, which is a quartet of two copies each of two components – alpha and beta globin. In every part of the world where malaria is now or has previously been common, humans have evolved changes in the globin genes.
A single change in the beta globin sequence and hence protein structure causes what is known as sickle haemoglobin (HbS). Carriers of HbS (who have one mutant and one normal copy of the gene) have little difference in their blood counts and no symptoms. But they have about a 30% reduction in susceptibility to malaria – a pretty heavy protection.
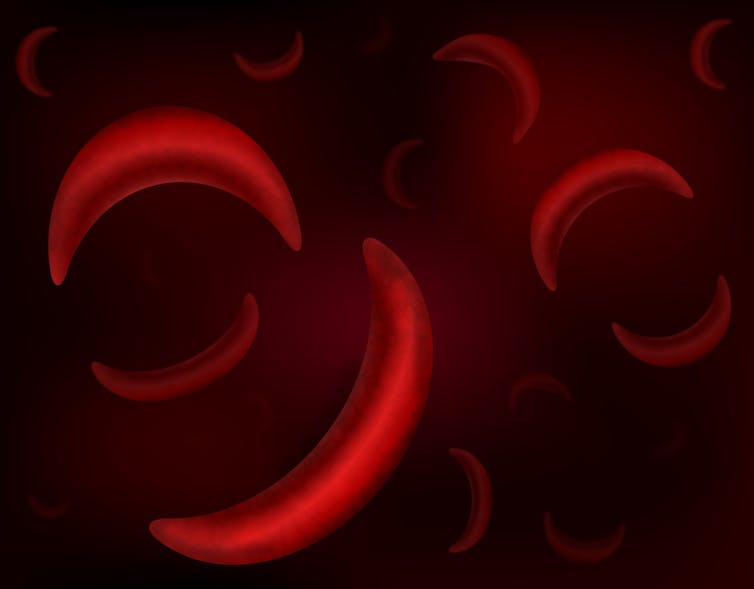 A sickle-like shape prevents the red blood cell from doing its job.
from shutterstock.com
A sickle-like shape prevents the red blood cell from doing its job.
from shutterstock.com
This gives an enormous advantage for children living in an endemic malaria setting. All cases of HbS are caused by an identical genetic change occurring under high pressure of malaria infection. It appears to have arisen spontaneously at least five times over our evolution in different regions in Africa, India and the Middle East.
Proportions of populations in these places, or those descended from them, still commonly carry the mutant gene. About 10% of the African American population are carriers of the sickle cell trait. Individuals of Indian, Eastern Mediterranean, Caribbean and Middle Eastern descent can also be affected.
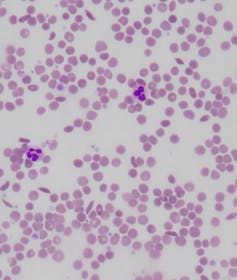 Laboratory slide of sickle cell disease, showing several sickle-shaped blood cells.
Dr Salvatore Fiorenza/Dr Giles Kelsey, Author provided
Laboratory slide of sickle cell disease, showing several sickle-shaped blood cells.
Dr Salvatore Fiorenza/Dr Giles Kelsey, Author provided
While those who carry a single copy of HbS don’t have symptoms, carriers of two copies of HbS (which means they have no normal copy of beta globin) can suffer a life-altering genetic condition known as sickle cell anaemia.
Their red blood cells become susceptible to changing to a rigid, sickle-like shape. This prevents blood from flowing and can result in frequent, unpredictable attacks of pain, organ damage and even stroke.
The severity of sickle cell disease is reduced for those fortunate to have increased levels of fetal haemoglobin persisting into adulthood. Amazingly, to help defend people with sickle cell disease from the severe consequences of this condition, an otherwise silent genetic condition – hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin – has arisen in populations where sickle cell disease is common.
Read more: Explainer: one day science may cure sickle cell anaemia
Thalassaemia
Other populations have evolved different changes in their globin genes to try to defend themselves against malaria. Deletions of part, or all, of the alpha or beta globin genes result in people carrying the blood disease alpha or beta thalassaemia.
Carriers are usually completely healthy, except for a symptomless anaemia detectable only when a blood test is performed. But these conditions are increasingly recognised as perhaps one of main causes of mild anaemia in parts of Asia, the Pacific and the Middle East.
Just like the sickle cell mutation, this protects against invasion by a malaria parasite. But people who carry two deleted copies of their beta globin gene suffer severe anaemia and may require lifelong blood transfusions to survive.
The consequences of deletions of alpha globin genes are more variable, but infants with deletion of all copies of their alpha globin genes usually have such severe anaemia in utero that they do not even survive to birth.
The red cell membrane
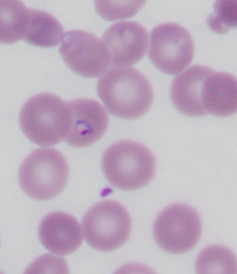 A laboratory slide showing a red blood cell containing a malaria parasite (purple ring with a dark purple dot).
Dr Salvatore Fiorenza/Dr Giles Kelsey, Author provided
A laboratory slide showing a red blood cell containing a malaria parasite (purple ring with a dark purple dot).
Dr Salvatore Fiorenza/Dr Giles Kelsey, Author provided
Then there are evolutionary changes to the Duffy protein. This is a receptor found on the red cell membrane, which is also the protein through which the parasite Plasmodium vivax – the second-most-common cause of malaria – enters the cell.
Almost all the populations in West Africa and well over half of all Africans have inactivated the expression of this gene in their red blood cells. This means they have red cells that are resistant to P. vivax invasion.
Other changes to the red cell membrane can also protect against malaria. People living in Papua New Guinea and other parts of the Pacific may have red blood cells that resemble Nutri-Grain breakfast cereal, with a horizontal stripe or two.
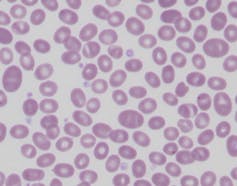 Laboratory slide of Southeast Asian ovalocytosis, showing Nutri-Grain-like cells with one or two horizontal bands.
Dr Salvatore Fiorenza/Dr Giles Kelsey, Author provided
Laboratory slide of Southeast Asian ovalocytosis, showing Nutri-Grain-like cells with one or two horizontal bands.
Dr Salvatore Fiorenza/Dr Giles Kelsey, Author provided
This often asymptomatic condition is called Southeast Asian ovalocytosis. It occurs due to a mutation of a red blood cell protein (which determines the structure of the cell), which makes the rest of the red cell scaffold more rigid than normal. This renders the individual resistant to malarial parasite invasion and protects them from infection.
New mechanisms evolved by our red cells to protect us from malaria are still being discovered. Iron deficiency anaemia, which affects hundreds of millions of (mainly) children and women around the world, has been thought to be mainly due to inadequate nutritional intake of iron.
But now it appears to protect red blood cells from malaria parasite invasion. Many studies show iron-deficient children have a reduced risk of developing malaria. This means improving iron status (for example, through iron supplementation) could predispose children to risk of infection.
Malaria is fighting back
In recent years, human evolution has been complemented by scientific breakthroughs. Effective antimalarial drugs, insecticide-treated bed nets that protect sleeping children from mosquitoes, and rapid tests that can diagnose a case of malaria in a few minutes without the need for a trained microscopist have all helped.
But there is evidence the parasite (and its mosquito host) are evolving to win back the advantage. For example, almost all of a strain of Plasmodium falciparum parasites are resistant to one of the first anti-malarials, Chloroquine.
Now, multi-drug-resistant parasites rule in parts of Southeast Asia, particularly near the Thai-Burma border. Here, resistance to important antimalarials such as mefloquine and, increasingly, artermisinin, which is the backbone of effective therapy, has emerged.
Read more: Weekly Dose: mefloquine, an antimalarial drug made to win wars
Even more ingeniously, parasites have started learning to hide from rapid diagnostic testing by deleting the HRP2 protein these tests rely on to detect them. In this way, they allow the parasite to continue to live (and spread) undetected in an untreated host.
And the malaria-spreading Anopheles mosquito, found throughout the world where malaria is endemic, is learning to bite humans for its blood meal earlier in the evening, rather than later at night when people are sleeping, to subvert the protection offered by bed nets.
So the battle isn’t over. Our oldest foe remains with us and continues to be a formidable opponent.
Authors: Sant-Rayn Pasricha, Laboratory Head, Population Health and Immunity/ Infection and Immunity, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute
Read more http://theconversation.com/how-our-red-blood-cells-keep-evolving-to-fight-malaria-96117



























