Carry-over credits and carbon offsets are hot topics this election – but what do they actually mean?
- Written by Alan Pears, Senior Industry Fellow, RMIT University
In this election, often dubbed the “climate election”, voters are refusing to settle for weak policies on climate change.
But between the “will they/won’t they” question of whether the coalition will meet their climate targets and the costing of the ALP’s targets, there is a lot of misunderstanding, even among experts.
Unsurprisingly, even the best-informed voter is liable to struggle, particularly when generic terms like “carbon credits” are used to describe completely different things.
Read more: Australia is counting on cooking the books to meet its climate targets
Broadly, carbon credits work as a certificate permitting someone to emit greenhouse gases. To assess Australia’s performance, it’s important to understand the differences between the types of certificate.
Just because we can count something as climate performance does not mean we should. Both approaches from the two major parties have their own issues, but that does not mean they are equal.
What are Kyoto carry-over credits and carbon offsets?
Kyoto carry-over credits
Carry-over credits are “certificates” that translate our international commitments as a number of tonnes. These credits represent emissions we could have released into the atmosphere under our international commitments, but didn’t.
As we come to the end of the second international commitment period, we have a lot of leftover credits. The government wants to use credits from the first and second periods (2008-2012 and 2013-2020) to satisfy our obligations under the third (2021-2030).
Carbon offset credits
In the case of offsets, these certificates come from actions that reduce emissions. These actions should be measurable and new. Sadly, they do not always meet that simple standard.
Read more: The government is miscounting greenhouse emissions reductions
Offset credits are a trading “currency” that, in principle, reduces the overall cost of emission reduction.
Emission reduction can be costly or difficult for some, and offsets allow individuals or businesses to buy certificates from others who can cut or capture emissions at lower cost.
Rules to create, trade and monitor offsets can be set at an international, regional or national level. Some offsetting is voluntary, but most is to comply with legal requirements.
The carry-over credit debate
The Coalition plans to use credit from our “over-achievement” in meeting Kyoto targets, as a shortcut to meet the Paris Agreement targets.
Under the Paris Agreement, Australia has voluntarily agreed to reduce its cumulative emissions to 26-28% below 2005 levels by 2030. If we use the Kyoto-era credit for the Paris Agreement, it will take only a 15% reduction on 2005 levels to successfully meet our commitment.
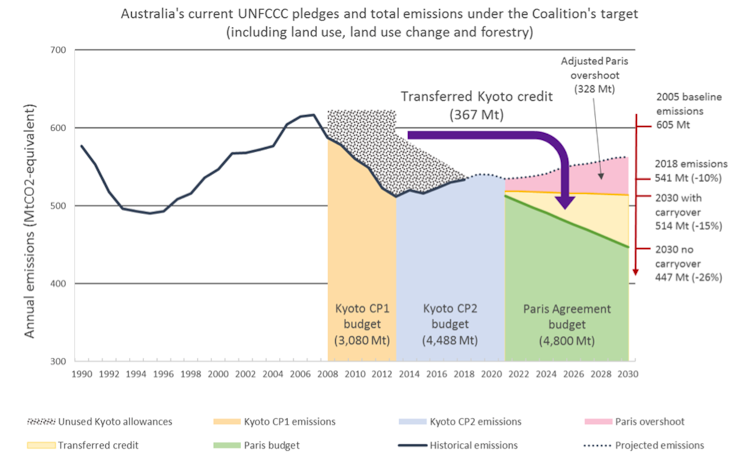 Australia’s current and projected emissions and targets with Kyoto carry-over credit transfer.
Tim Baxter, 'In a Canter'? Demystifying Australia's Emissions Budget for Paris., Author provided
Australia’s current and projected emissions and targets with Kyoto carry-over credit transfer.
Tim Baxter, 'In a Canter'? Demystifying Australia's Emissions Budget for Paris., Author provided
But the Kyoto Protocol only applied to developed countries, while the Paris agreement applies to many developing countries.
This means many signatories to Paris have no “carry-over” credits they can use. Among those developed nations that do have this credit, almost all have said they will not use Kyoto carry-over credits to meet their Paris commitments.
So the coalition’s position is widely seen as morally dubious. And there are real questions around whether our supposed credit from the Kyoto era can be used at all.
Read more: Flying home for Christmas? Carbon offsets are important, but they won't fix plane pollution
Given the nature of the Paris Agreement, the international community will unlikely enforce an express ban on using carry-over credit.
But that doesn’t mean we should use it. Australia’s international reputation depends on rejecting the use of Kyoto carry-over. More importantly, so does our climate.
Carbon offsets
Under the Kyoto Protocol, several offsetting schemes were created between countries, so-called “flexible mechanisms”. Among these emission reduction opportunities is the Clean Development Mechanism.
The Clean Development Mechanism is an offset scheme where developed countries fund emission reduction action in developing countries.
If projects meet the requirements of the mechanism, the developing country claims certificates equal to the amount of emissions reduction they can prove. They then sell the certificates they have earned to developed countries.
This scheme has seen a number of renewable energy projects constructed, such as hydroelectric dams and projects that consume waste to create electricity.
Offsetting carbon voluntarily
Voluntary use of carbon offsets has also grown. For example, Australia’s voluntary National Carbon Offsets Standard allows organisations to use offsets as part of their emission reduction strategy.
Australia’s Carbon Farming Initiative is one such example. This offsetting scheme was originally designed by the ALP, but now underpins the coalition’s Emissions Reduction Fund.
Read more: The Nationals should support carbon farming, not coal
Projects registered under this scheme can create Australian Carbon Credit Units through methods such as revegetation, capture and combustion of methane or surrender of land clearing rights.
 Sydney’s School Strike 4 Climate, March 2019. Climate change is one of the top issues voters care about in the upcoming election.
Shutterstock
Sydney’s School Strike 4 Climate, March 2019. Climate change is one of the top issues voters care about in the upcoming election.
Shutterstock
The government buys these credits through reverse auctions – one buyer with many potential sellers. They’re also frequently purchased by Australian facilities caught by the safeguard mechanism (a framework for the largest emitters to measure, report and manage their emissions) and individuals looking to voluntarily offset their own emissions.
The ALP plans to tighten the baselines under the safeguard mechanism, compelling Australia’s major emitters, such as our largest resource companies, to either reduce on-site emissions or purchase Australian Carbon Credit Units.
In a 2014 report, the Climate Change Authority recommended Australia adopt an emission reduction target between 45% and 65% below 2005 levels by 2030. It noted international carbon offsets would help ensure Australia could meet this more ambitious target.
Read more: Fixing the gap between Labor's greenhouse gas goals and their policies
The ALP’s approach is superficially compatible with the Climate Change Authority, though it plans to negotiate the detail if elected. A lot will hang on where these negotiations fall.
Using offset credits is undoubtedly better than taking no action at all. But offsetting must have integrity, not accounting sleight-of-hand. If genuine, they can help cut global emissions at the lowest cost while also delivering local social, economic and environmental benefits.
It is important offsetting methods continue to be refined and debated, while keeping a critical eye on whether they provide environmental benefit.
Authors: Alan Pears, Senior Industry Fellow, RMIT University



















