Face masks cut disease spread in the lab, but have less impact in the community. We need to know why
- Written by Paul Glasziou, Professor of Medicine, Bond University
In controlled laboratory situations, face masks appear to do a good job of reducing the spread of coronavirus (at least in hamsters) and other respiratory viruses. However, evidence shows mask-wearing policies seem to have had much less impact on the community spread of COVID-19.
Why this gap between the effectiveness in the lab and the effectiveness seen in the community? The real world is more complex than a controlled laboratory situation. The right people need to wear the right mask, in the right way, at the right times and places.
The real-world impact of face masks on the transmission of viruses depends not just on the behaviour of the virus but also on the behaviour of aerosol droplets in diverse settings, and on the behaviour of people themselves.
We carried out a comprehensive review of the evidence about how face masks and other physical interventions affect the spread of respiratory viruses. Based on the current evidence, we believe the community impact is modest and it may be better to focus on mask-wearing in high-risk situations.
The evidence
Simply comparing infection rates in people who wear masks with those who don’t can be misleading. One problem is people who don’t wear masks are more likely go to crowded spaces, and less likely to socially distance. People who are more concerned often adhere to several protective behaviours — they are likely to avoid crowds and socially distance as well as wearing masks.
That correlation between mask wearing and other protective behaviours might explain why studies comparing mask-wearers with non-mask-wearers (known as “observational studies”) show larger effects than seen in trials. Part of the effect is due to those other behaviours.
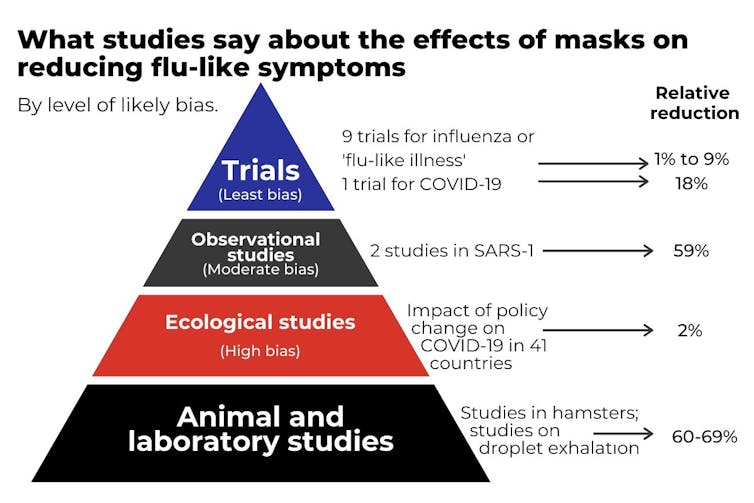
The most rigorous, but difficult, way to evaluate the effectiveness of masks is to take a large group of people and ask some to wear masks and others not to, in a so-called controlled trial. We found nine such trials have been carried out for influenza-like illness. Surprisingly, when combined, these trials found only a 1% reduction in influenza-like illness among mask-wearers compared with non-mask-wearers, and a 9% reduction in laboratory-confirmed influenza. These small reductions are not statistically significant, and are most likely due to chance.
None of these trials studied COVID-19, so we can’t be sure how relevant they are to the pandemic. The SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus is a similar size to influenza, but has a different capacity to infect people, so it is possible masks might be more or less effective for COVID-19. A recently published trial in Denmark of 4,862 adults found infection with SARS-CoV-2 occurred in 42 participants randomised to masks (1.8%) compared to 53 control participants (2.1%), a (non-significant) reduction of 18%.
The most comprehensive between-country study of masks for COVID-19 infection is a comparison of policy changes, such as social distancing, travel restrictions, and mask wearing, across 41 countries. It found introducing a mask-wearing policy had little impact, but mask policies were mostly introduced after social distancing and other measures were already in place.
 The Conversation, Author provided
What might diminish the effect of masks?
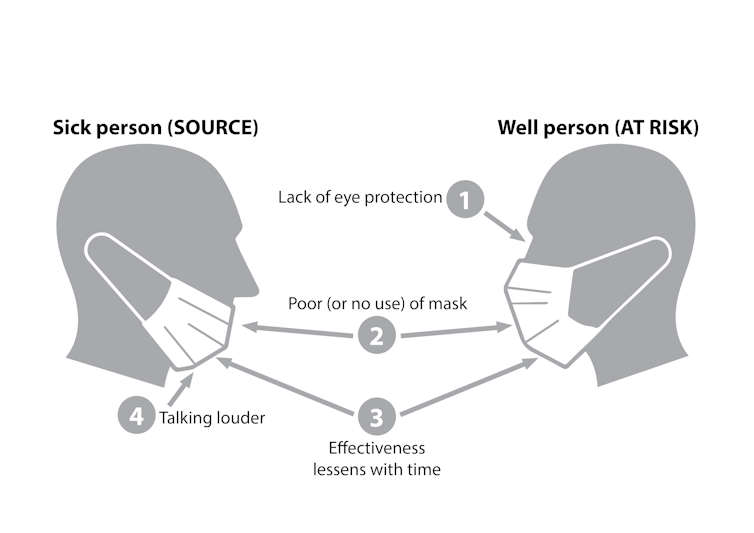
Why might masks not protect the person wearing them? There are several possibilities. Standard masks only protect your nose and mouth incompletely, for one thing. For another, masks don’t protect your eyes.
The importance of eye protection is illustrated by a study of community health workers in India. Despite protection by three-layer surgical masks, alcohol hand rub, gloves, and shoe covers, 12 of 60 workers developed COVID-19. The workers were then supplied with face shields (which provide eye protection) — in addition to the personal protective equipment (PPE) described above — and none of the 50 workers became infected despite higher case load.
Why masks might fail to clearly protect others is more complex. Good masks reduce the spread of droplets and aerosols, and so should protect others.
The Conversation, Author provided
What might diminish the effect of masks?
Why might masks not protect the person wearing them? There are several possibilities. Standard masks only protect your nose and mouth incompletely, for one thing. For another, masks don’t protect your eyes.
The importance of eye protection is illustrated by a study of community health workers in India. Despite protection by three-layer surgical masks, alcohol hand rub, gloves, and shoe covers, 12 of 60 workers developed COVID-19. The workers were then supplied with face shields (which provide eye protection) — in addition to the personal protective equipment (PPE) described above — and none of the 50 workers became infected despite higher case load.
Why masks might fail to clearly protect others is more complex. Good masks reduce the spread of droplets and aerosols, and so should protect others.
 Things that might make masks less effective.
Paul Glasziou, Author provided
However, in our systematic review we found three trials that assessed how well mask wearing protects others, but none of them found an obvious effect. The two trials in households where a person with influenza wore a mask to protect others in fact found a slight increase in flu infections; and the third trial, in college dormitories, found a non-significant 10% relative reduction.
We don’t know if the failure was the masks or participants’ adherence. In most studies adherence was poor. In the trials very few people wear them all day (an average of about four hours by self-report, and even less when directly observed). And this adherence declined with time.
But we also have little research on how long a single mask is effective. Most guidelines suggest around four hours, but studies on bacteria show masks provide good protection for the first hour and by two hours are doing little. Unfortunately, we could not identify similar research examining viruses.
Things that might make masks less effective.
Paul Glasziou, Author provided
However, in our systematic review we found three trials that assessed how well mask wearing protects others, but none of them found an obvious effect. The two trials in households where a person with influenza wore a mask to protect others in fact found a slight increase in flu infections; and the third trial, in college dormitories, found a non-significant 10% relative reduction.
We don’t know if the failure was the masks or participants’ adherence. In most studies adherence was poor. In the trials very few people wear them all day (an average of about four hours by self-report, and even less when directly observed). And this adherence declined with time.
But we also have little research on how long a single mask is effective. Most guidelines suggest around four hours, but studies on bacteria show masks provide good protection for the first hour and by two hours are doing little. Unfortunately, we could not identify similar research examining viruses.
 Making masks mandatory only in crowded places, close-contact settings, and confined and enclosed spaces may be more effective.
Dan Himbrechts / AAP
Is it better to focus masks on the 3 Cs: covered, crowded and close contact?
In addition to the completed Danish trial, another ongoing trial in Guinea-Bissau with 66,000 participants randomised as whole villages may shed more light as it tests the idea of source control. But given the millions of cases and billions of potential masks and mask wearers, more such trials are warranted.
We know masks are effective in laboratory studies, and we know they are effective as part of personal protective equipment for health care workers. But that effect appears diminished in community usage. So in addition to the trials, new research is urgently needed to unravel each of the reasons why laboratory effectiveness does not seem to have translated into community effectiveness. We must also develop ways to overcome the discrepancy.
Until we have the needed research, we should be wary about relying on masks as the mainstay for preventing community transmission. And if we want people to wear masks regularly, we might do better to target higher-risk circumstances for shorter periods. These are generally places described by “the three Cs”: crowded places, close-contact settings, and confined and enclosed spaces. These would include some workplaces and on public transport.
We are likely to be better off if we get high usage of fresh masks in the most risky settings, rather than moderate usage everywhere.
Read more:
How should I clean my cloth mask?
Making masks mandatory only in crowded places, close-contact settings, and confined and enclosed spaces may be more effective.
Dan Himbrechts / AAP
Is it better to focus masks on the 3 Cs: covered, crowded and close contact?
In addition to the completed Danish trial, another ongoing trial in Guinea-Bissau with 66,000 participants randomised as whole villages may shed more light as it tests the idea of source control. But given the millions of cases and billions of potential masks and mask wearers, more such trials are warranted.
We know masks are effective in laboratory studies, and we know they are effective as part of personal protective equipment for health care workers. But that effect appears diminished in community usage. So in addition to the trials, new research is urgently needed to unravel each of the reasons why laboratory effectiveness does not seem to have translated into community effectiveness. We must also develop ways to overcome the discrepancy.
Until we have the needed research, we should be wary about relying on masks as the mainstay for preventing community transmission. And if we want people to wear masks regularly, we might do better to target higher-risk circumstances for shorter periods. These are generally places described by “the three Cs”: crowded places, close-contact settings, and confined and enclosed spaces. These would include some workplaces and on public transport.
We are likely to be better off if we get high usage of fresh masks in the most risky settings, rather than moderate usage everywhere.
Read more:
How should I clean my cloth mask?
Authors: Paul Glasziou, Professor of Medicine, Bond University


















